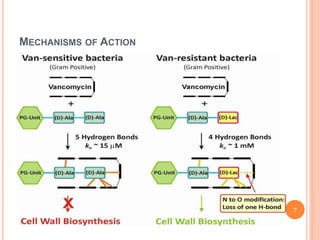
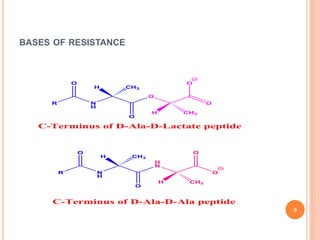
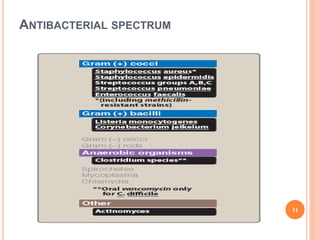
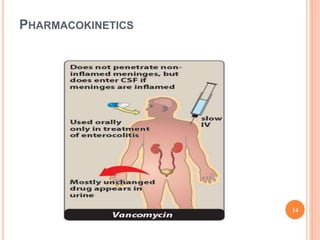
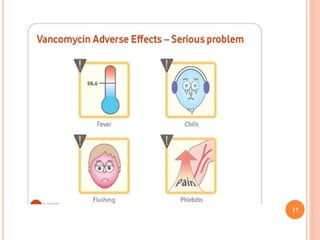
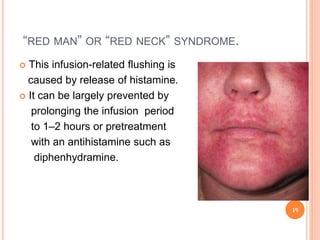
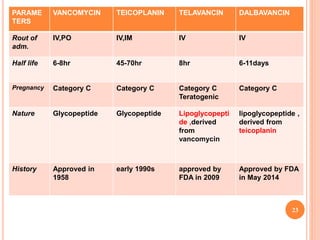
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic produced by bacteria. It works by binding to D-Ala-D-Ala sites on bacterial cell walls, inhibiting cell wall synthesis. It is administered intravenously and excreted renally. Vancomycin is used to treat serious infections caused by gram-positive bacteria like MRSA and is generally well-tolerated though it can cause histamine-related flushing. Other glycopeptide antibiotics discussed include teicoplanin, telavancin, and dalbavancin, which have similar mechanisms of action to vancomycin but varying pharmacokinetic properties and clinical applications.