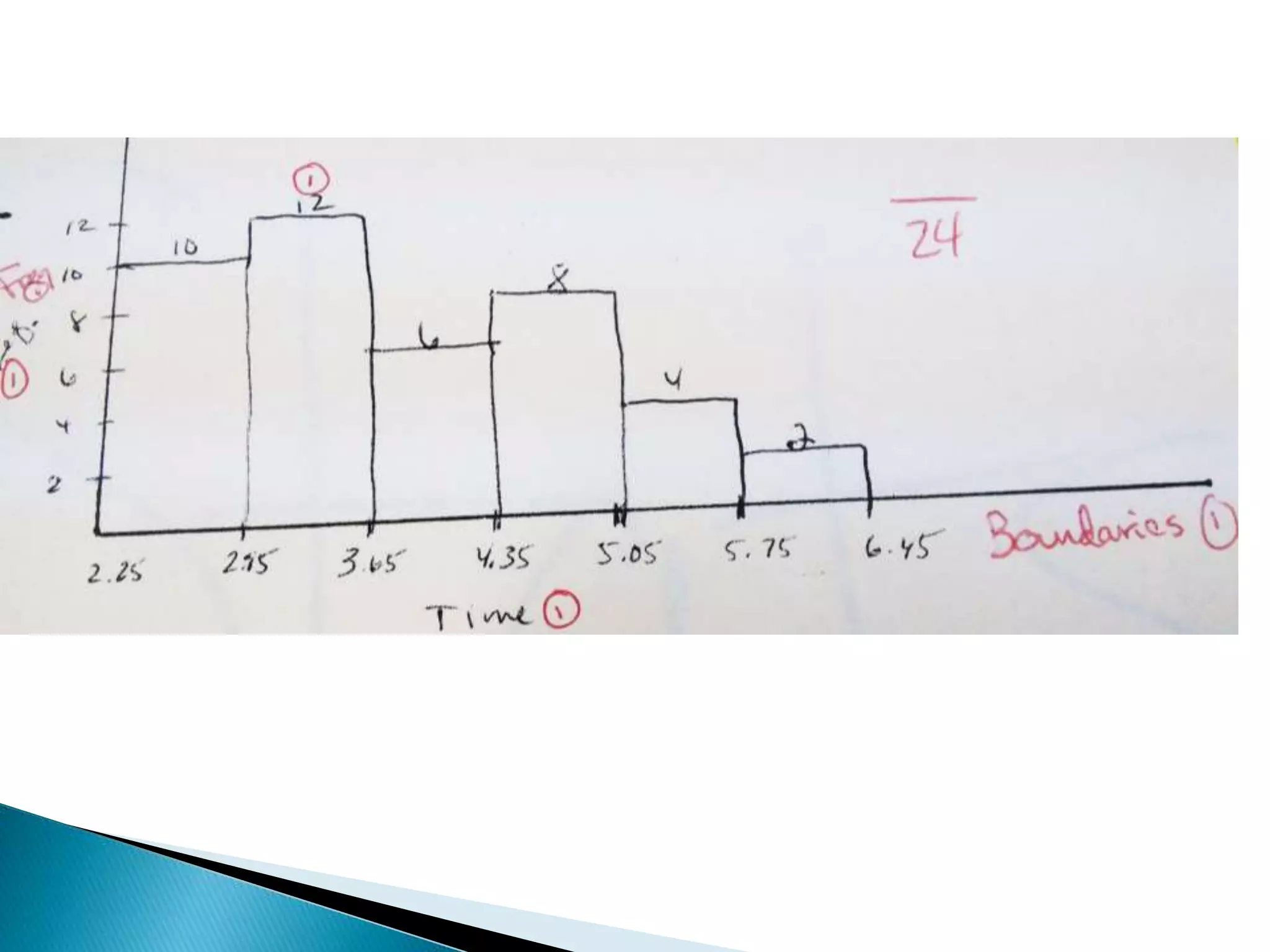
