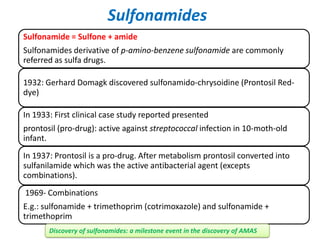
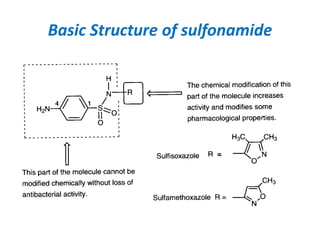
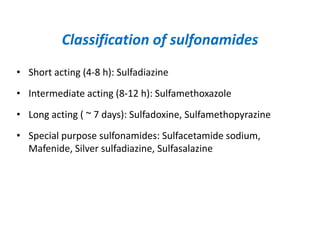
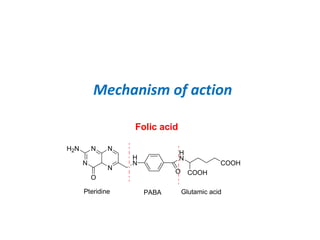
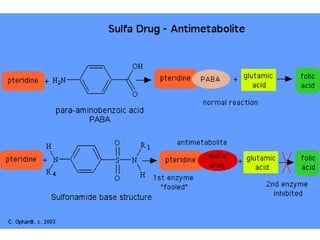
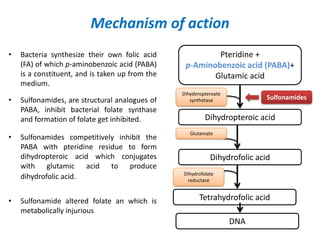
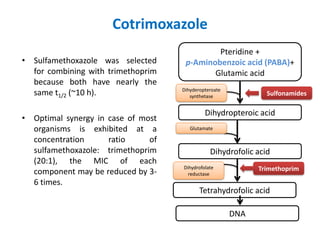
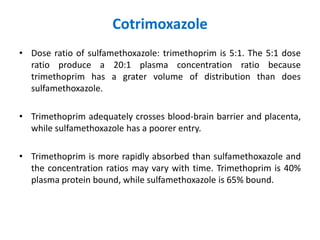
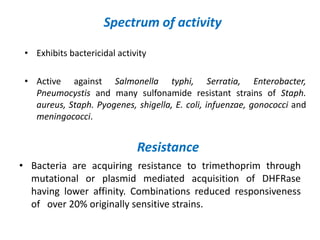
Sulfonamides and trimethoprim are antibacterial drugs that work by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. Sulfonamides were the first antibacterial sulfone drugs discovered in the 1930s. Trimethoprim inhibits a different enzyme in the folic acid pathway. The combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is highly synergistic and known as cotrimoxazole. It is used to treat urinary tract, respiratory, and other infections. Both drugs can cause side effects like rash, nausea, and bone marrow suppression if not used carefully, especially in pregnancy, renal impairment, or the elderly.