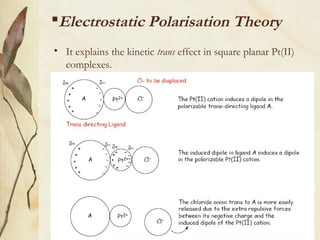
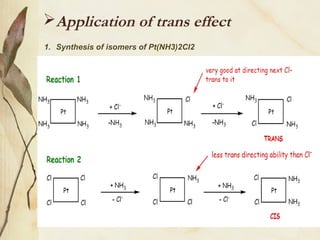
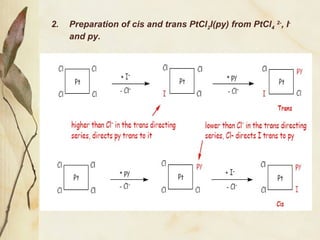
This document discusses ligand substitution reactions in coordination compounds. It begins by defining ligand substitution and classifying the mechanisms as dissociative, associative, or interchange. For octahedral complexes, dissociative mechanisms are seen at high concentrations of the entering ligand and associative at low concentrations. Evidence for dissociative mechanisms includes little effect of the entering ligand on rate. Ligand substitution can also occur in octahedral complexes without breaking the metal-ligand bond. The document also discusses substitution in square planar complexes, factors affecting rate, and the trans effect, providing theories to explain it such as electrostatic polarization and pi bonding. Applications of the trans effect in synthesis are also mentioned.


![Introduction
One of the most general reactions exhibited by coordination
compounds is that of substitution, or replacement, of one ligand by
another.
Ligand substitution involves the exchange of one ligand for
another, with no change in oxidation state at the metal center
[MLxX] + Y = [MLxY] + X
X is the leaving group and Y is the entering group.
Metal complexes that undergo substitution reactions with t1/2= 1
min. at 25 C are called kinetically labile. If t1/2 > 1 min., the
complex is kinetically inert (H. Taube).
Examples:
Cr(III) complexes are generally inert.
Cu(II) complexes are generally very labile.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ligandsubstitutionreactions-170615164137/85/Ligand-substitution-reactions-3-320.jpg)


![Ligand substitution in
octahedral complexes
ML6 + Y = ML5Y + L
• For substitution reactions of octahedral metal
complexes the following is very often observed:
At high concentration of Y, the rate is
independent of [Y], suggesting a dissociative
mechanism. At low concentrations of Y, the rate
depends on [Y] and [ML6], suggesting an
associative mechanism.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ligandsubstitutionreactions-170615164137/85/Ligand-substitution-reactions-6-320.jpg)


![Mechanism
• Kinetic studies show the reacting species is the bicarbonato
complex [Co(NH ) CO H].
• It is formed by the attack of proton on oxygen atom
bonded to Co.
• Decarboxylation of this bicarbonate complex then occurs
as the rate determining step.
• This step is then followed by protonation to give the aquo
complex.
3 35
2+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ligandsubstitutionreactions-170615164137/85/Ligand-substitution-reactions-9-320.jpg)

![Associative Mechanism at D4h Centers
ML3X + Y ML3Y + X
[PtCl4]2-
+ NH3 [PtCl3(NH3)]-
+ Cl-
The incoming ligand (colored blue)
approaches a vacant axial site of the square
planar complex to form a square pyramidal
intermediate (or transition state).
Intramolecular rearrangement via a trigonal
bipyramid generates a different square
pyramidal structure with the incoming
ligand now in the basal plane. (This motion
is closely related to Berry Pseudorotation).
The reaction is completed by the leaving
group departing from an axial site with
the stereochemistry being retained
during the substitution process.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ligandsubstitutionreactions-170615164137/85/Ligand-substitution-reactions-11-320.jpg)

![• [Pt(dien)X]+
+ py [Pt(dien)(py)]+
+ X-
• In H2O at 25o
C the sequence of lability is : H2O > Cl-
>Br -
> I-
> N3
-
> SCN-
> NO2
-
> CN-
a spread of over 106
in rate across series.
The Role Of The Leaving Group:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ligandsubstitutionreactions-170615164137/85/Ligand-substitution-reactions-13-320.jpg)