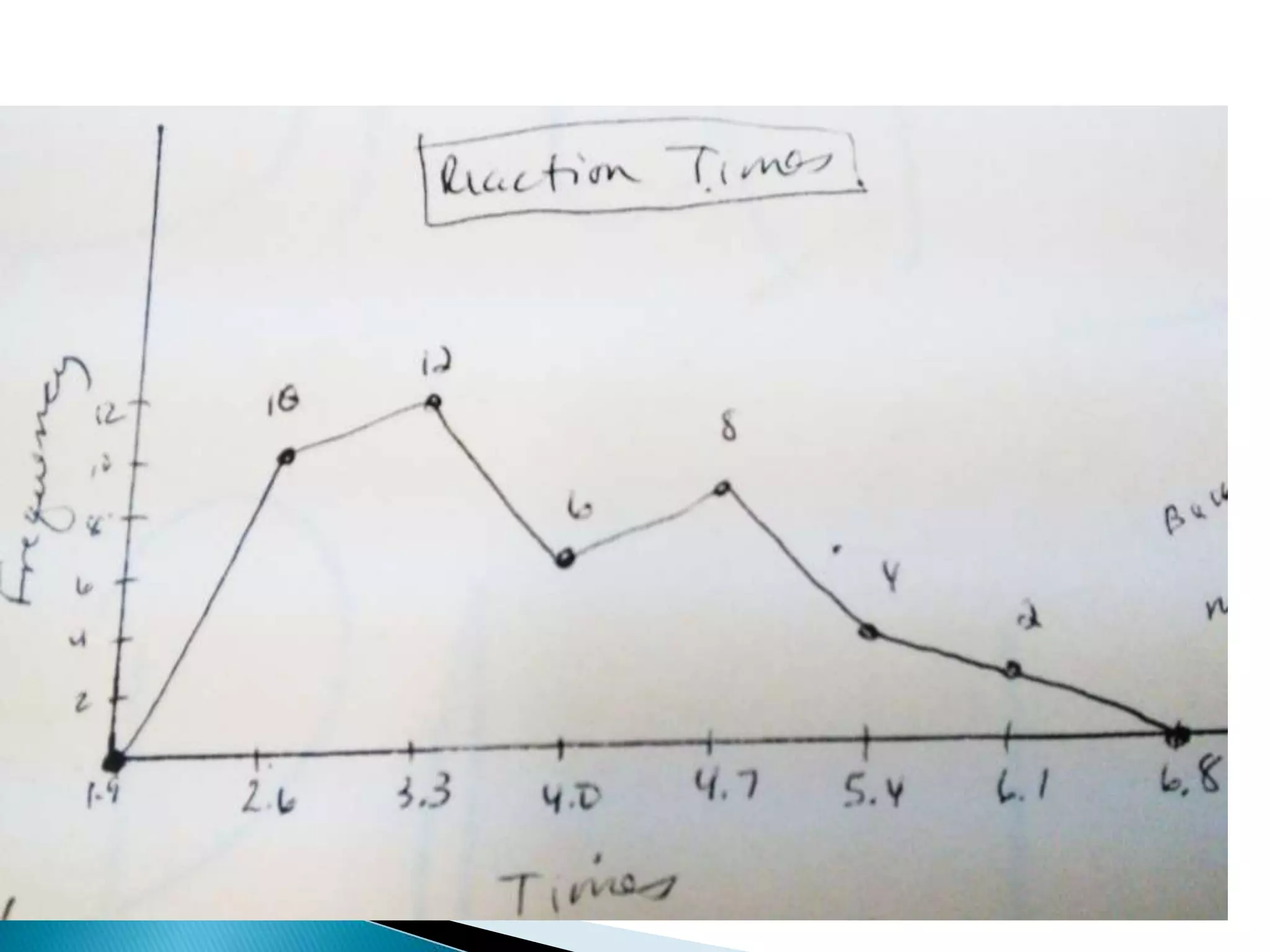
