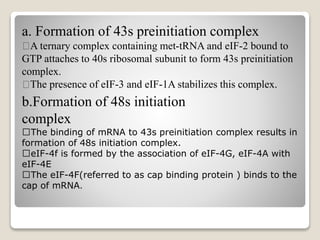
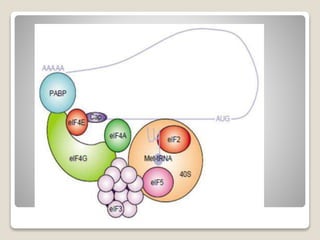
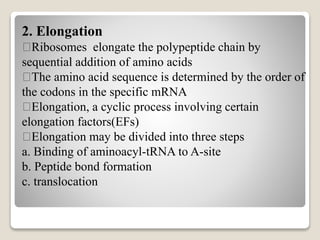
Translation in eukaryotes involves several initiation factors and multiple complex formation steps. It begins with a 43S preinitiation complex that binds mRNA to form a 48S initiation complex. This then binds the 60S ribosomal subunit to form an 80S initiation complex. Elongation occurs as amino acids are sequentially added through binding of aminoacyl-tRNAs and translocation of the ribosome along the mRNA. Termination happens when a release factor binds to the ribosome at a stop codon, causing the ribosomal subunits to separate and release the finished polypeptide chain.