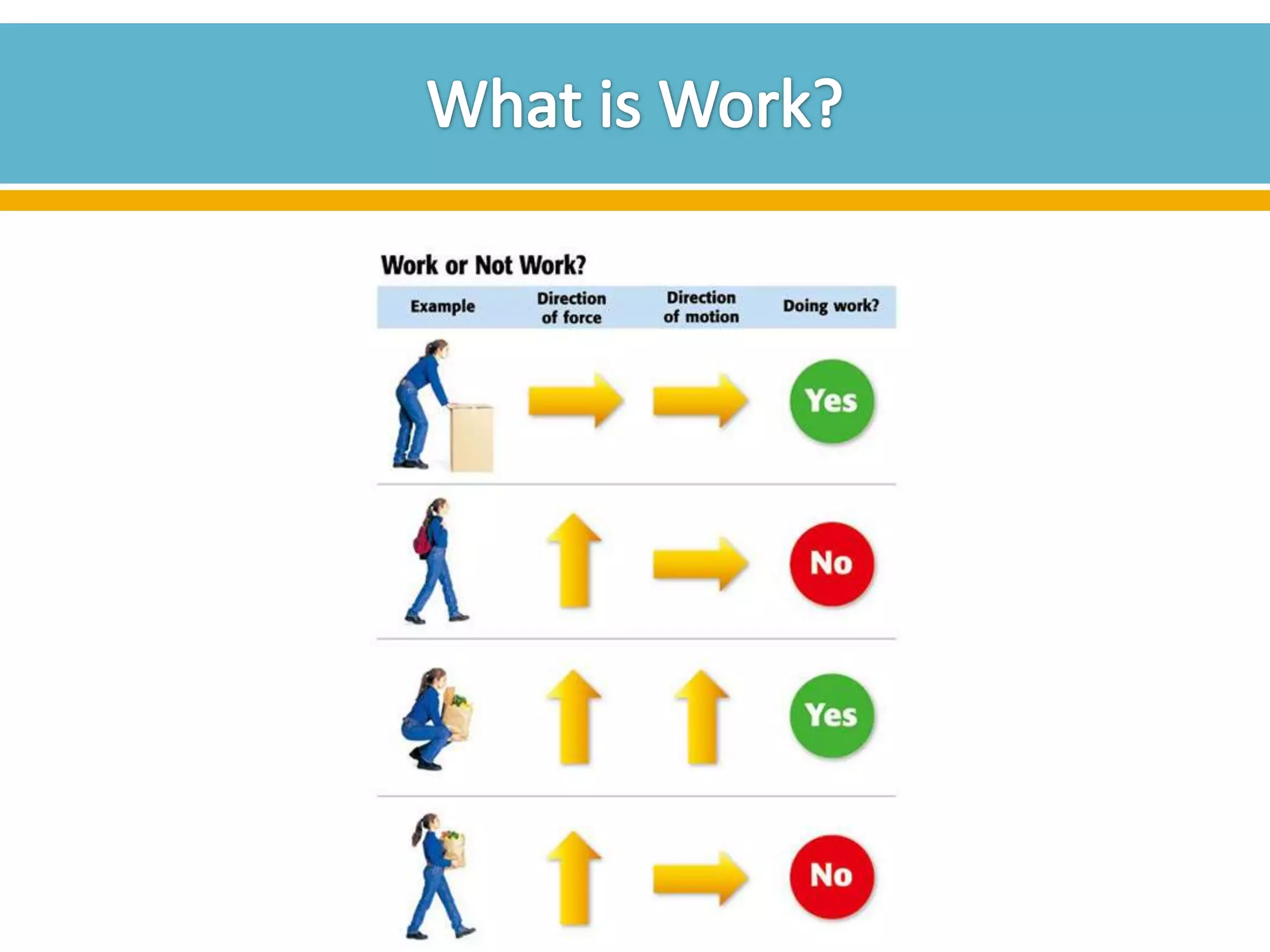
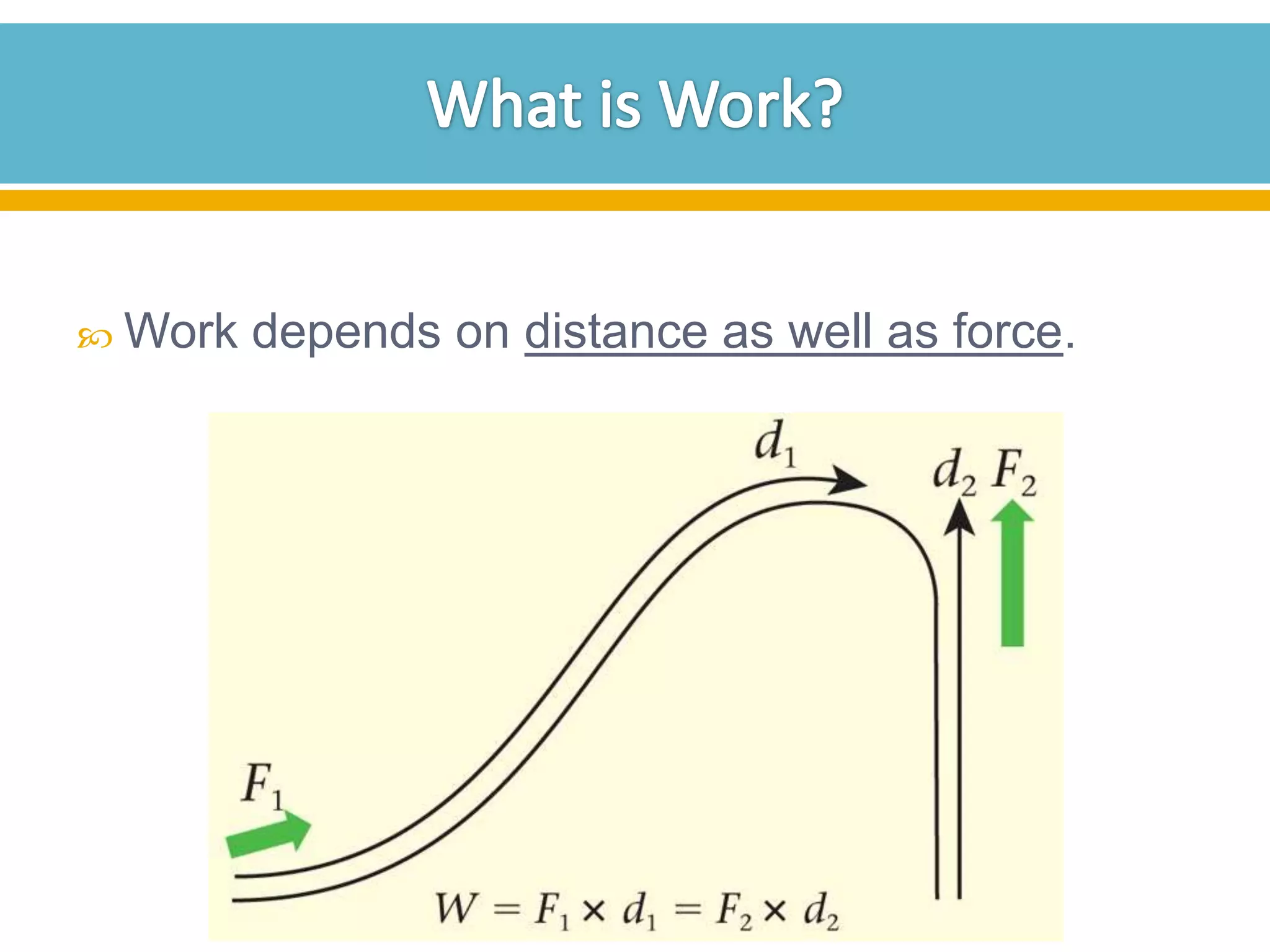
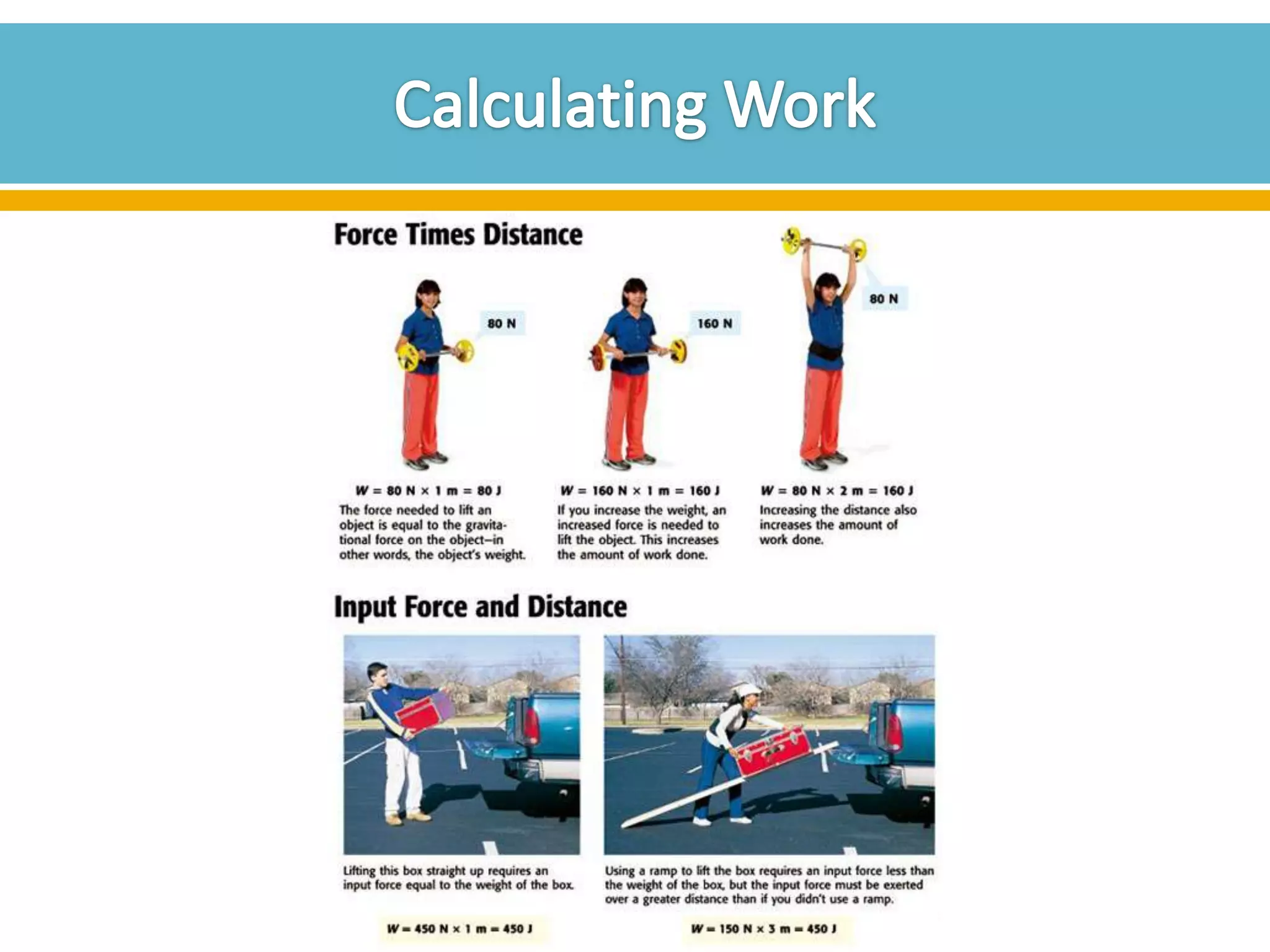
