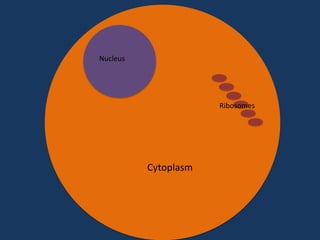
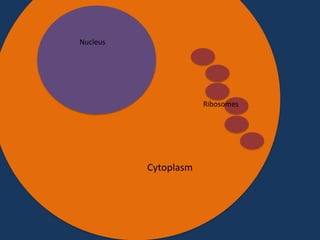
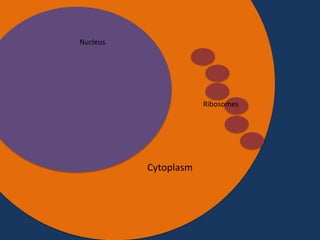
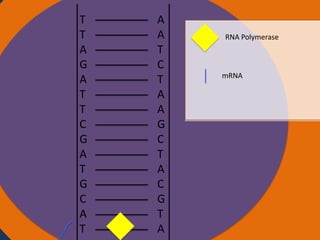
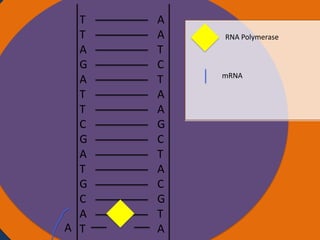
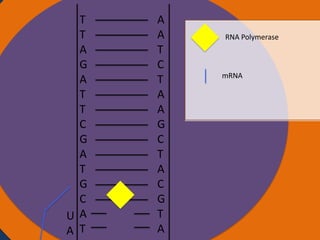
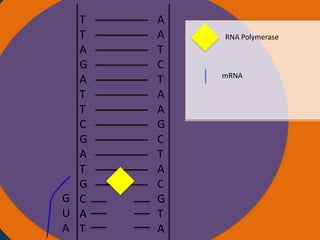
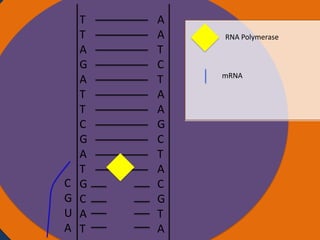
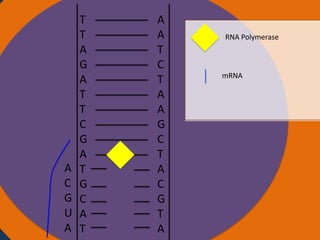
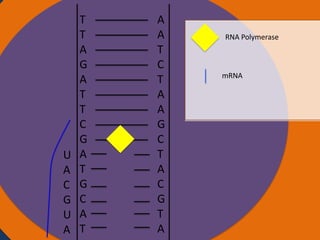
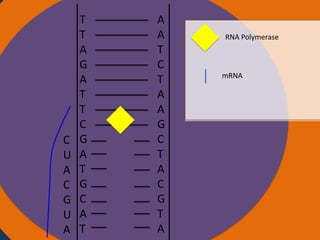
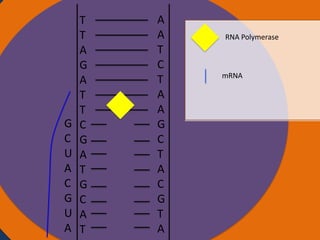
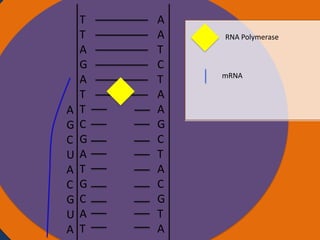
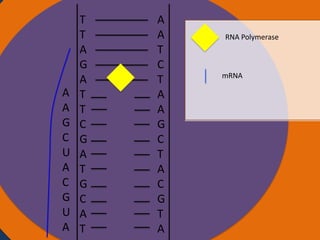
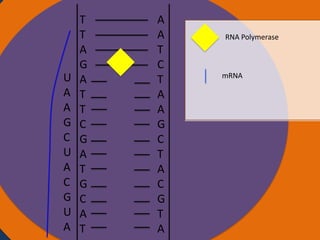
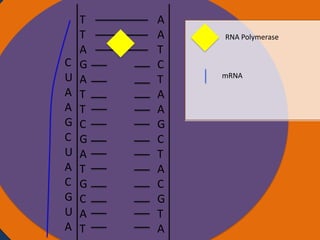
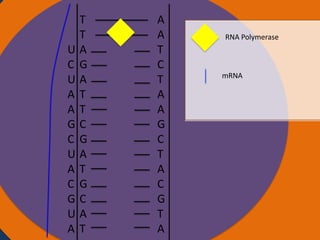
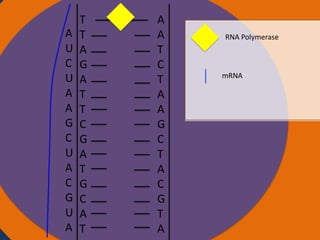
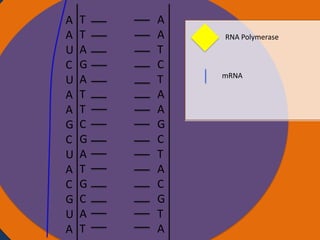
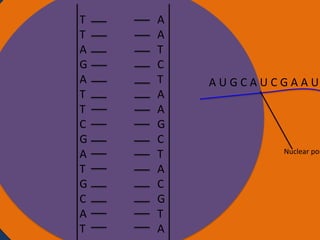