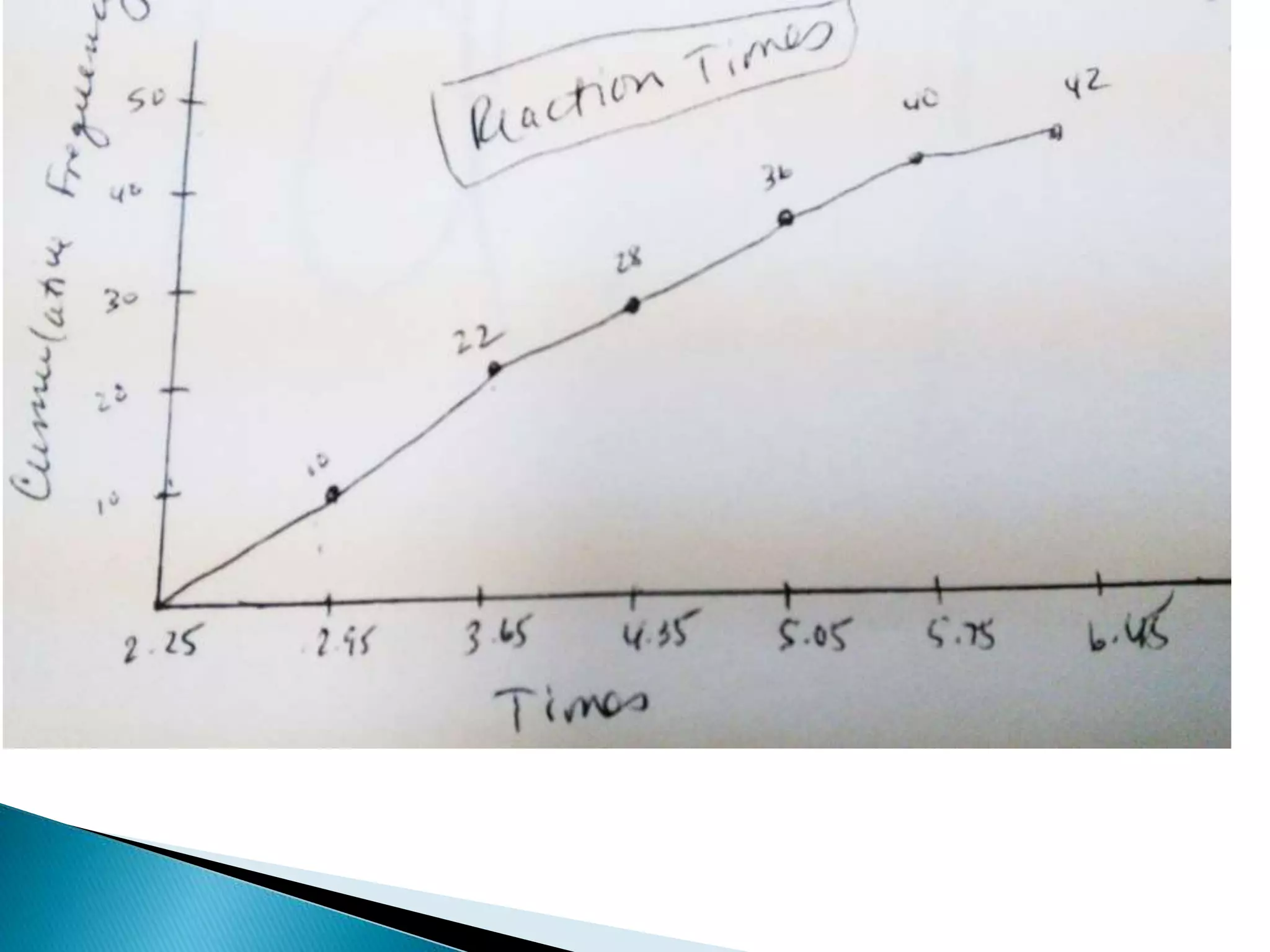
