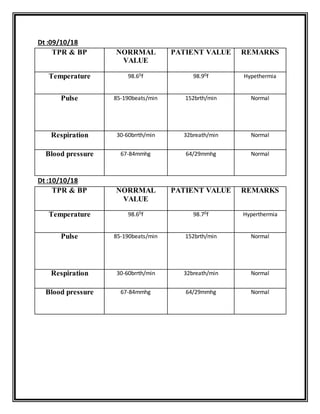
The document describes a medical case report for a 3-day-old female infant admitted to the NICU for neonatal jaundice. She presented with yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes. Her vital signs were normal except for occasional hypothermia. Her physical exam found jaundice, poor nutrition, and abnormal neurological responses. She was treated and discharged after her jaundice improved over a few days.