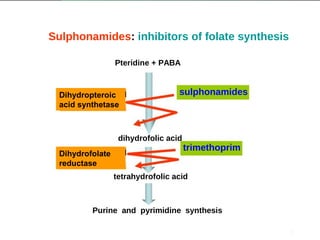
This document discusses sulfonamides and their mechanism of action as folic acid antagonists. It provides details on:
1. How sulfonamides inhibit the synthesis of folic acid by competing with para-aminobenzoic acid for the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase.
2. The classification, antibacterial spectrum, mechanisms of resistance and uses of various sulfonamides like sulfamethoxazole.
3. How trimethoprim inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, preventing the conversion of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate. When combined with sulfamethoxazole as co-trimoxazole it has a synergistic