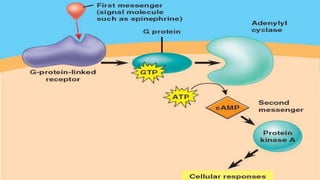
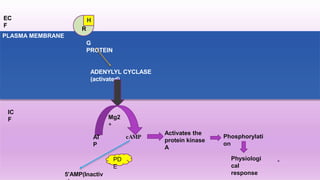
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is an important second messenger in intracellular signal transduction. It is derived from ATP and conveys signals from hormones that bind to cell surface receptors. Many hormones such as epinephrine, glucagon, and others activate adenylate cyclase, which produces cAMP from ATP. cAMP then activates protein kinase A and triggers physiological responses in the cell. The effects of cAMP are terminated by phosphodiesterases that break it down or by phosphatases dephosphorylating protein kinase A. Deregulation of cAMP pathways has been implicated in cancer and cognitive disorders.







![Role in eukaryotic cells
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA[N 1]) is a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on
cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase.
Protein kinase A has several functions in the cell, including regulation of glycogen, sugar,
and lipid metabolism.
Role in bacteria
In bacteria, the level of cAMP varies depending on the medium used for growth. In particular,
cAMP is low when glucose is the carbon source. This occurs through inhibition of the cAMP-
producing enzyme, adenylate cyclase, as a side-effect of glucose transport into the cell.
The transcription factor cAMP receptor protein (CRP) also called CAP (catabolite gene activator
protein) forms a complex with cAMP and thereby is activated to bind to DNA. CRP-cAMP increases
expression of a large number of genes, including some encoding enzymes that can supply energy
independent of glucose.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cyclicamp-200605152900/85/Cyclic-amp-10-320.jpg)


