Embed presentation
Download to read offline


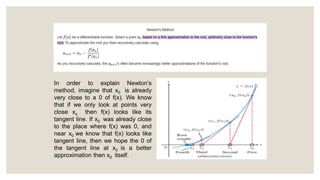

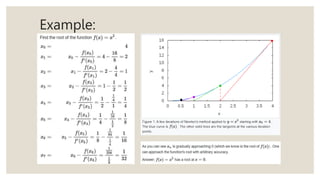

Newton's method is a recursive algorithm that uses the tangent line of a function at a given point to approximate the roots, or zeros, of that function. It starts with an initial guess and iteratively calculates better approximations of the root by taking the tangent line's x-intercept as the next guess, continuing until reaching a value close enough to the actual root. This method can find approximations of roots for any differentiable function, whether polynomial or not, as long as the function is differentiable in the desired interval.





