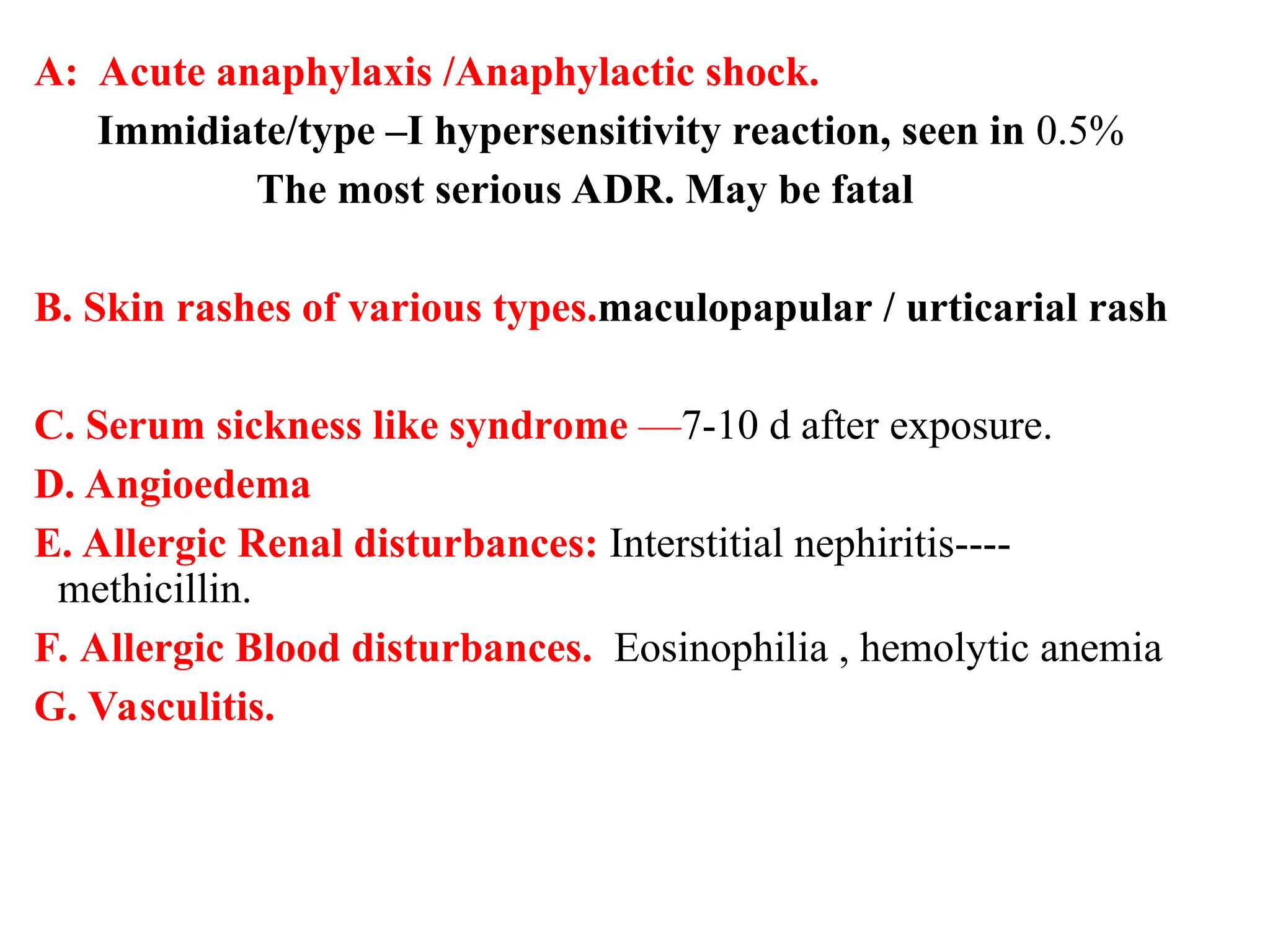
Inhibitors of bacterial cell wall synthesis are bactericidal drugs targeting the peptidoglycan structure unique to bacteria, effective during rapid bacterial growth. Key classifications include beta-lactam drugs (like penicillins and cephalosporins) and non-beta-lactam drugs (such as vancomycin and daptomycin). Penicillins, discovered by Alexander Fleming, are among the most widely used antibiotics and have various therapeutic applications, but may lead to allergic reactions in some patients.