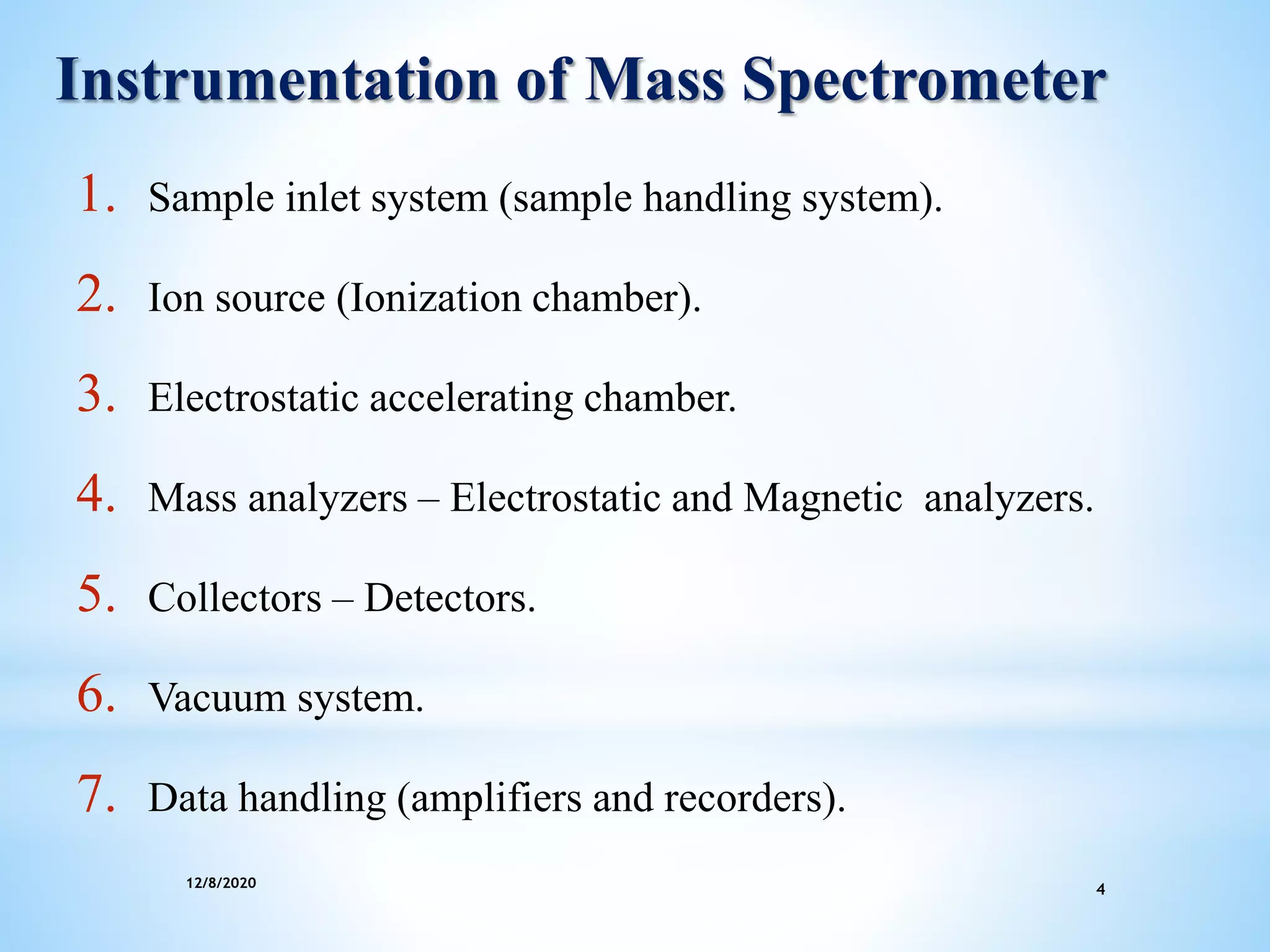
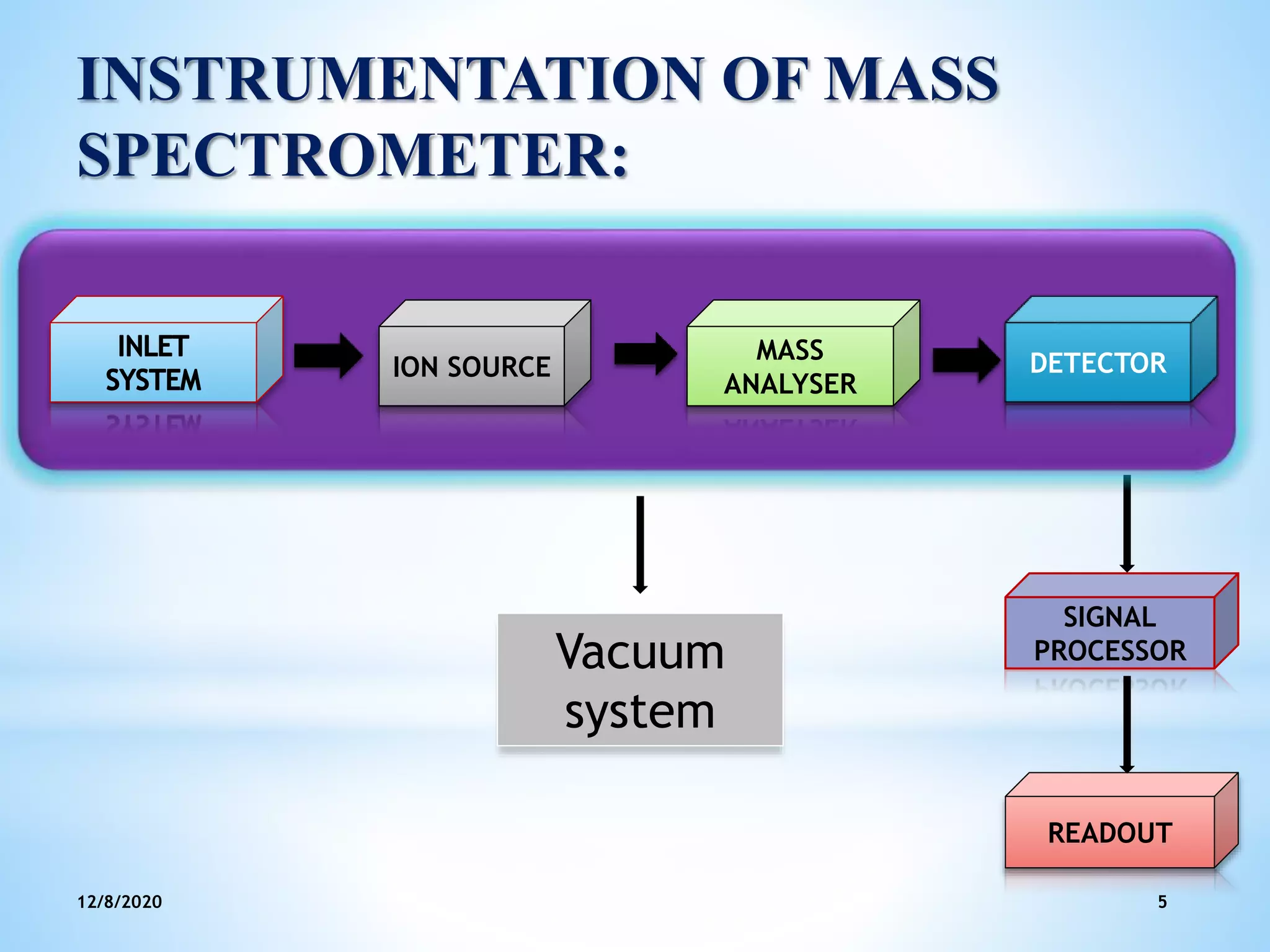
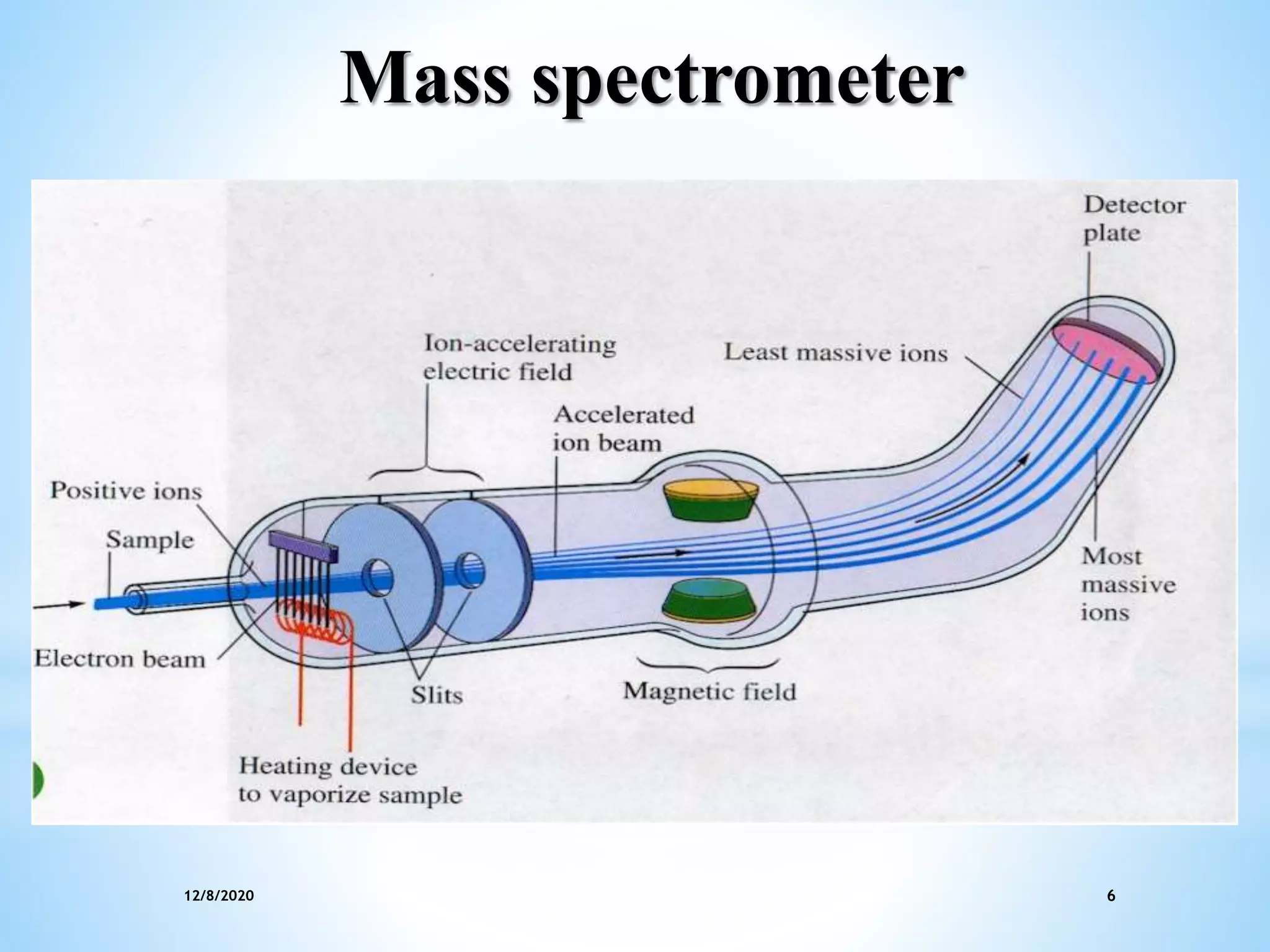
