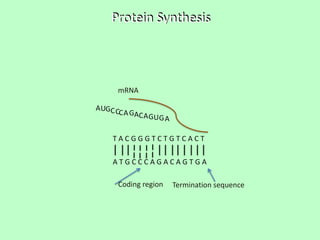
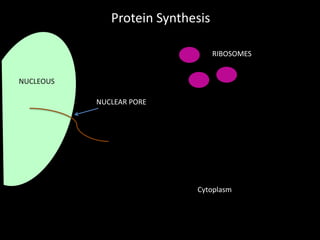
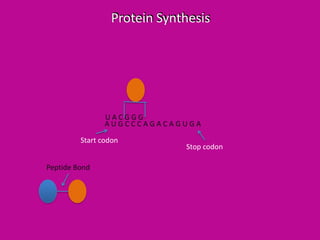
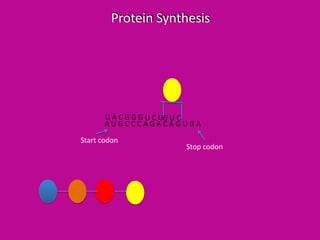
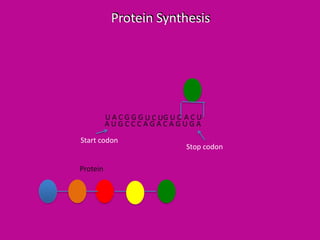
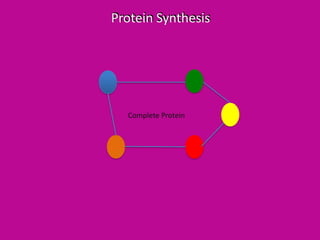
DNA is transcribed into mRNA which is then translated into proteins. Transcription involves RNA polymerase making a complementary mRNA copy of a DNA gene. Translation occurs when ribosomes read the mRNA and join amino acids specified by codons until reaching a stop codon, forming a polypeptide chain that folds into a functional protein. tRNA molecules carry amino acids to the ribosome and recognize codons via complementary anticodons.