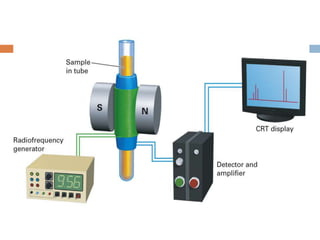
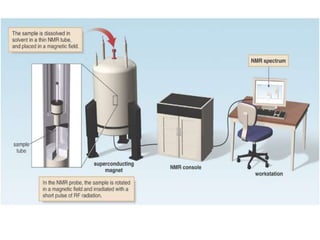
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is an analytical technique that uses radio waves and strong magnetic fields to characterize organic molecules. The key components of an NMR spectrometer include a sample holder, permanent magnet, magnetic coil, radio frequency generator and receiver, and readout system. The magnet provides a strong and uniform magnetic field, the generator produces radio waves to excite the nuclei, and the receiver and readout system detect and display the resonance signals to identify the molecules.