Embed presentation
Downloaded 82 times







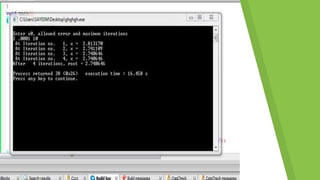



The Newton-Raphson method is an iterative method for finding successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function. It starts with an initial guess x0 and the function's derivative f', and calculates a better approximation x1. The document includes code implementing the Newton-Raphson method to find the root of a cubic function f(x)=x^3 - 2x - 5. It takes inputs of the initial guess x0, allowed error, and maximum iterations and outputs the root if convergence is achieved or indicates non-convergence otherwise. The method has applications in finding extrema of functions, inverting numbers, and solving transcendental equations.









