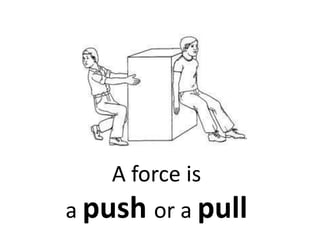
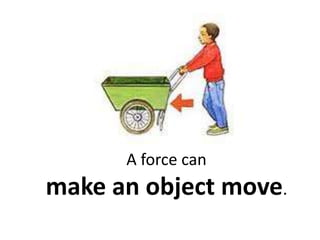
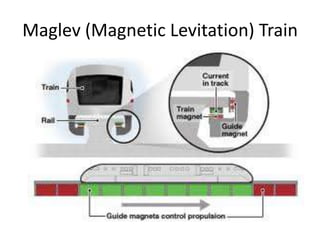
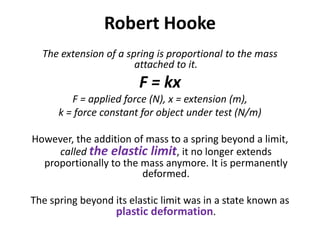
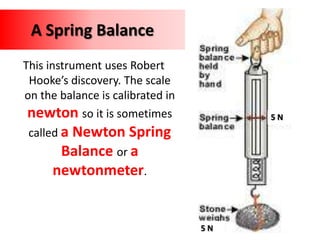
Forces can make objects move, change speed or direction, or deform shape. A force is measured in Newtons and can be exerted through contact or non-contact. Contact forces include tension, strain, and impact forces. Non-contact forces include magnetic, electrostatic, and gravitational forces. Magnetic forces involve attraction or repulsion between poles, while gravitational forces act between all masses and decrease with distance.