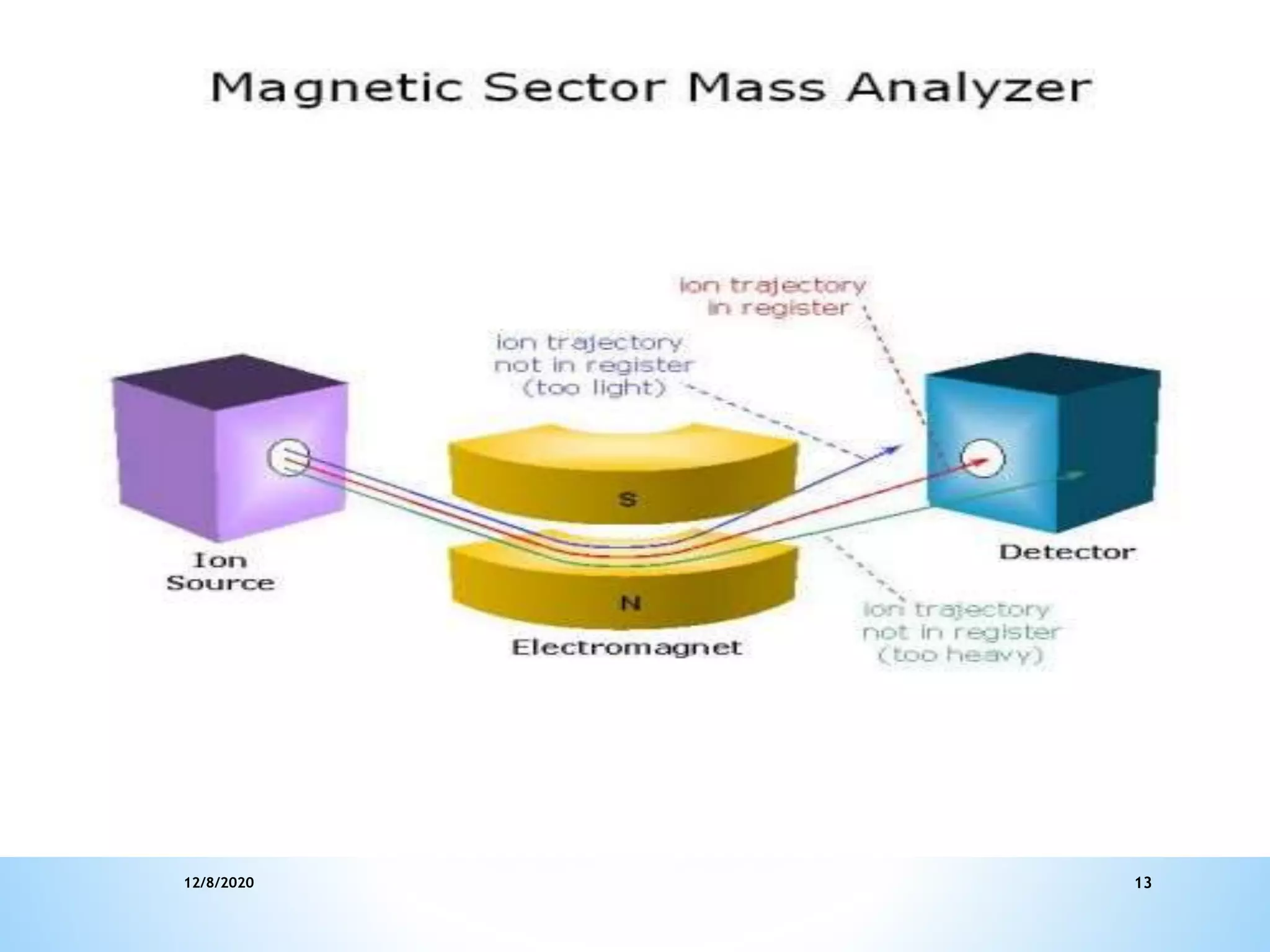
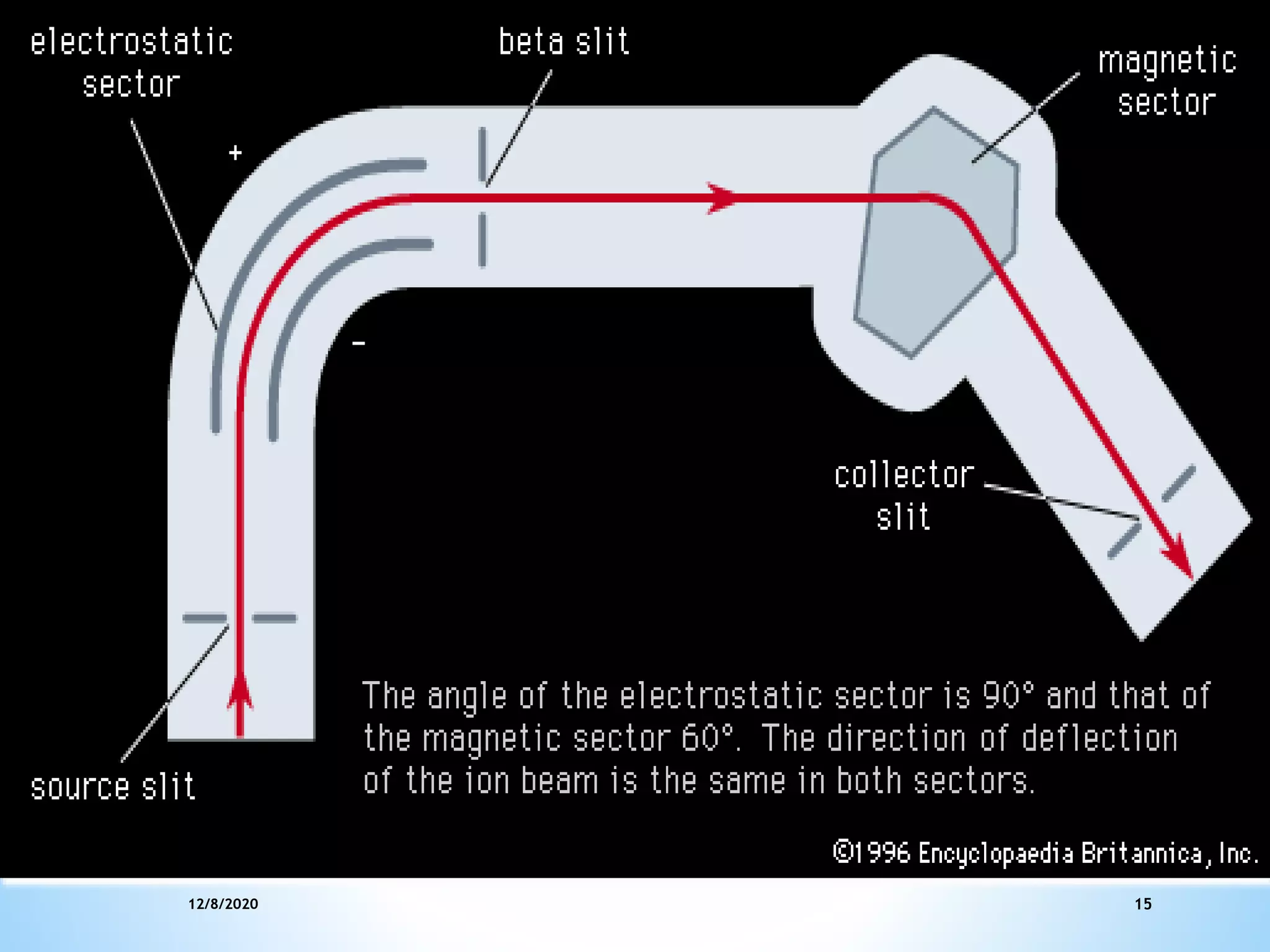
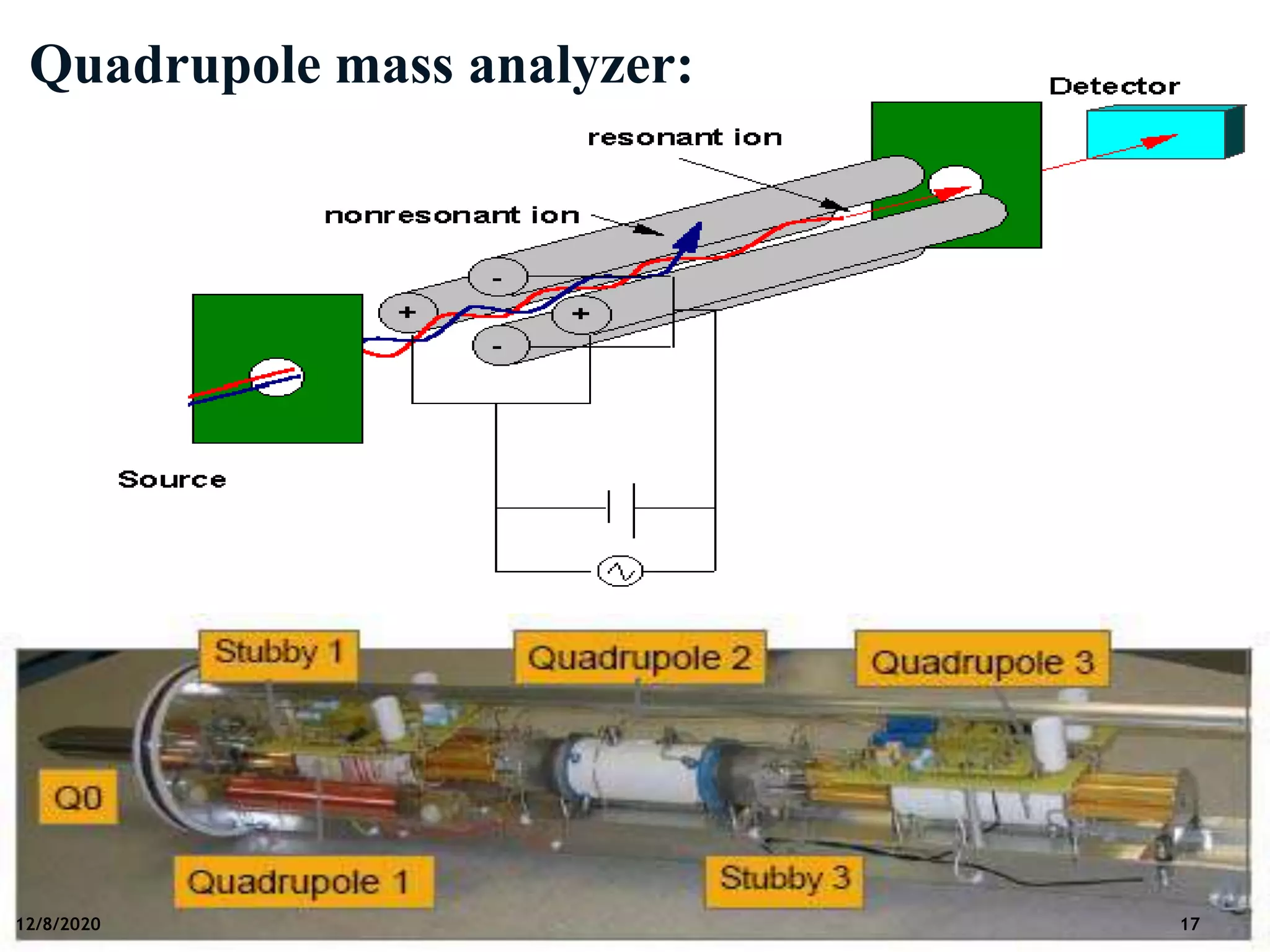
