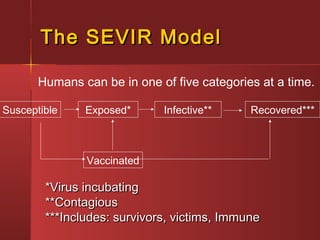
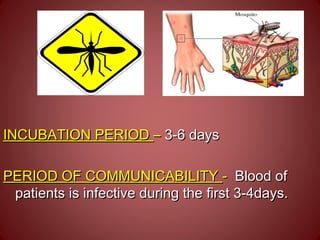
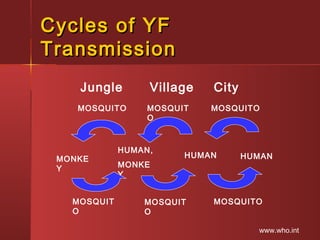
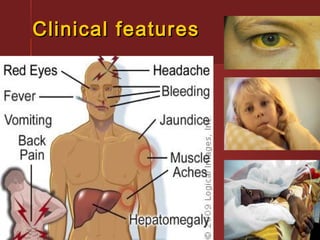
Yellow fever is caused by a flavivirus transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. It occurs in tropical areas of Africa and South America, putting over 900 million people at risk. Each year there are approximately 200,000 cases and 30,000 deaths worldwide. The virus is maintained in non-human primates, and humans can be infected either through forest exposure or urban cycles involving humans and mosquitoes. Prevention focuses on vaccination and mosquito control to limit transmission between humans and mosquitoes.