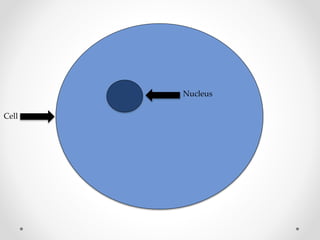
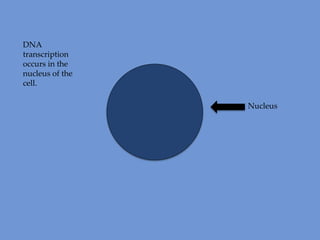
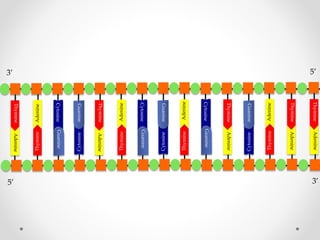
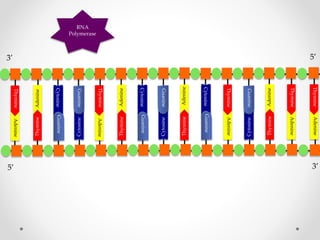
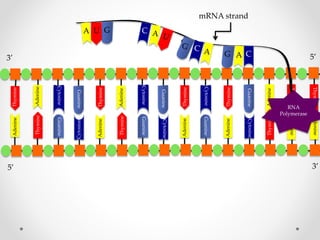
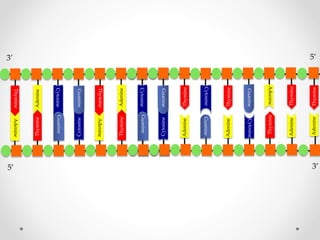
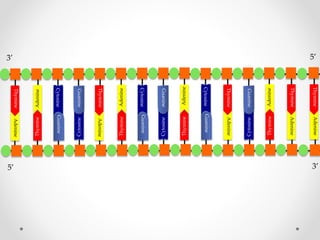
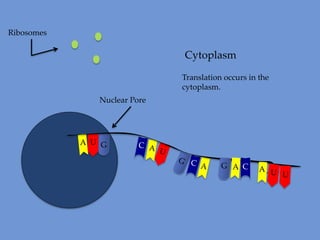
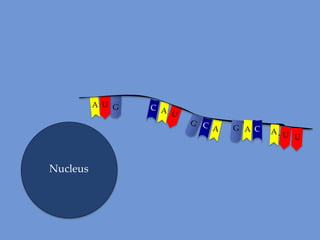
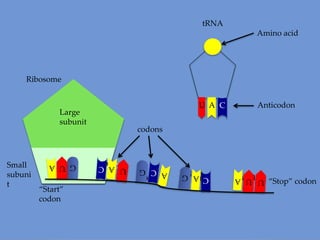
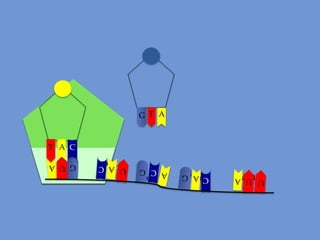
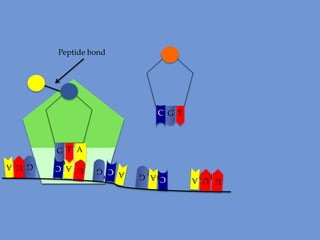
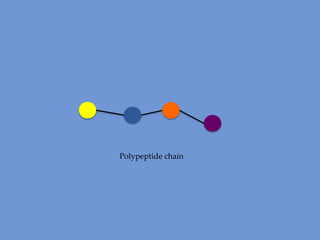
DNA is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus. The mRNA is then transported to the cytoplasm where it undergoes translation using ribosomes. During translation, tRNA molecules matching the mRNA codons bring amino acids to the ribosome where they are linked together into a polypeptide chain. The process continues until a stop codon is reached, resulting in a complete protein.