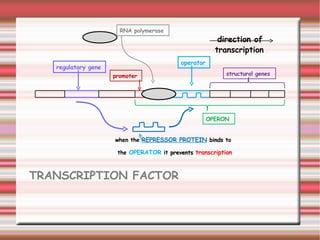
The document outlines the components of gene expression, detailing the roles of RNA polymerase, transcription initiation, termination, and translation processes. It explains how a regulatory gene and repressor protein can influence transcription, and describes the mechanics of translation involving ribosomes and tRNA. The summary includes references to key biological texts for further context.




![Transcription TERMINATION: - transcription occurs until defined codons that signal cessation are read by the DNA poly - called : STOP codons [UGA/ UAA/ UAG] - process stops and the mRNA transcript breaks away to float freely in the cytoplasm , until, it encounters a ribosome: translates to protein - RNA poly detaches from the DNA transcript (Campbell N. A, Reece J. B, 2005)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expression-1226000918340325-9/85/Describe-Gene-Expression-7-320.jpg)



