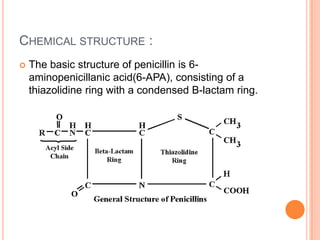
Penicillin, first described by Fleming in 1929 and clinically used since 1941, is a β-lactam antibiotic produced by Penicillium species, effective against various bacterial infections. The document details its classifications into natural, penicillinase-resistant, aminopenicillins, and extended spectrum penicillins, along with their indications for treating specific infections. It also covers the mechanism of action, chemical structure, biosynthesis, and production methods of penicillin, highlighting advancements in yield over time.