Embed presentation


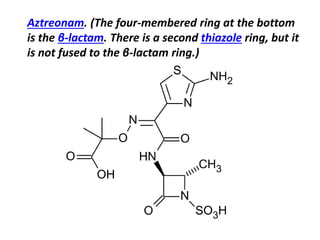
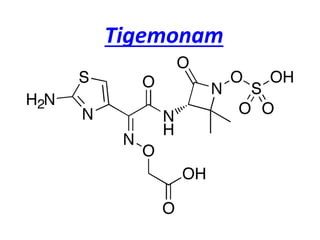


Monobactams are β-lactam compounds that contain an isolated β-lactam ring not fused to another ring, making them effective only against aerobic Gram-negative bacteria like Neisseria and Pseudomonas. Examples include aztreonam, tigemonam, nocardicin A, and tabtoxin. Potential adverse effects are skin rash, abnormal liver functions, and risk of seizures in susceptible individuals.




