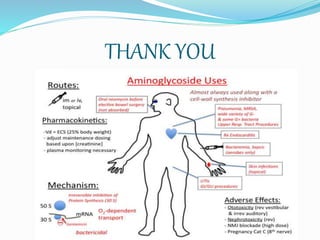
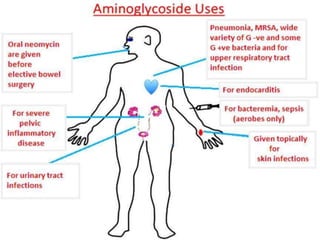
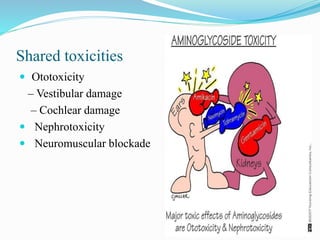
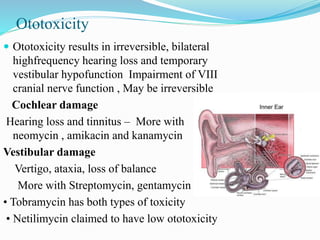
This document provides an overview of aminoglycoside antibiotics. It discusses that aminoglycosides are a group of bactericidal antibiotics used to treat aerobic Gram-negative bacteria by preventing bacterial protein synthesis. Some key points covered include:
- Aminoglycosides like streptomycin were first discovered in the 1940s from soil bacteria. Common systemic aminoglycosides include gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin.
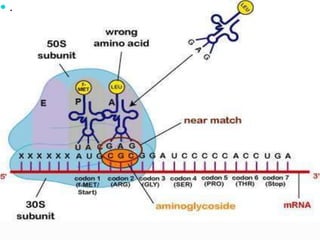
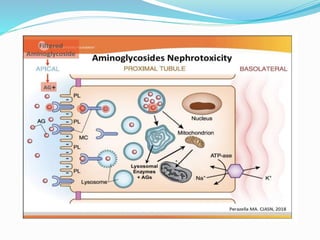
- Their mechanism of action involves binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit of bacteria to prevent proper initiation complex formation and protein synthesis.
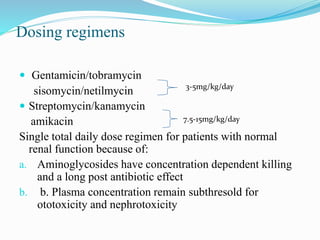
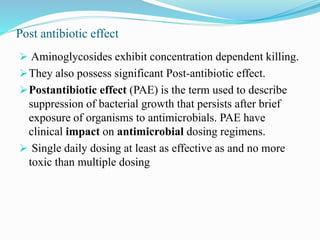
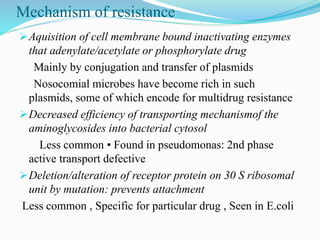
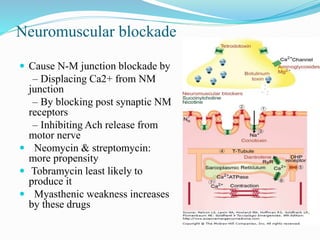
- They have concentration-dependent bacterial killing and a post-antibiotic effect. Resistance can develop via enzymatic modification or





















![REFERENCES
• Tripathi K.D. Essentials Of Medical Pharmacology. 7th
ed. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers; 2014:[182-191]
• Rang H.P ,Dale M.M, Ritter J.M, Flower
R.J.Pharmacology. 6th ed.Elsevire: Churchill
livingstone;2008:[226-237
• http://www.medindia.net/articles/aminoglucosides.htm
• http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/aminoglycosides](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aminoglycosides-200616062854/85/Aminoglycosides-31-320.jpg)