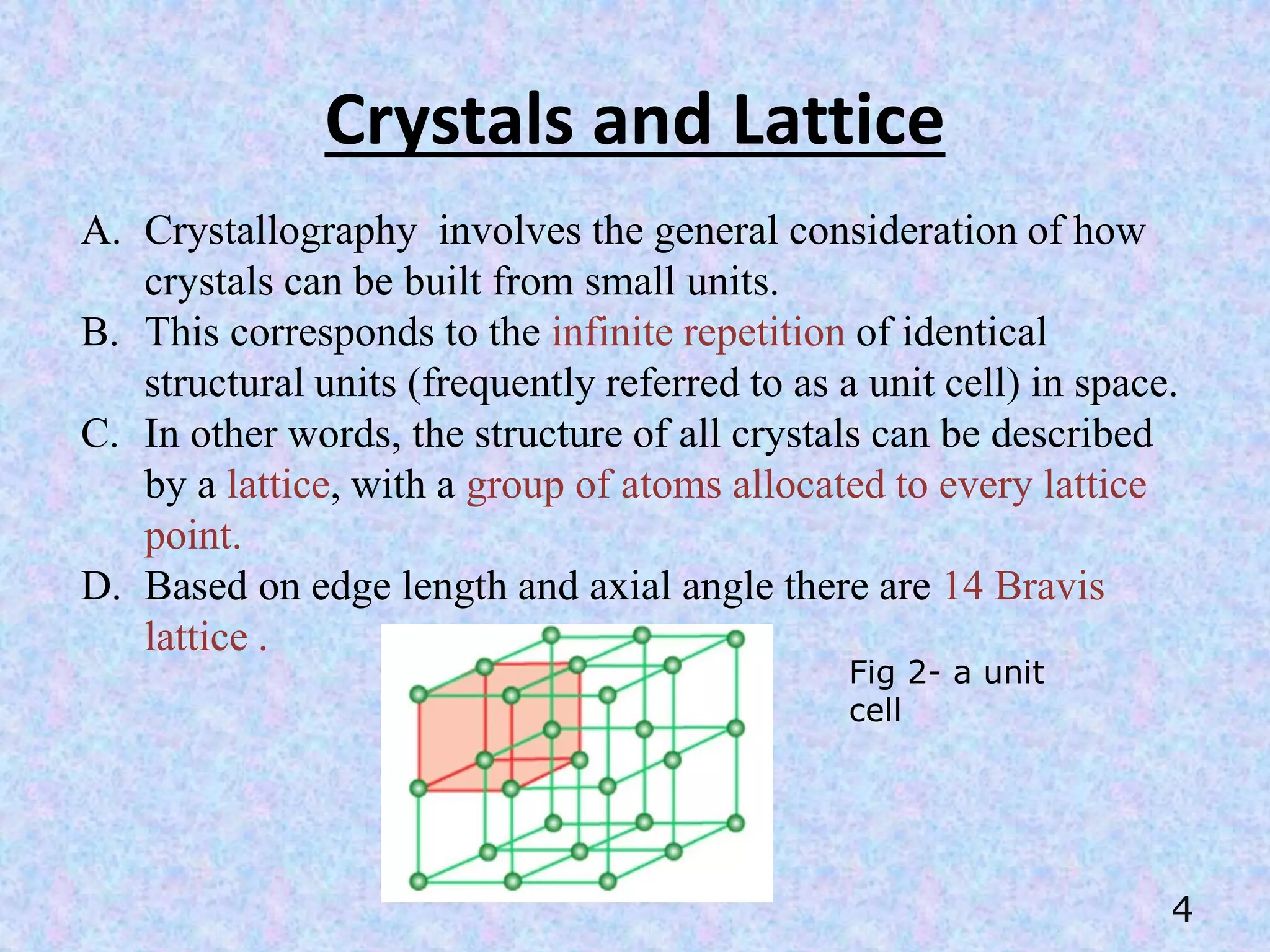
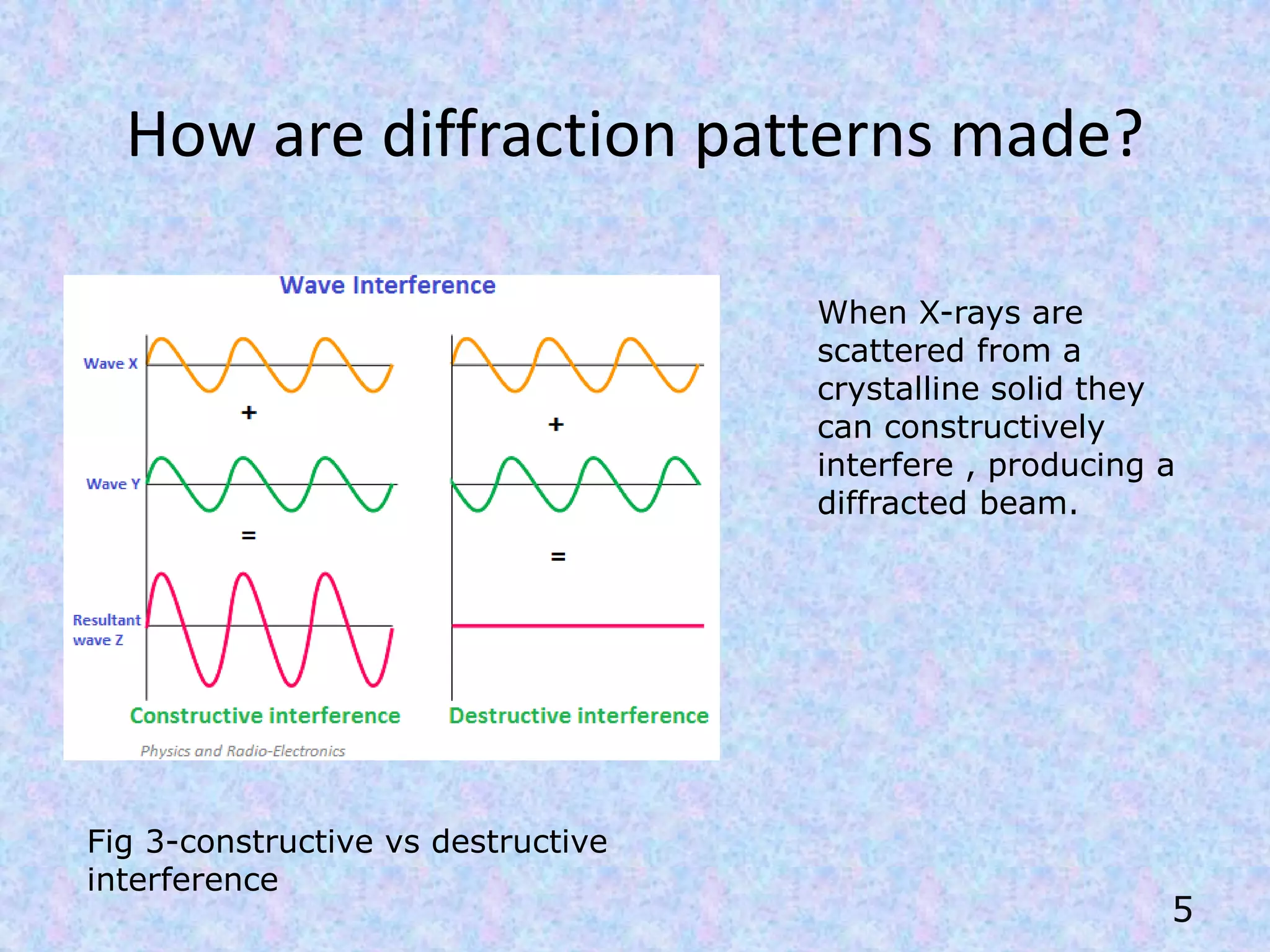
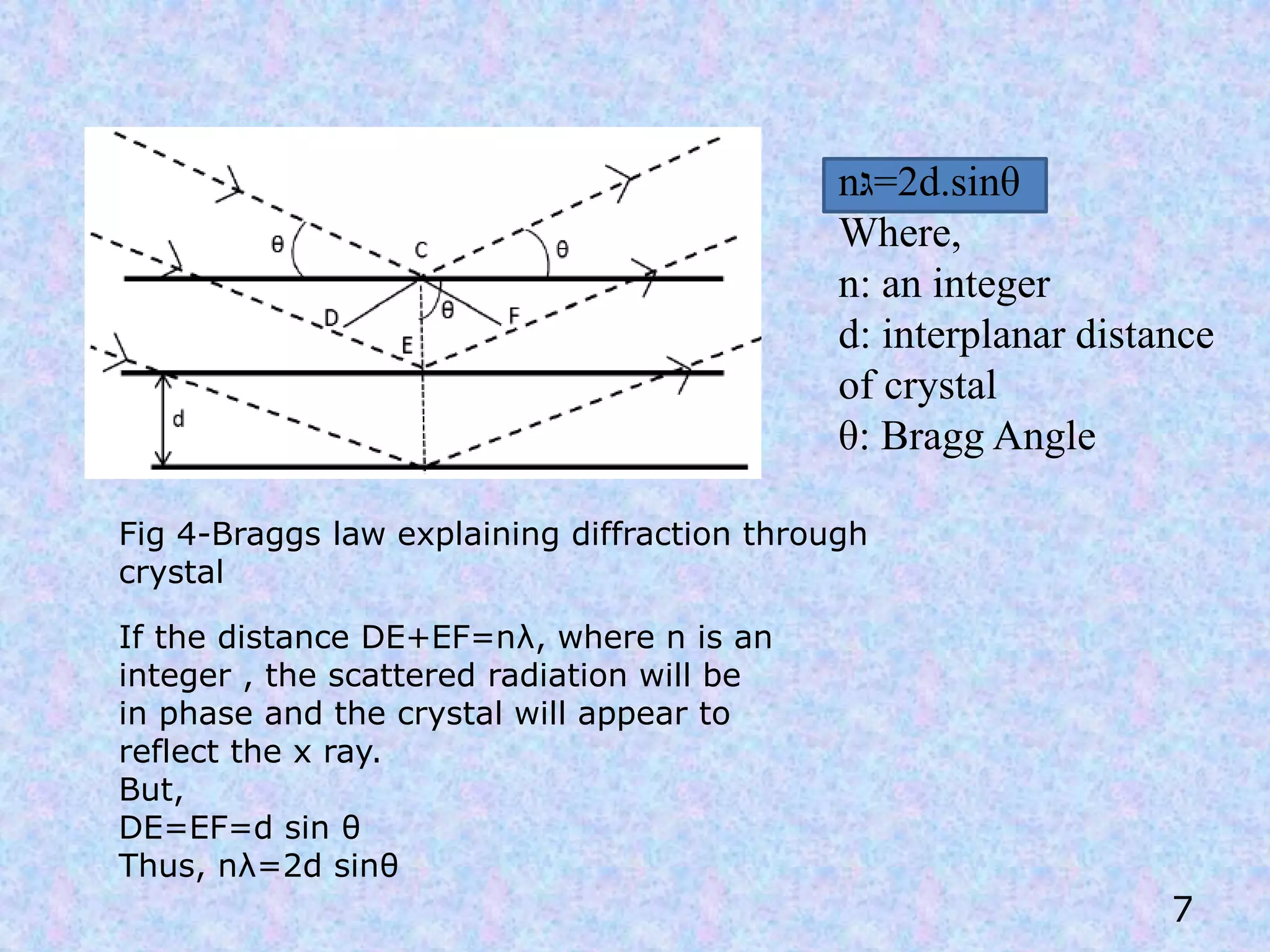
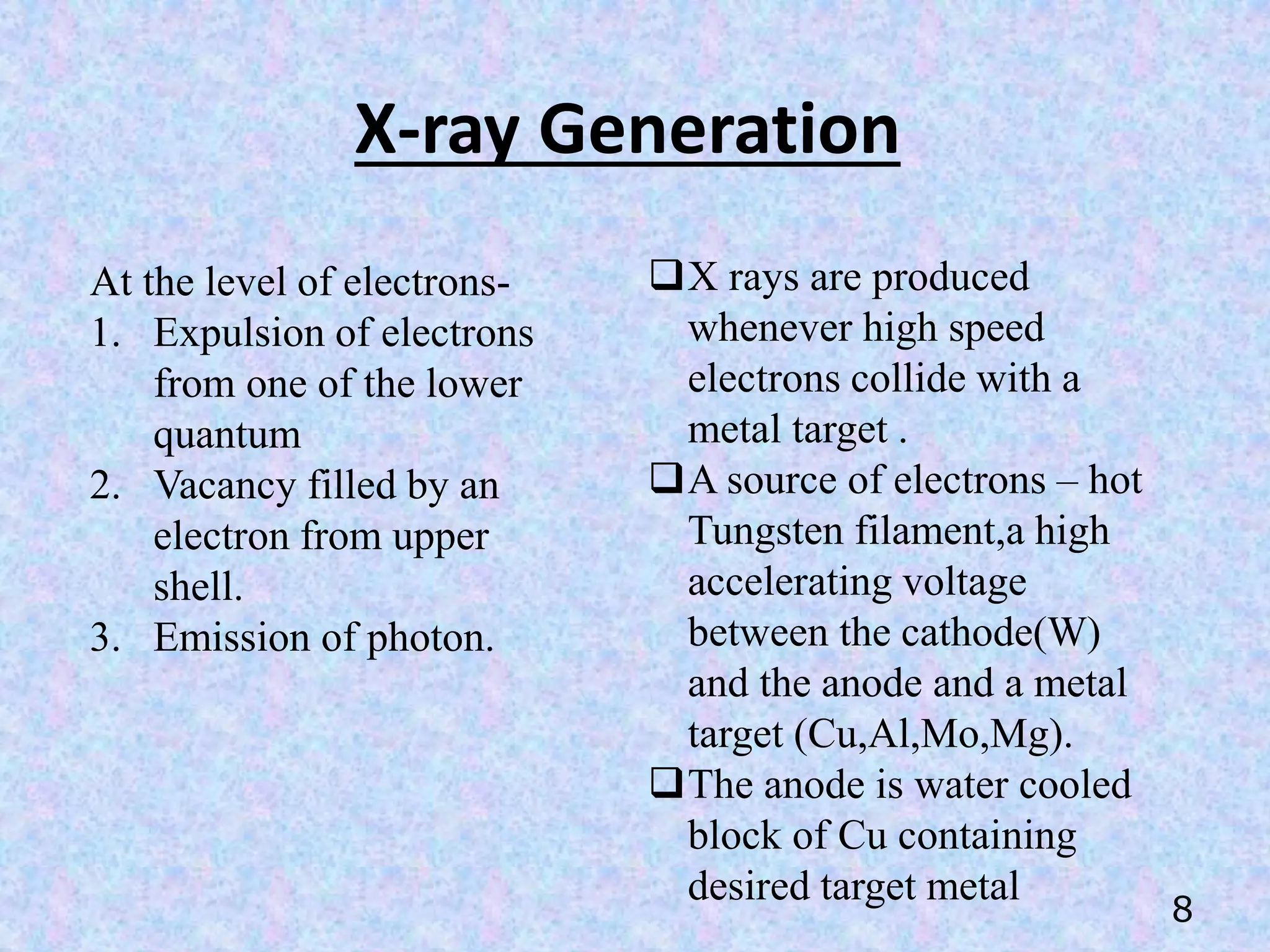
