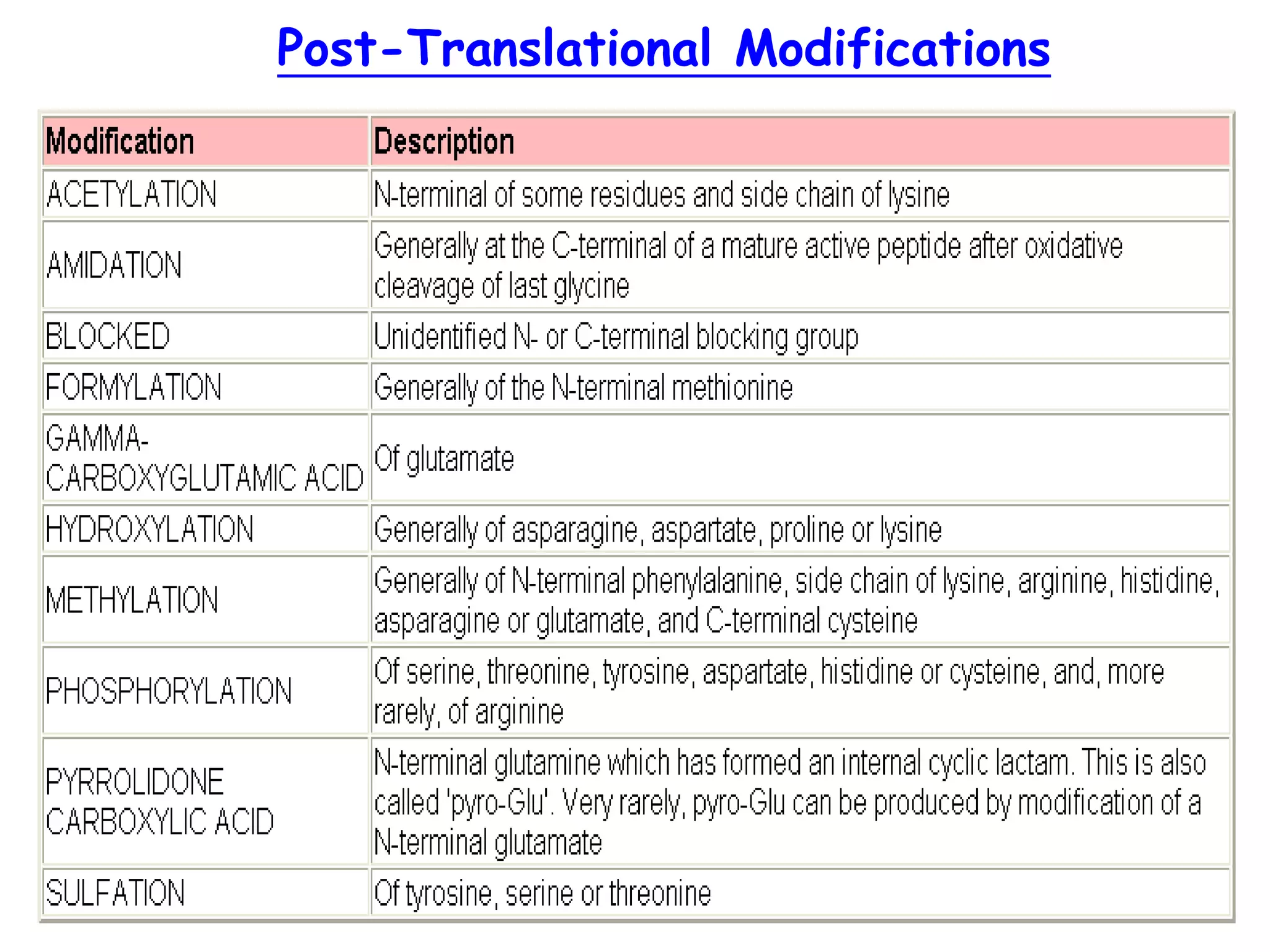
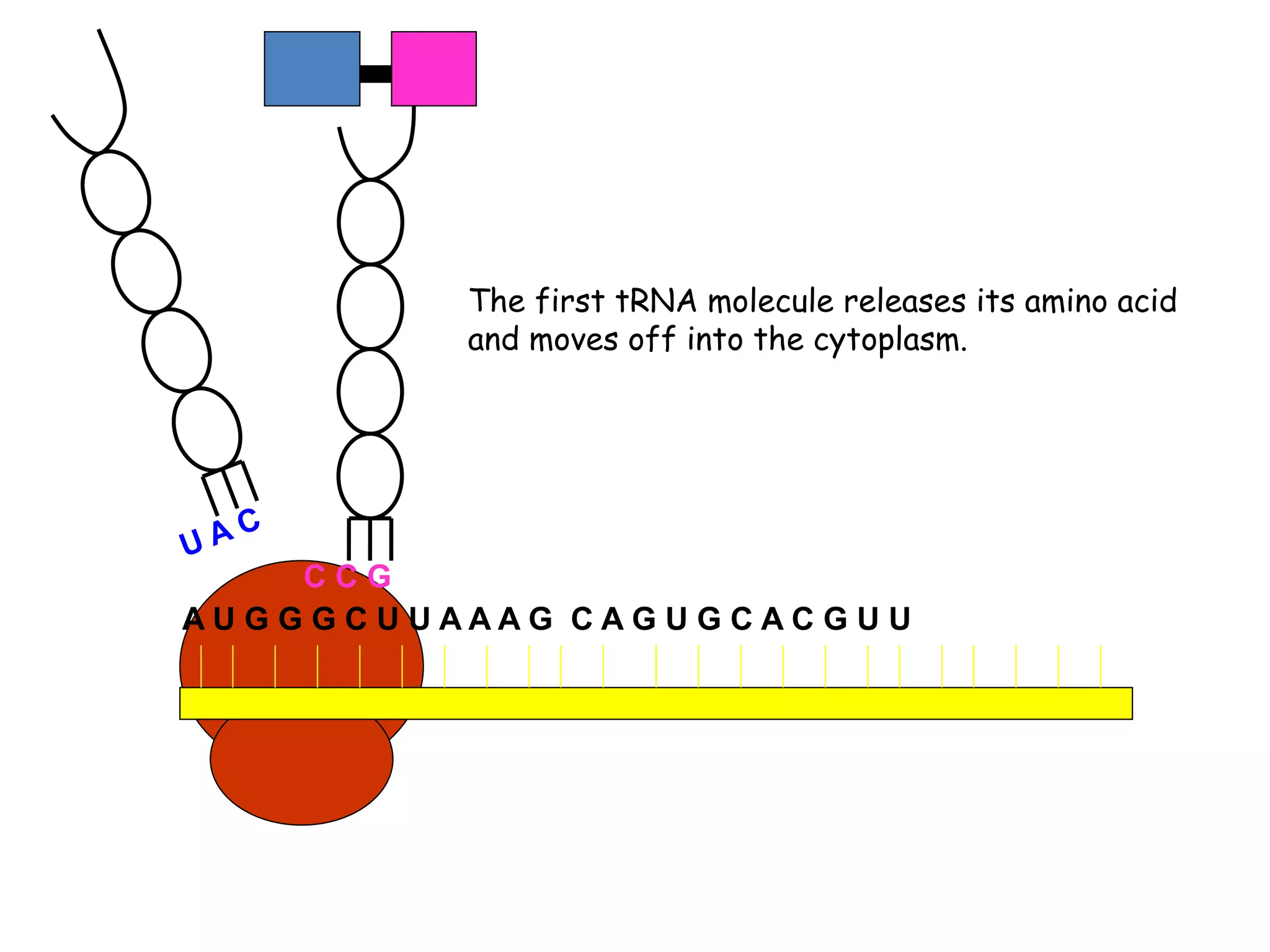
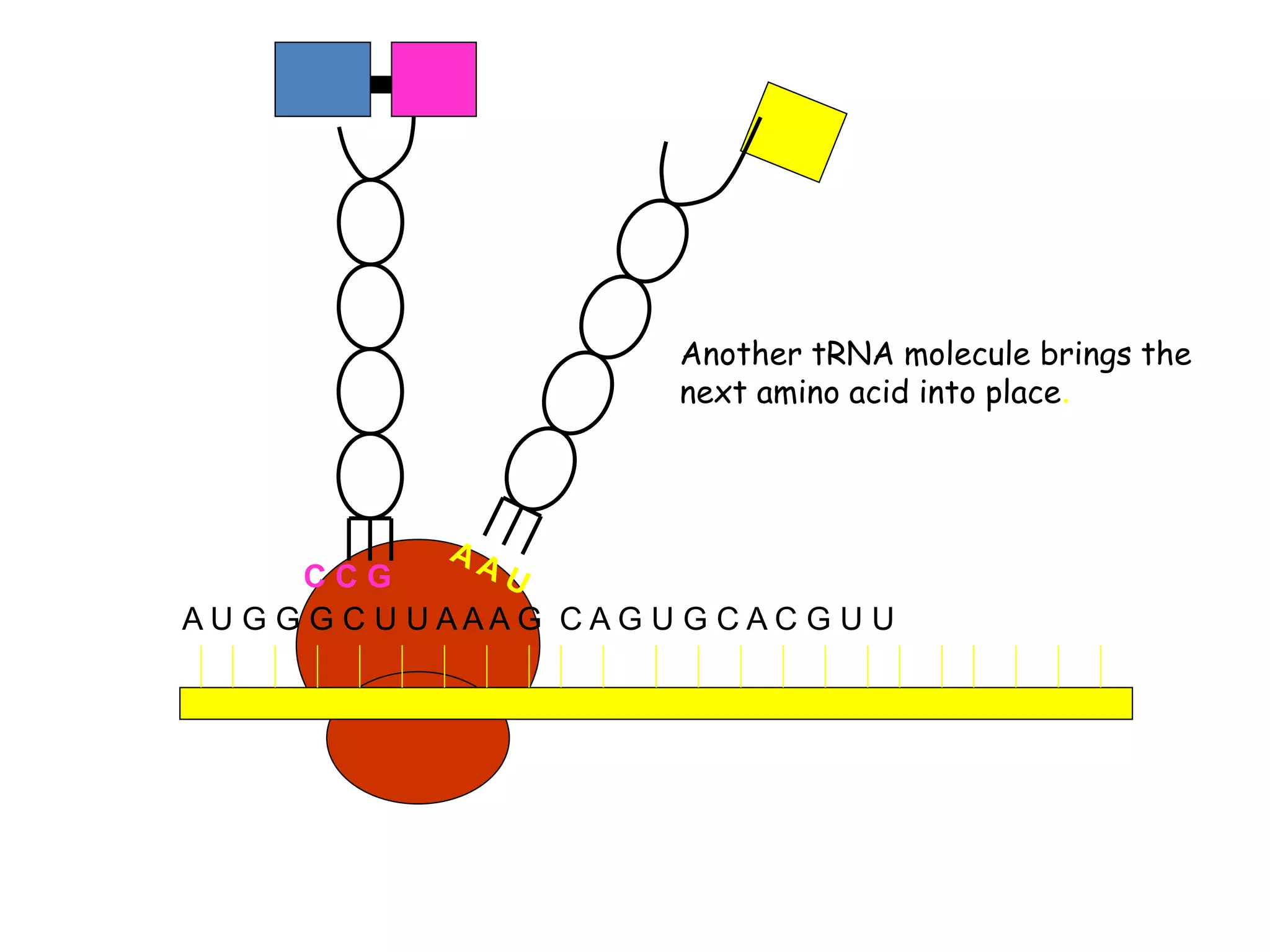
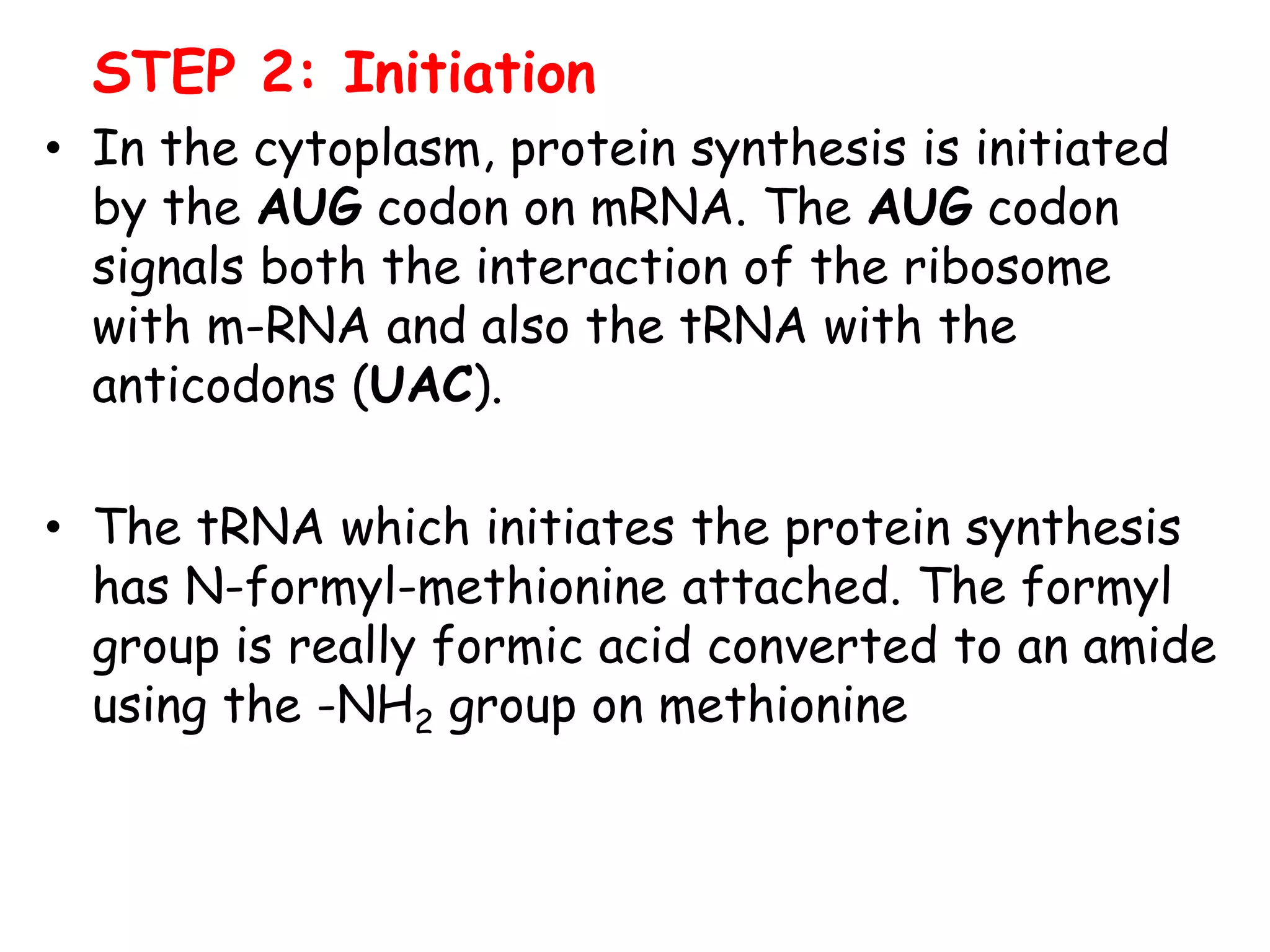
Translation is the process by which the ribosome produces proteins using information from mRNA. It occurs in three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the small ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA start codon and is joined by initiator tRNA. In elongation, aminoacyl-tRNAs bring amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codons, linking them together via peptide bonds. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached, releasing the full protein.





![(iii) Termination:
• The end of translation occurs when the ribosome
reaches one or more STOP codons (UAA, UAG,
UGA). (The nucleotides from this point to the
poly(A) tail make up the 3'-untranslated region
[3'-UTR] of the mRNA.)
• There are no tRNA molecules with anticodons
for STOP codons. (With a few special
exceptions: to mitochondrial genes and to non-
standard amino acids.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proteinsynthesis2022-230919131633-1cc42992/75/Protein-synthesis-2022-pdf-8-2048.jpg)











![STEP 4: Termination
• Translation ends when the ribosome reaches one
or more STOP codons (UAA, UAG, UGA). (The
nucleotides from this point to the poly(A) tail
make up the 3'-untranslated region [3'-UTR] of
the mRNA.)
• There are no tRNAs with anticodons for STOP
codons. However, protein release factors
recognize these codons when they arrive at the
A site.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proteinsynthesis2022-230919131633-1cc42992/75/Protein-synthesis-2022-pdf-24-2048.jpg)