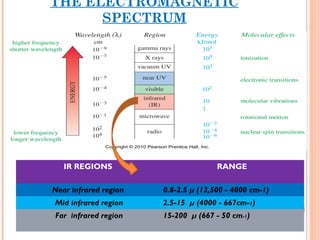
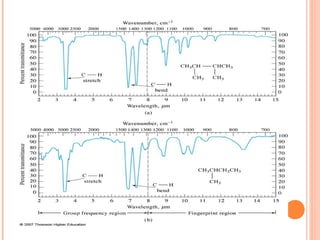
IR spectroscopy analyzes the vibrational frequencies of bonds in molecules to determine their structure. It works by measuring the absorption of IR radiation by molecular bonds. Different functional groups absorb at characteristic frequencies, producing a molecular "fingerprint". IR spectroscopy is useful for identification of unknown compounds, analyzing purity, and monitoring chemical reactions through changes in bond absorption. It is a nondestructive technique applied in various fields such as pharmaceutical analysis, biomedical research, forensic science, and atmospheric studies.