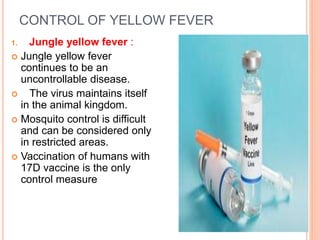
Yellow fever is a viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes that primarily affects monkeys and humans in tropical areas of Africa and South America. It causes fever, jaundice, and can lead to severe liver and kidney damage. There are three main transmission cycles: a sylvatic cycle between monkeys and wild mosquitoes in forests; an intermediate cycle between monkeys, humans and semi-domestic mosquitoes near forests; and an urban cycle between humans and the Aedes aegypti mosquito. The virus is controlled through vaccination programs and mosquito control measures like larval source reduction and insecticide spraying. International travel regulations require a valid yellow fever vaccination certificate for entry into affected areas.