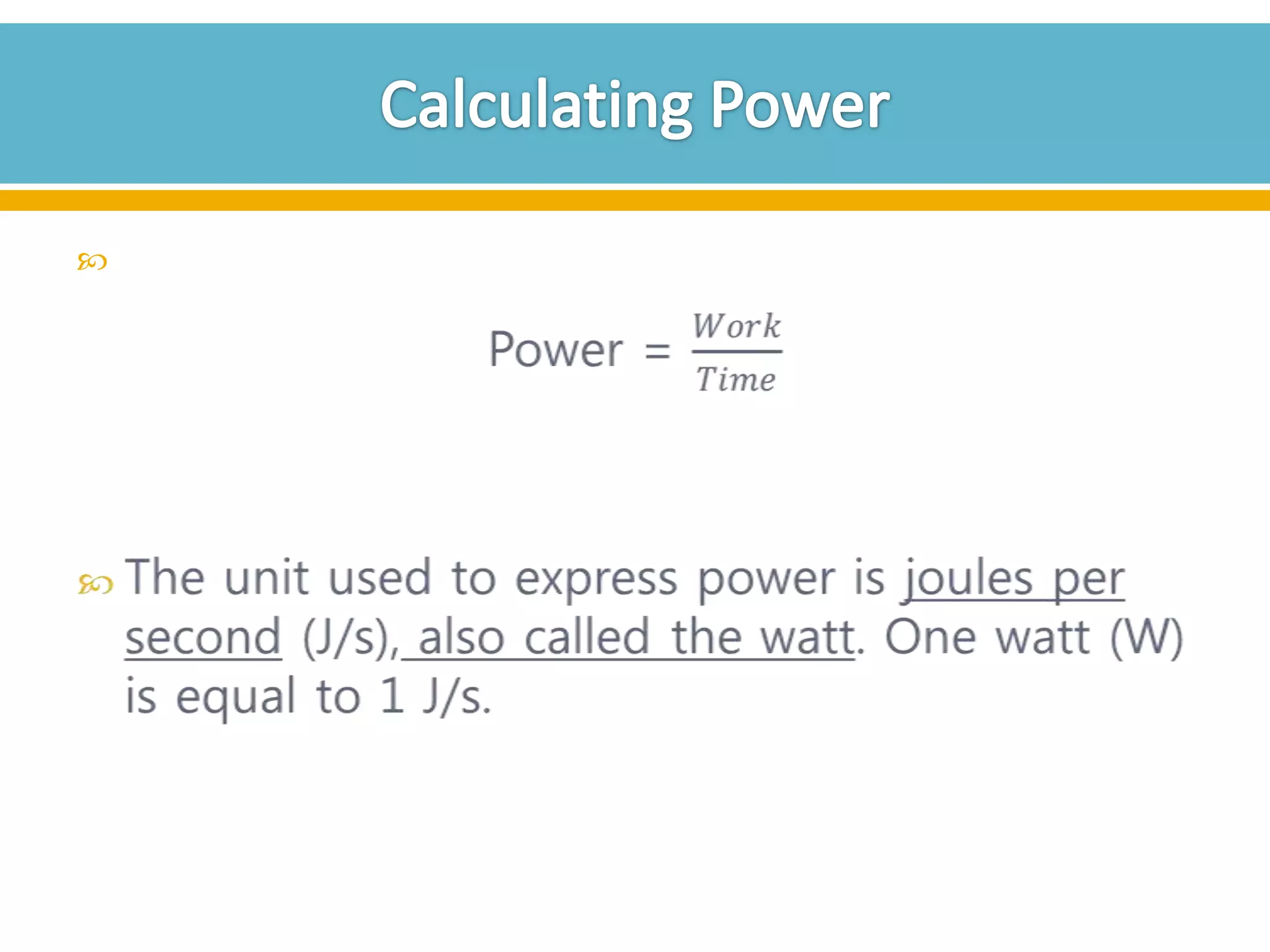
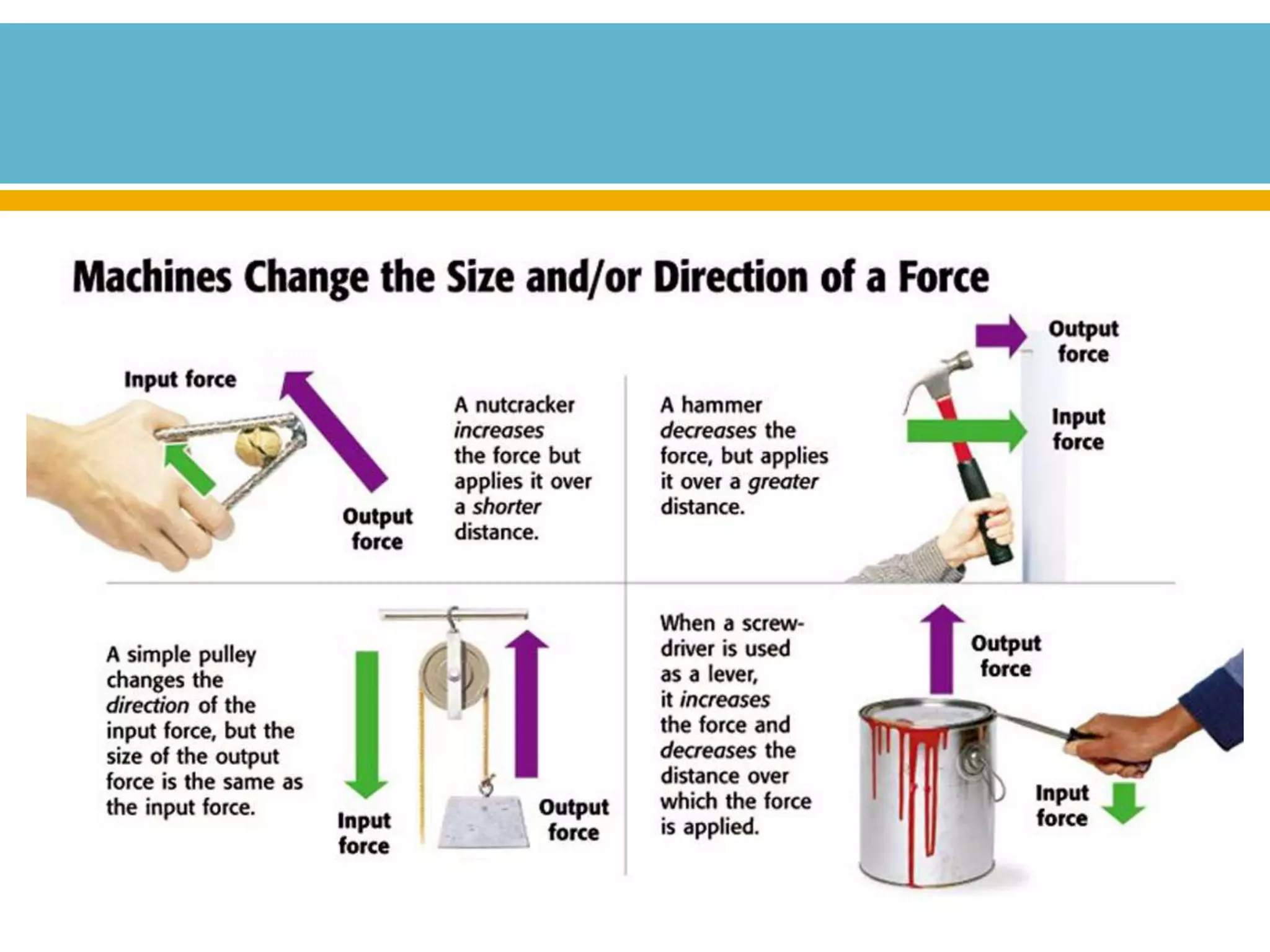
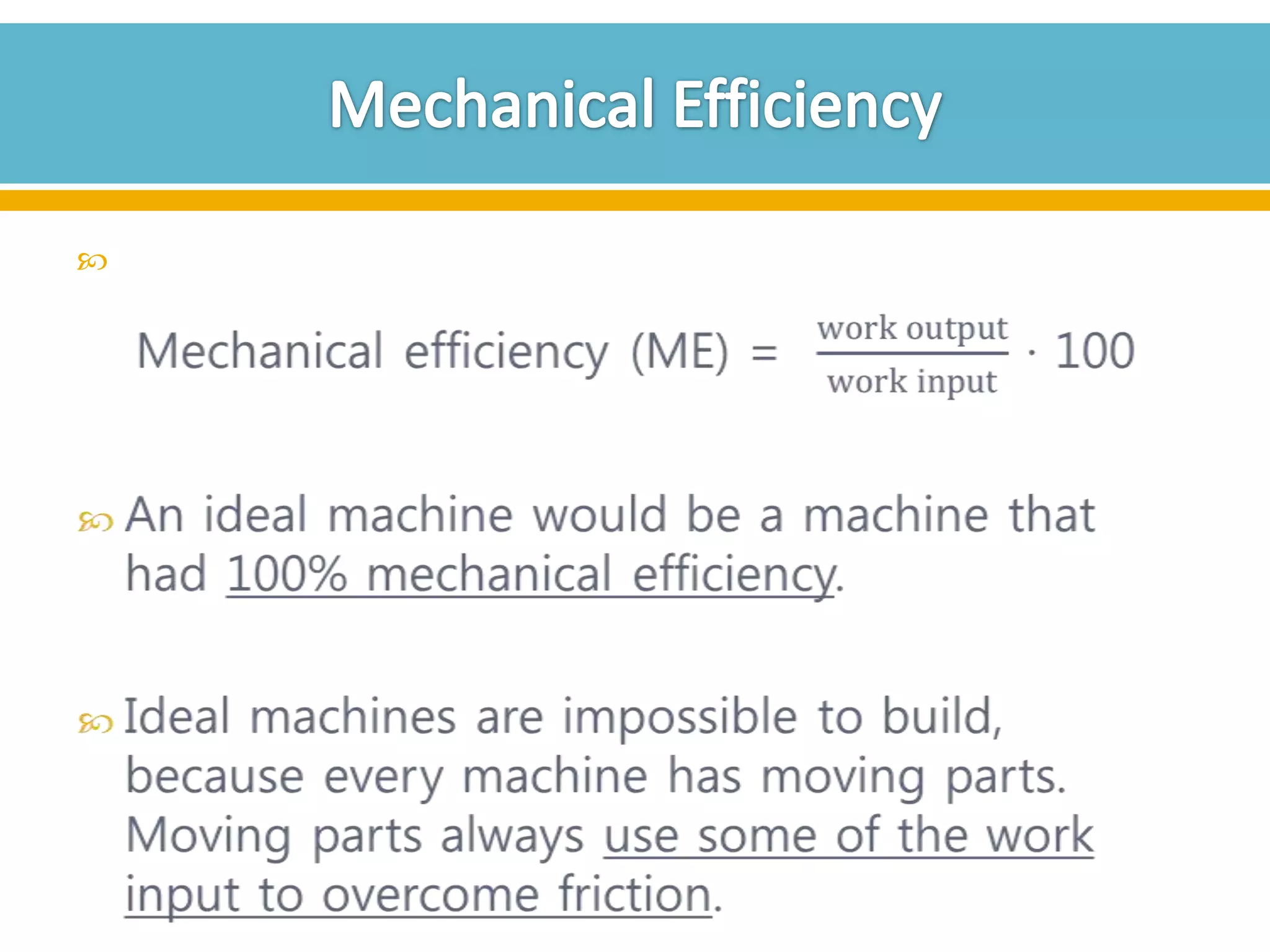
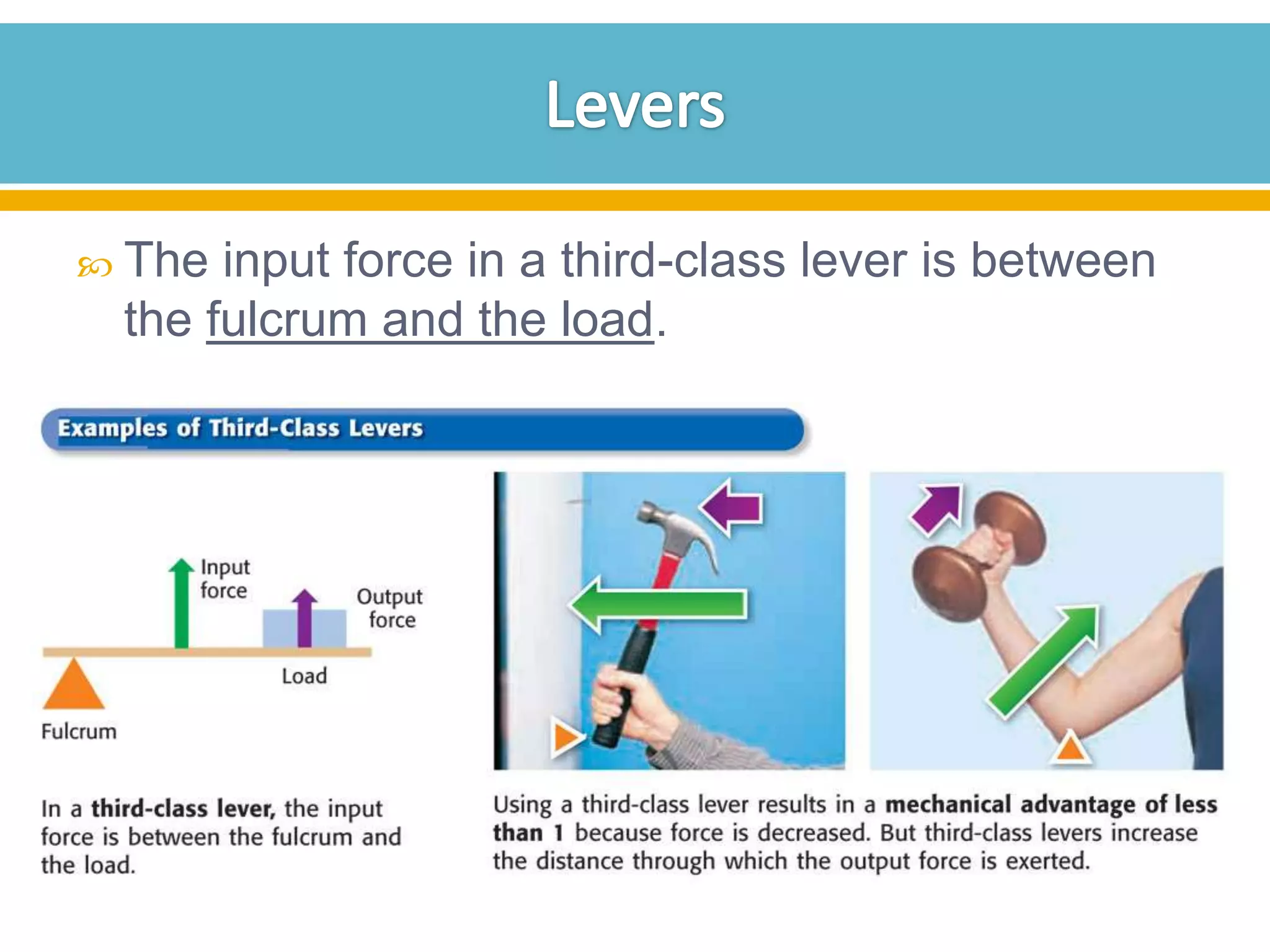