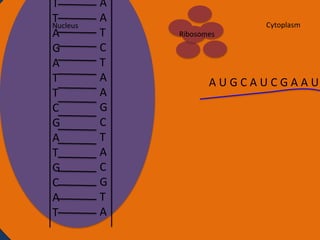
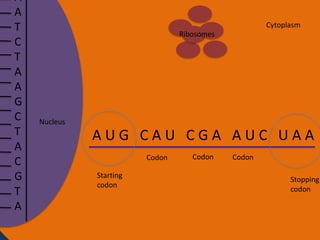
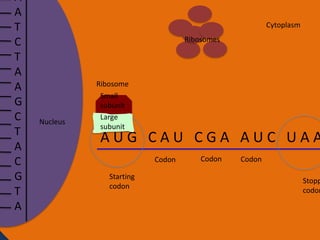
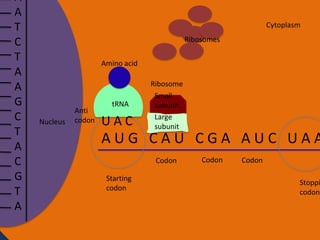
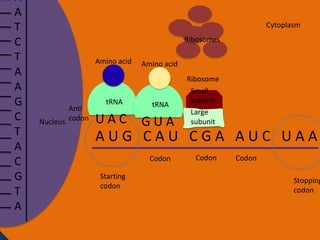
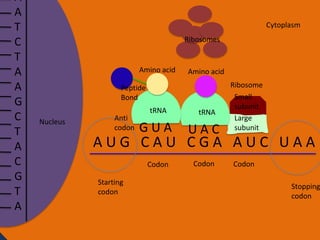
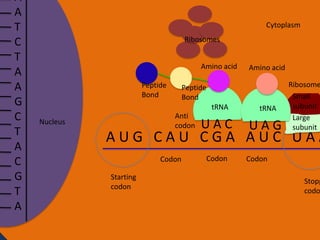
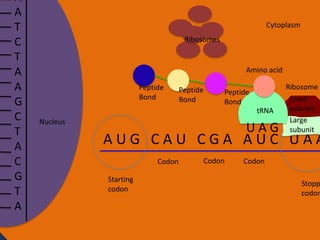
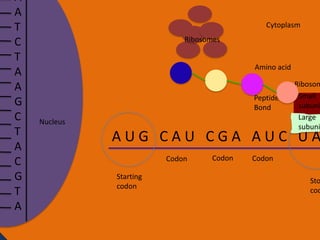
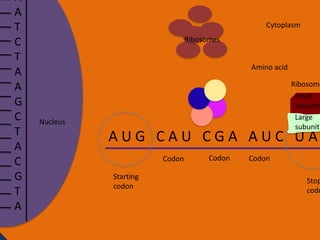
Protein synthesis involves two main steps: transcription and translation. In transcription, RNA polymerase uses DNA as a template to make mRNA strands in the nucleus. The mRNA then moves to the cytoplasm. In translation, ribosomes read the mRNA and join amino acids specified by codons through attachment to tRNAs. The amino acids bond together into a protein chain that eventually folds into its functional tertiary structure.