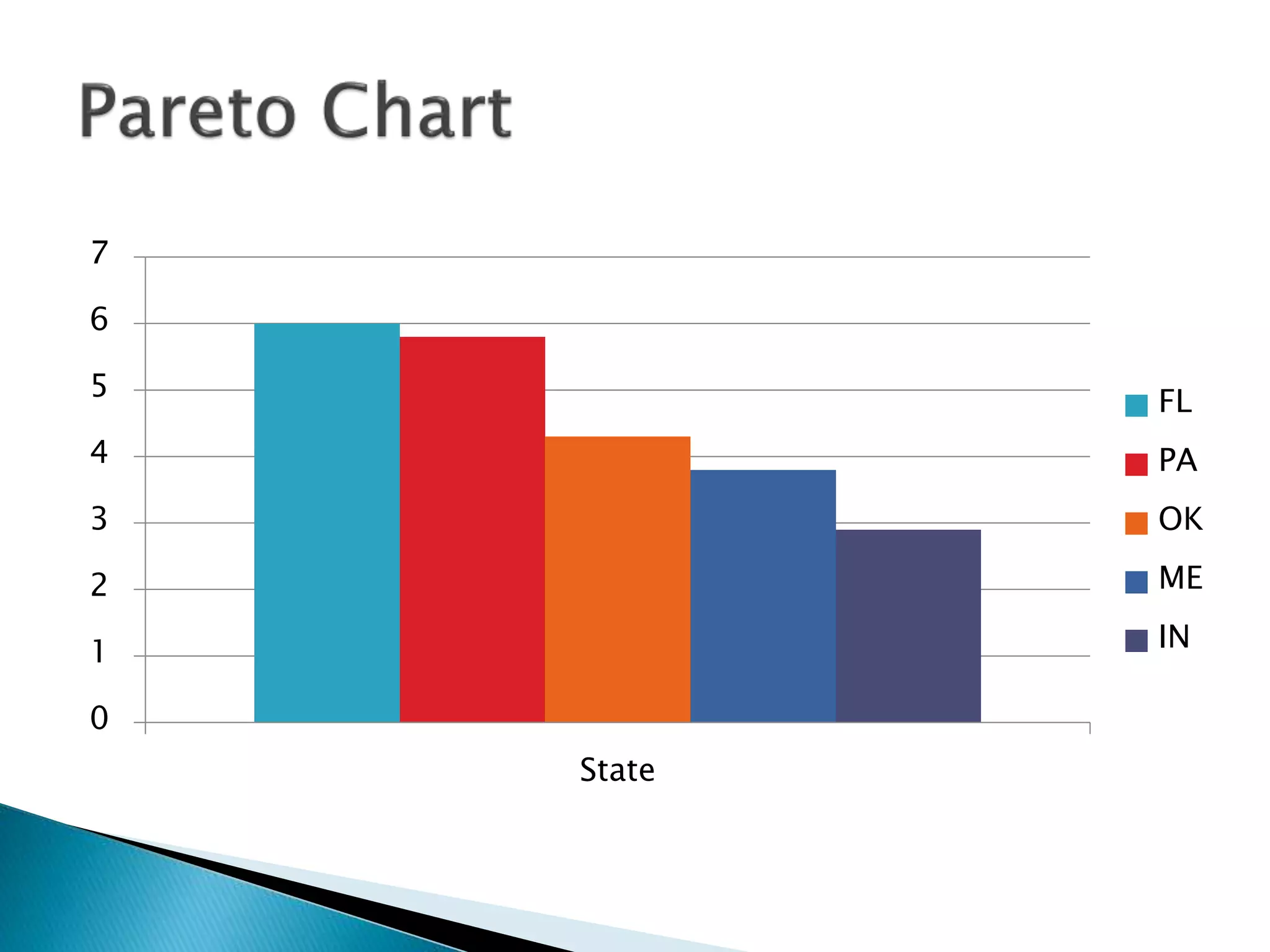