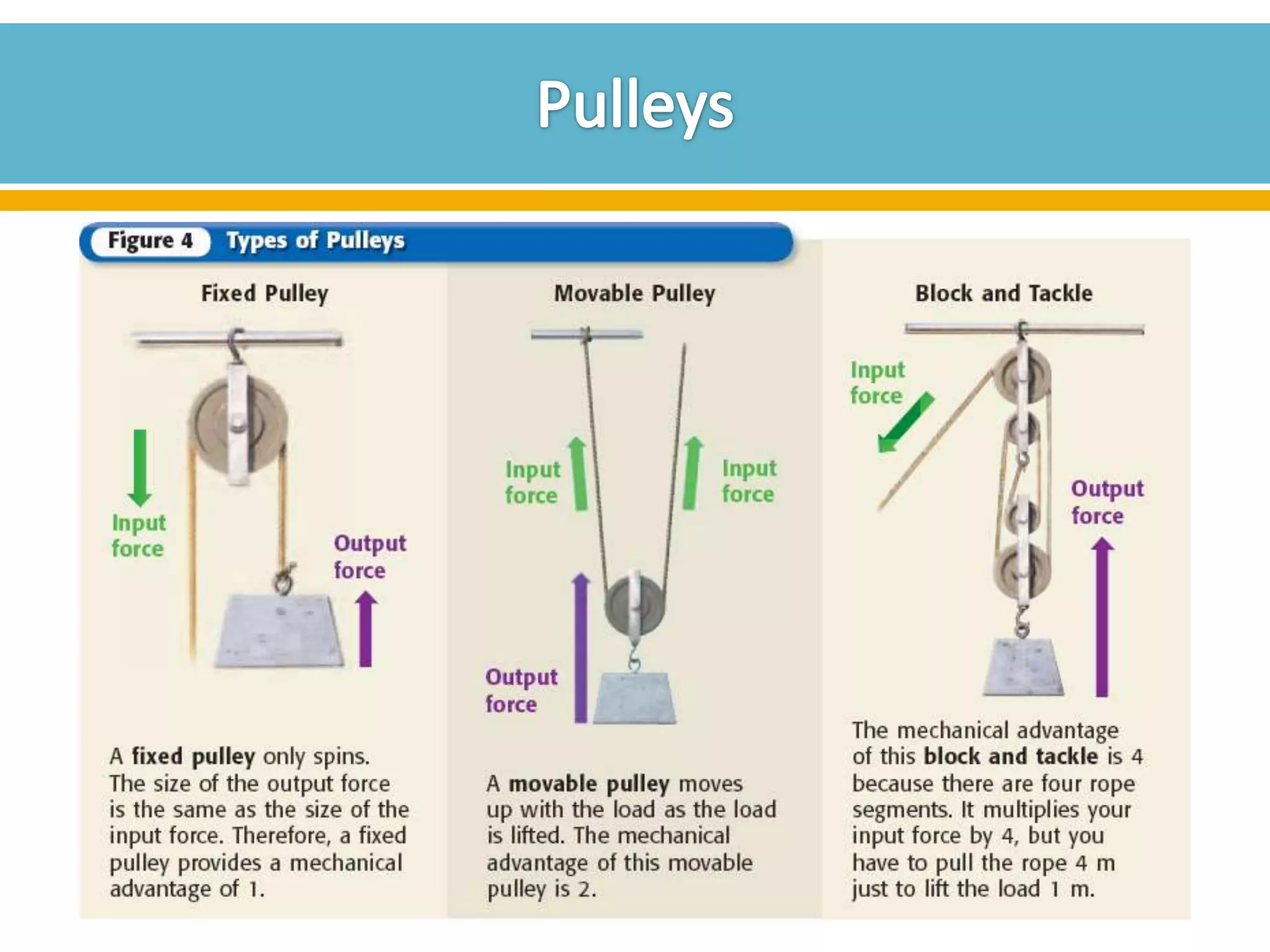
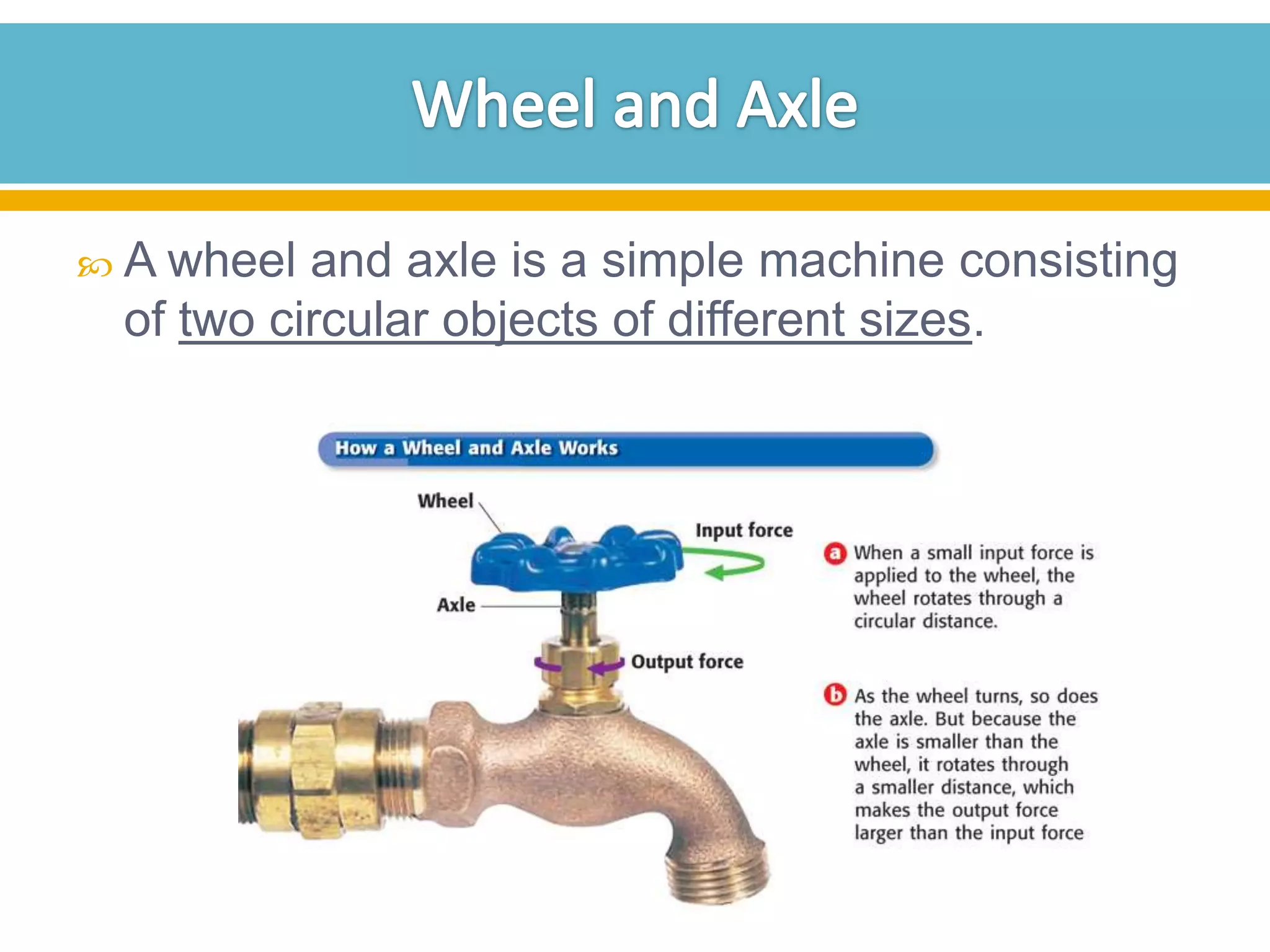
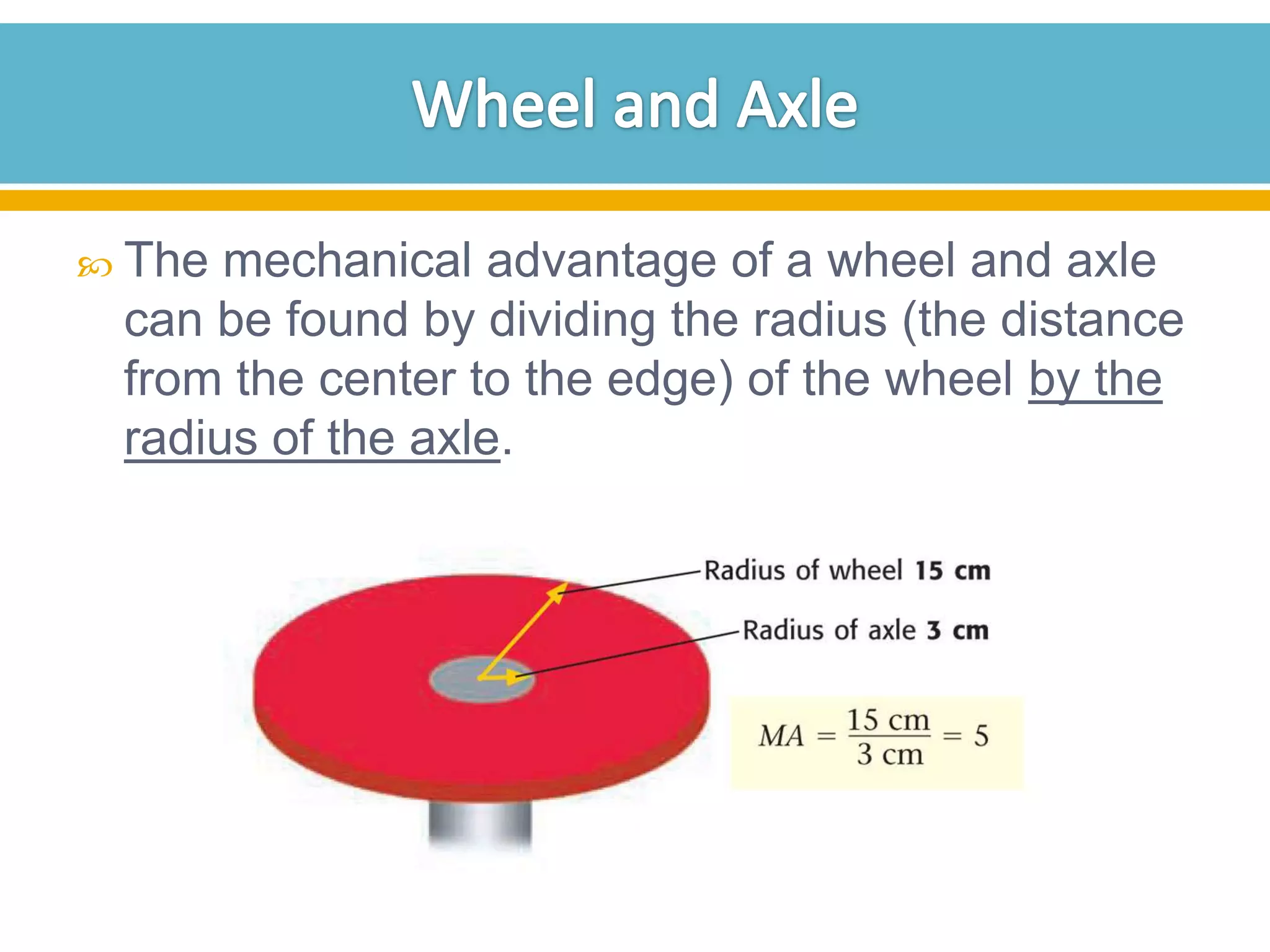