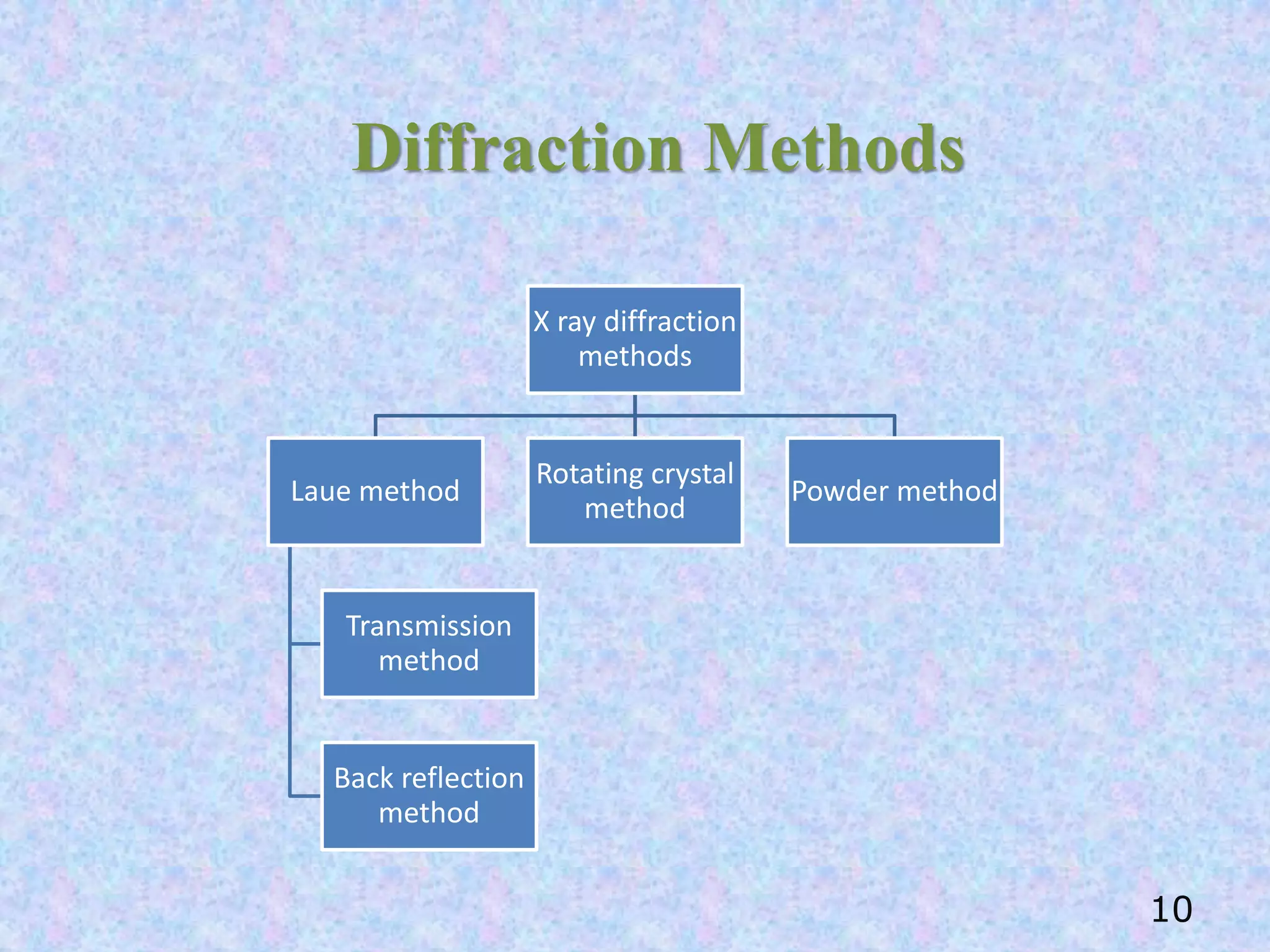
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) is a technique used in the pharmaceutical industry to analyze crystal structures. It involves using x-rays to diffract off the planes of atoms in a crystal. By analyzing the angles and intensities of the diffracted x-rays, properties of the crystal such as its unit cell, polymorphism, purity, and compatibility with excipients can be determined. These properties have important implications for drug development, manufacturing, and quality control in the pharmaceutical industry.