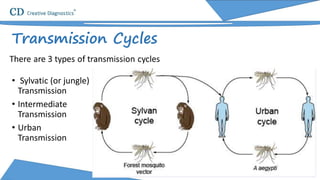
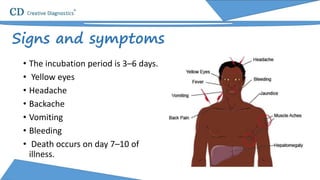
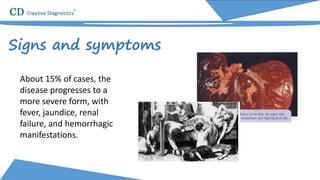
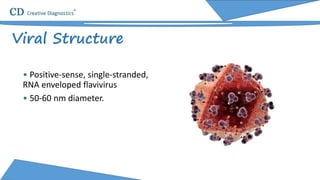
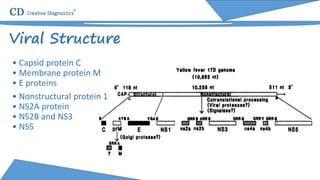
Yellow fever is an acute viral hemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes that originated in Central Africa. It causes symptoms like fever, jaundice, and in severe cases significant bleeding. While most cases resolve, 15% of infections progress severely and can result in death within 7-10 days. The virus is a positive-sense RNA flavivirus about 50-60nm in diameter. Diagnosis involves testing for viral RNA or antibodies in the blood. Vaccines can prevent yellow fever, but supplies of one major vaccine may be limited in the near future.