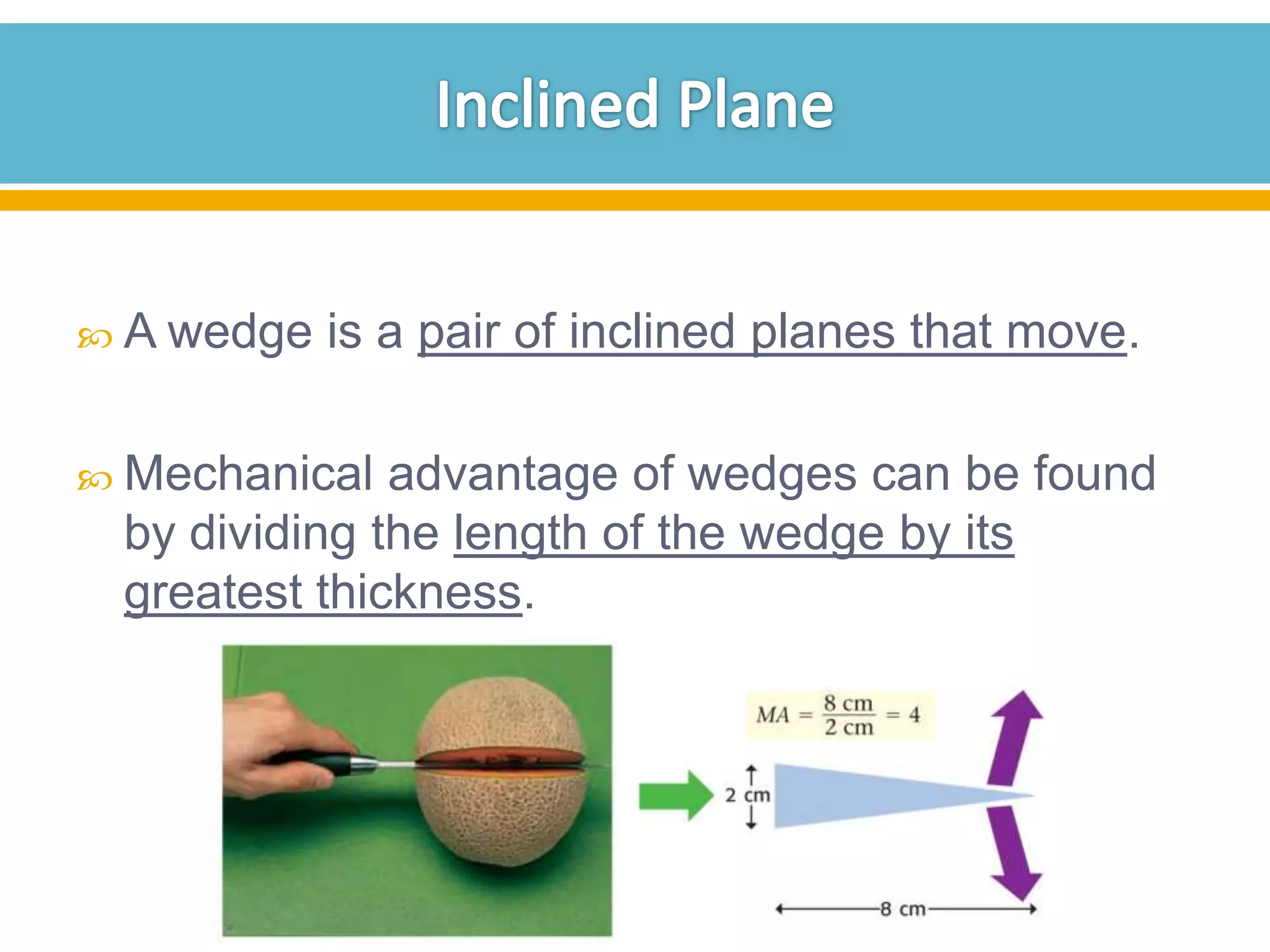
The document discusses different types of work and simple machines. It begins by defining work as the transfer of energy through a force causing an object to move in the direction of the force. It then describes six simple machines: the lever, pulley, wheel and axle, inclined plane, wedge, and screw. The summary provides the definitions of each machine, specifically that a lever is a bar that pivots on a fulcrum, a pulley allows a rope or chain to pass over a wheel, and a wheel and axle consist of two circular objects of different sizes. Compound machines are made up of combinations of two or more simple machines.