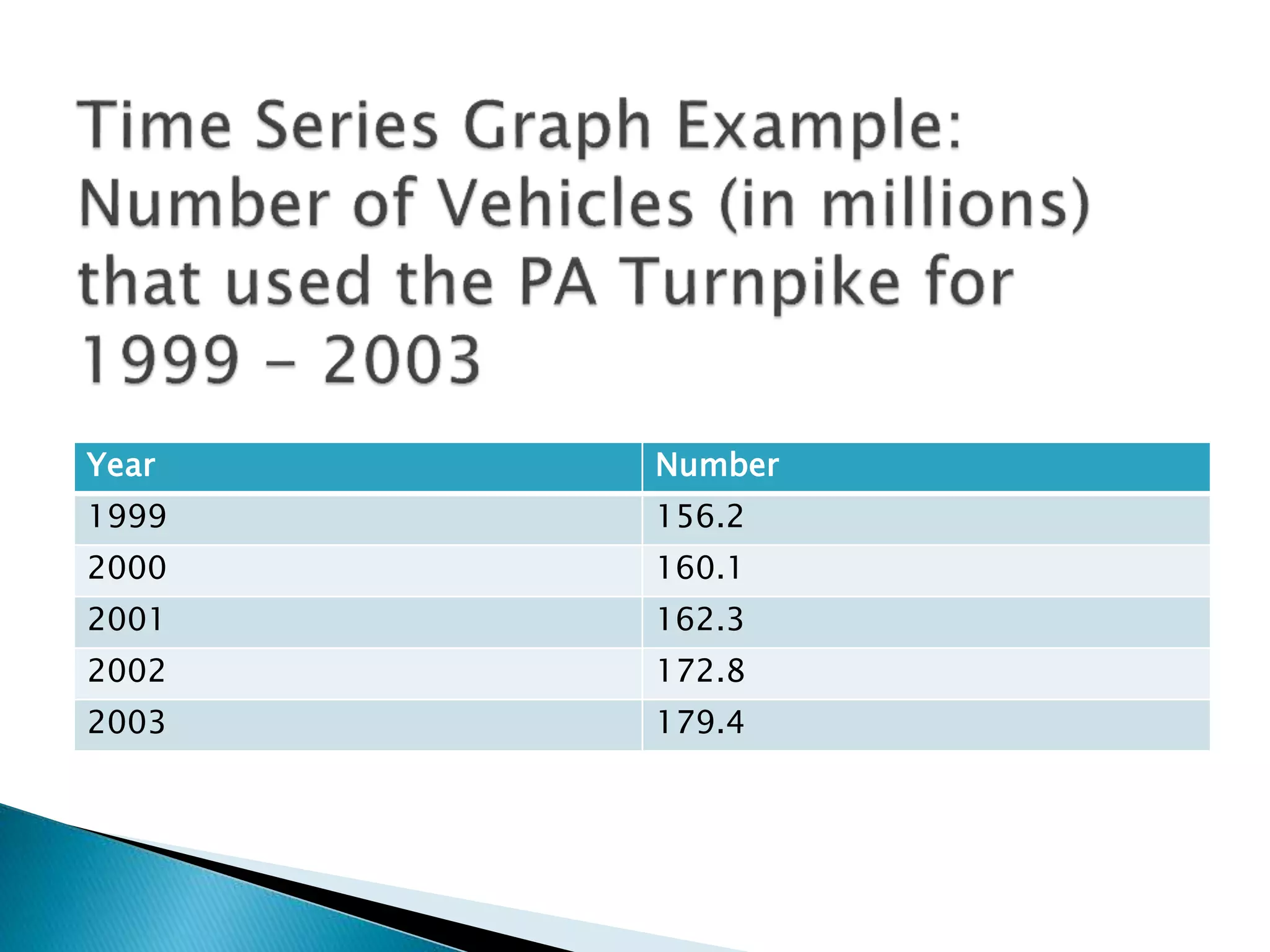
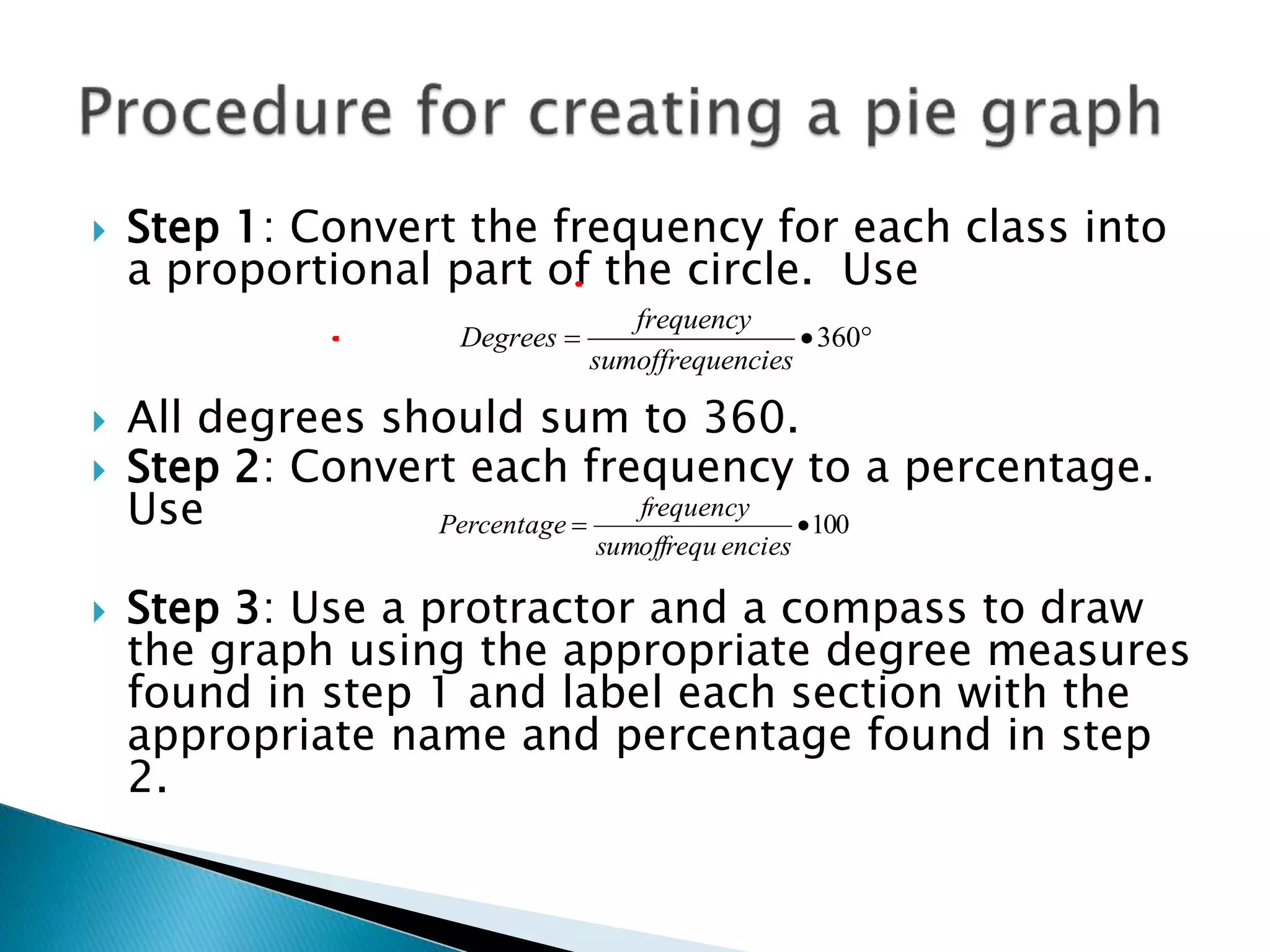