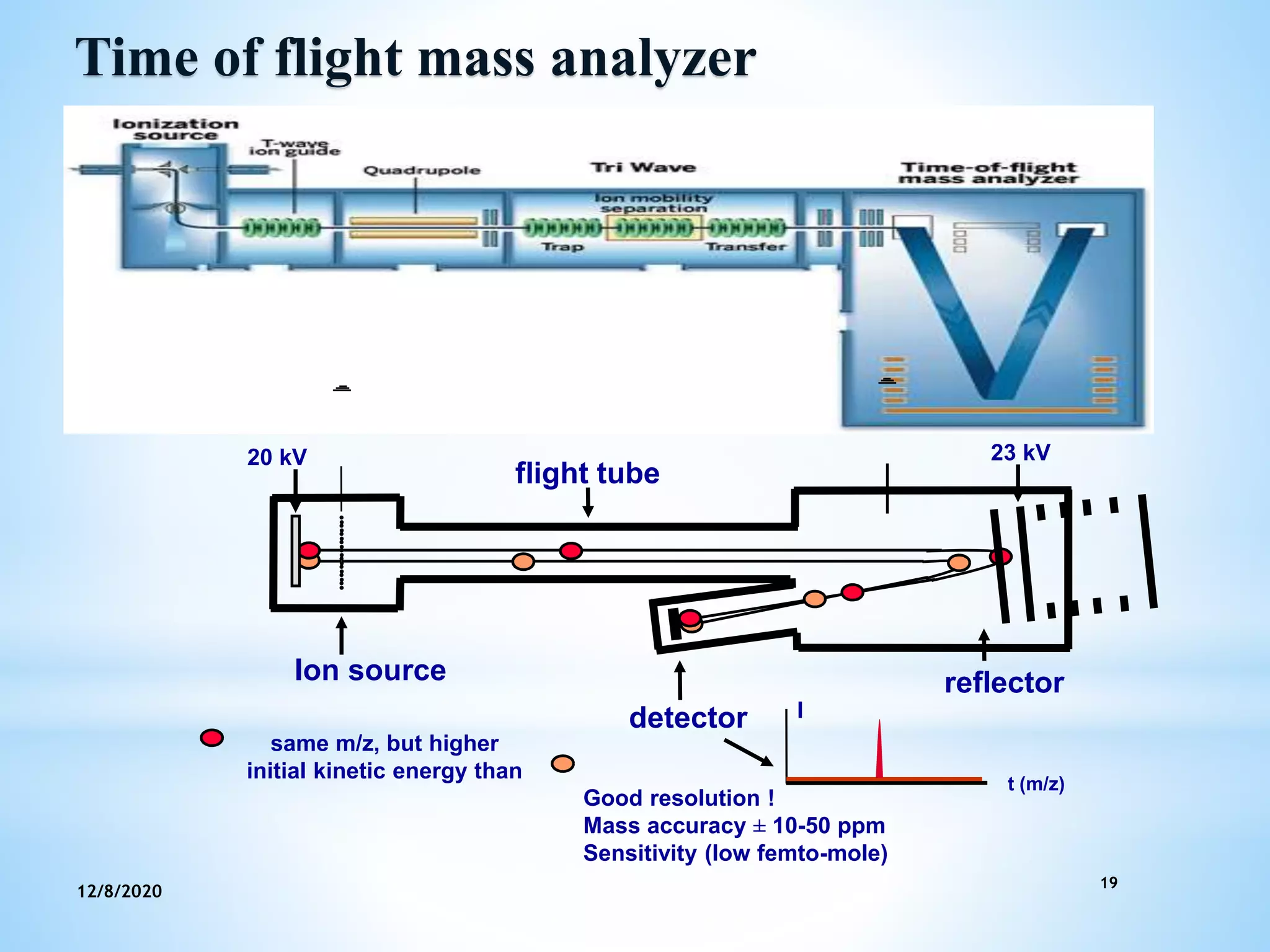
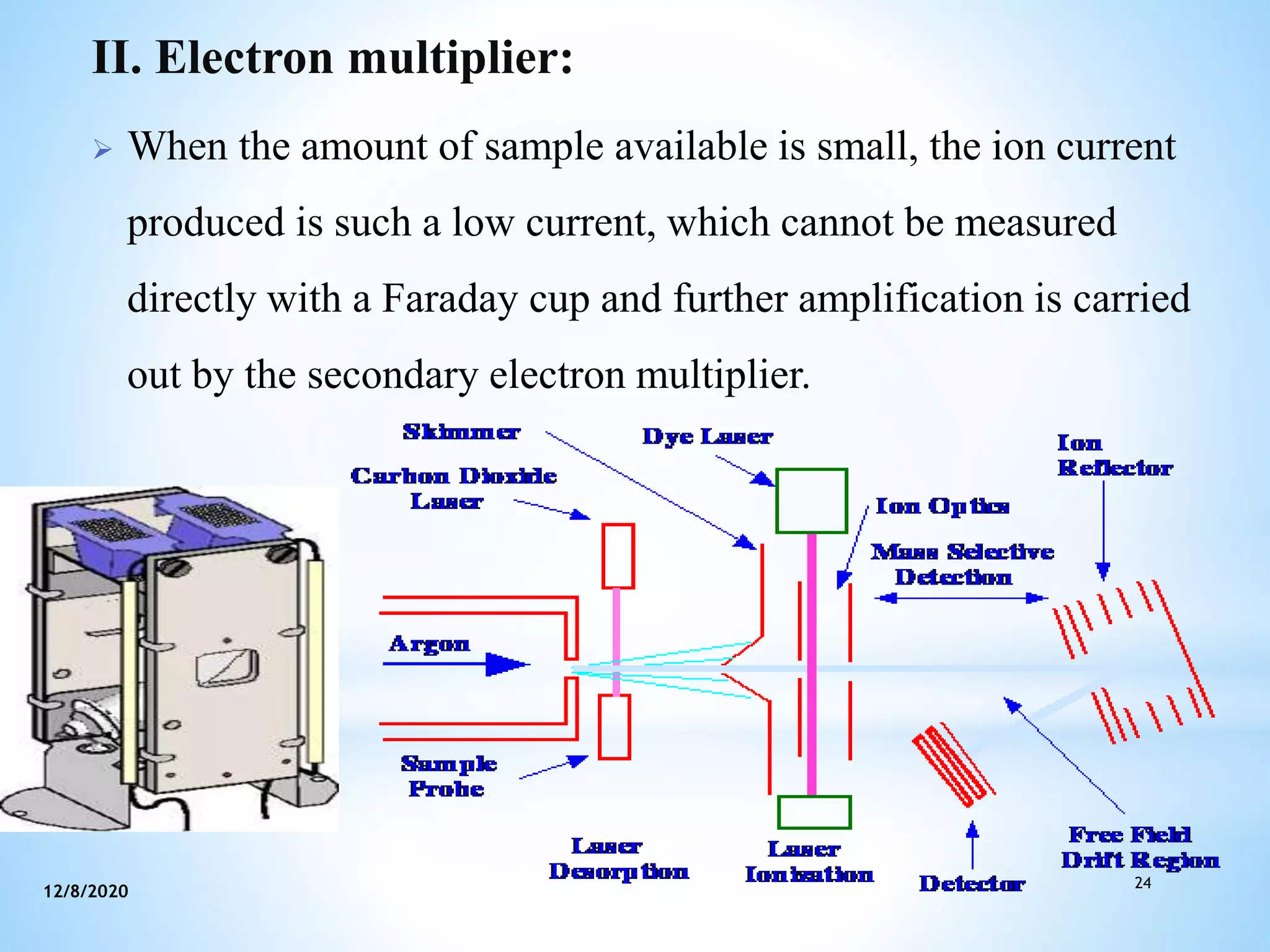
This document provides an overview of mass spectroscopy including its instrumentation and applications. It describes how mass spectroscopy works by bombarding compounds with electrons to produce ions or fragments that are then separated by mass and detected. The key components of a mass spectrometer are described as the sample inlet, ion source, mass analyzer, detector, and vacuum system. Common types of mass analyzers like magnetic sector, quadrupole, and time-of-flight are explained. Applications of mass spectroscopy include identification of unknown compounds, clinical research, and determination of molecular formulas and fragmentation patterns.