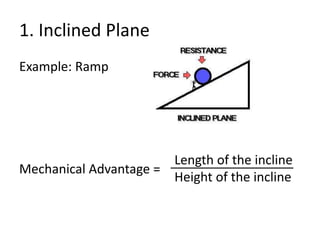
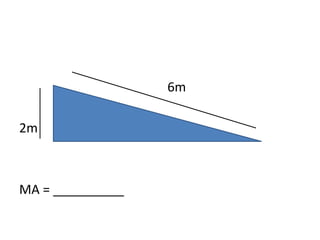
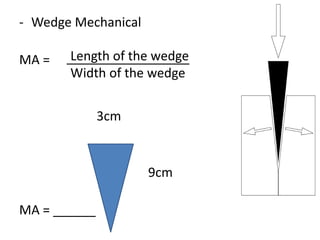
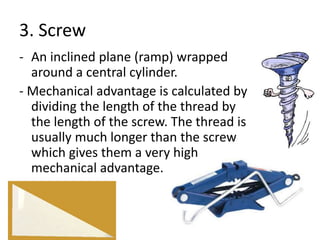
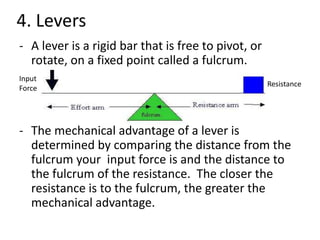
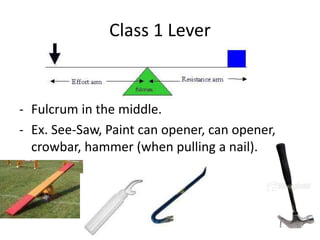
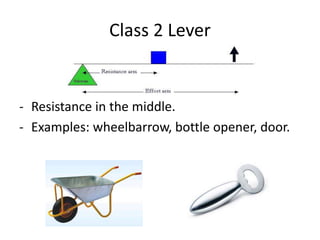
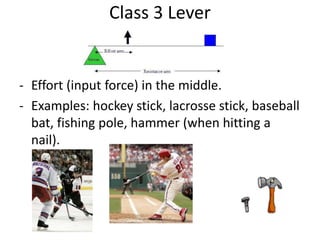
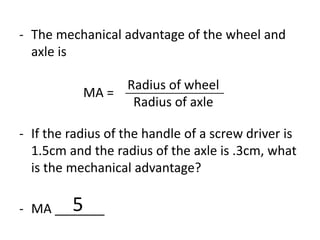
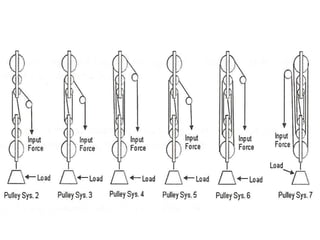
This document discusses simple machines and how they work. It defines key terms like work, power, mechanical advantage, and efficiency. It then describes the six simple machines: the inclined plane, wedge, screw, lever (which has three classes), wheel and axle, and pulley. For each machine it provides examples, diagrams, and how to calculate mechanical advantage. It notes that machines make work easier by changing the amount or direction of force needed. All machines lose some efficiency to friction, but more efficient machines lose less work. Compound machines use two or more simple machines and have a mechanical advantage equal to the product of the individual machines.