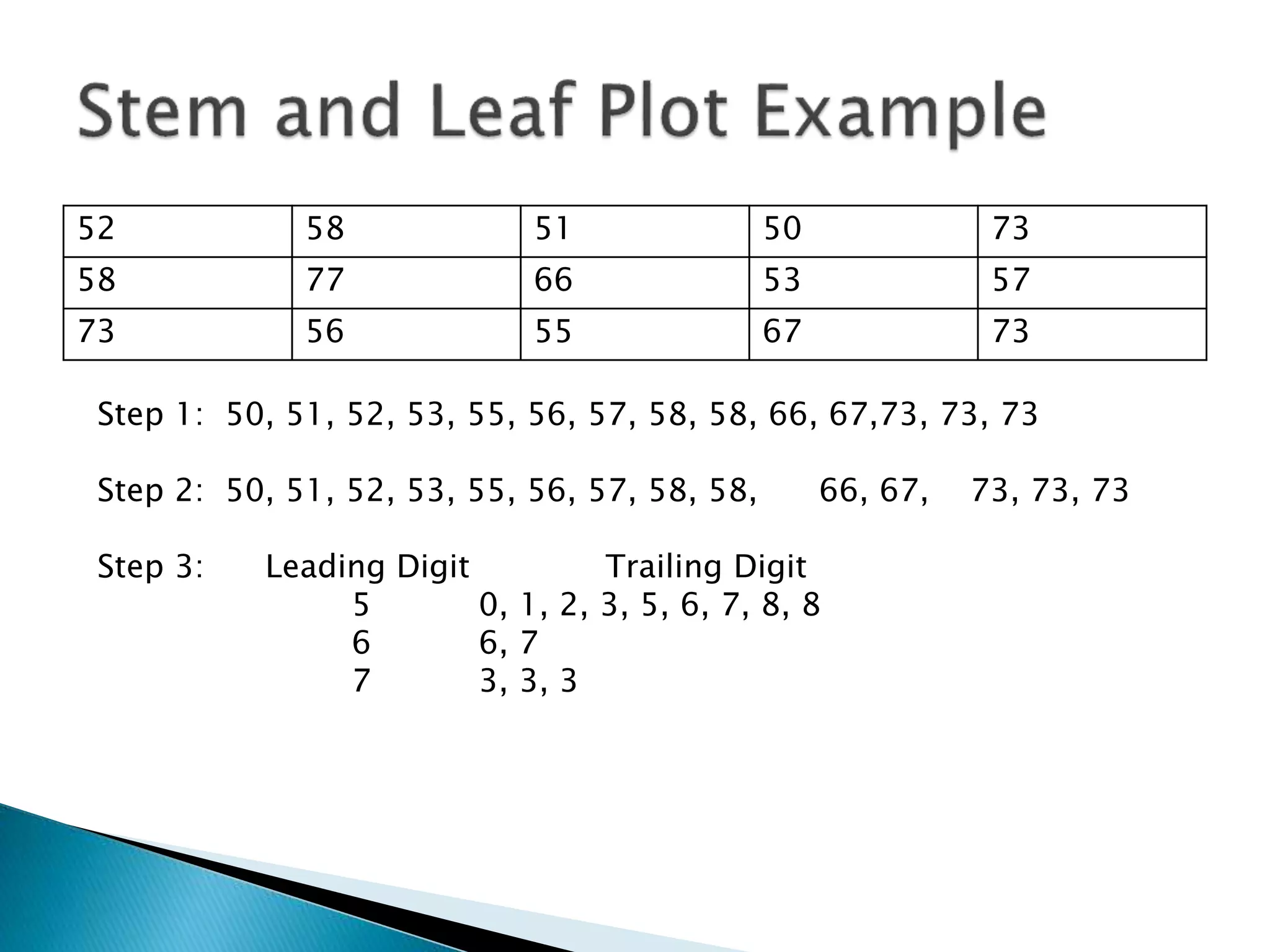
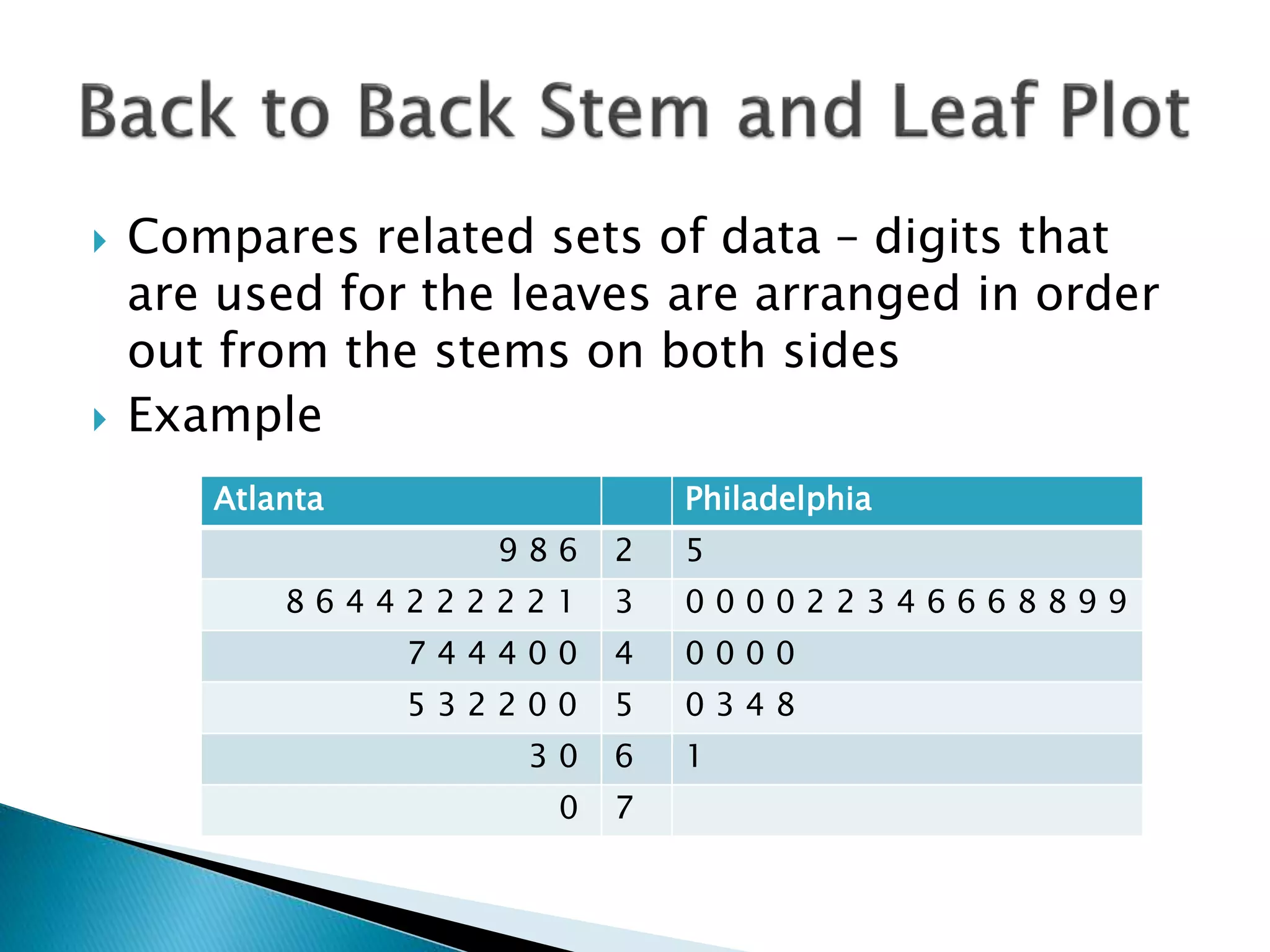
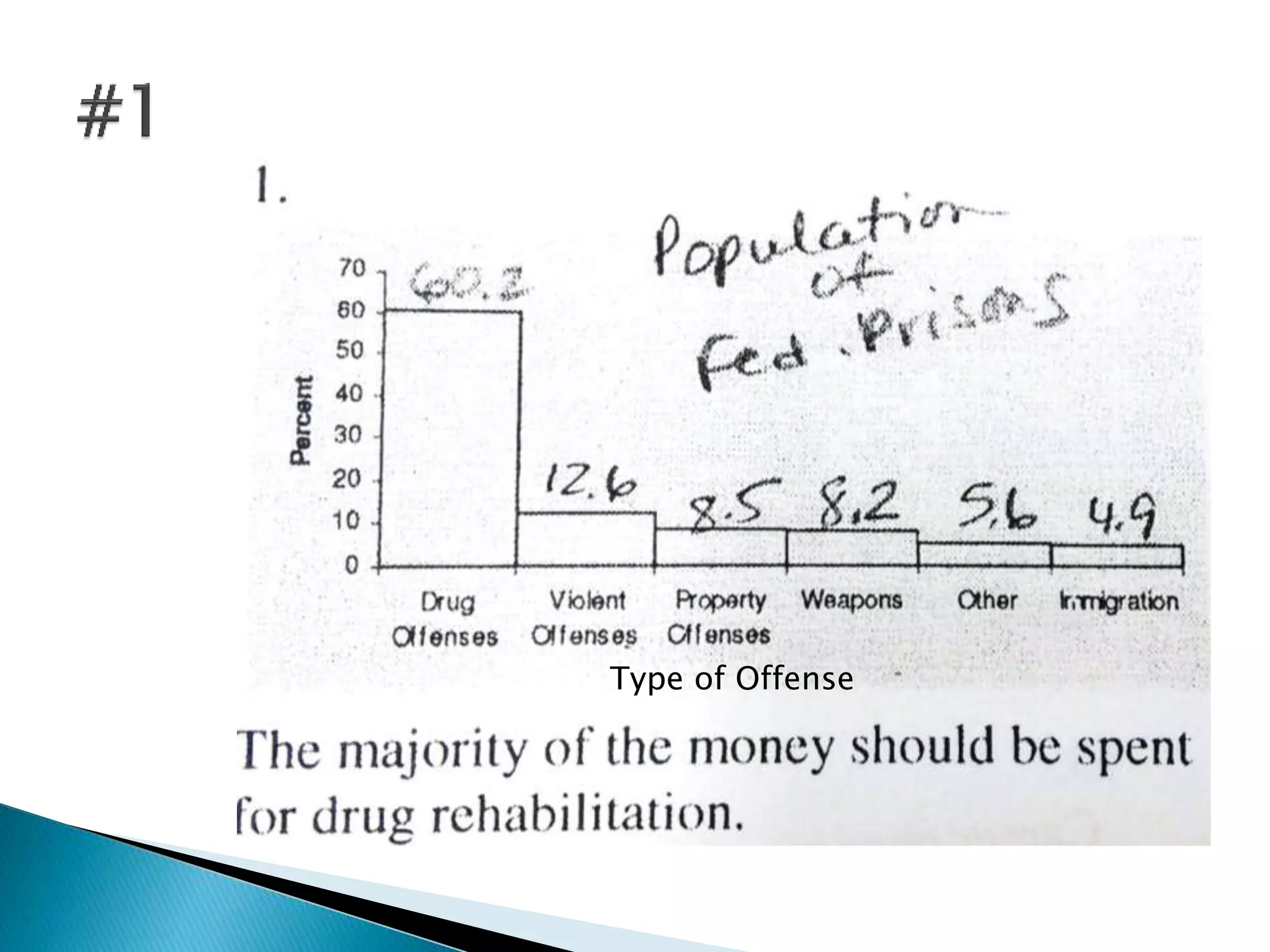
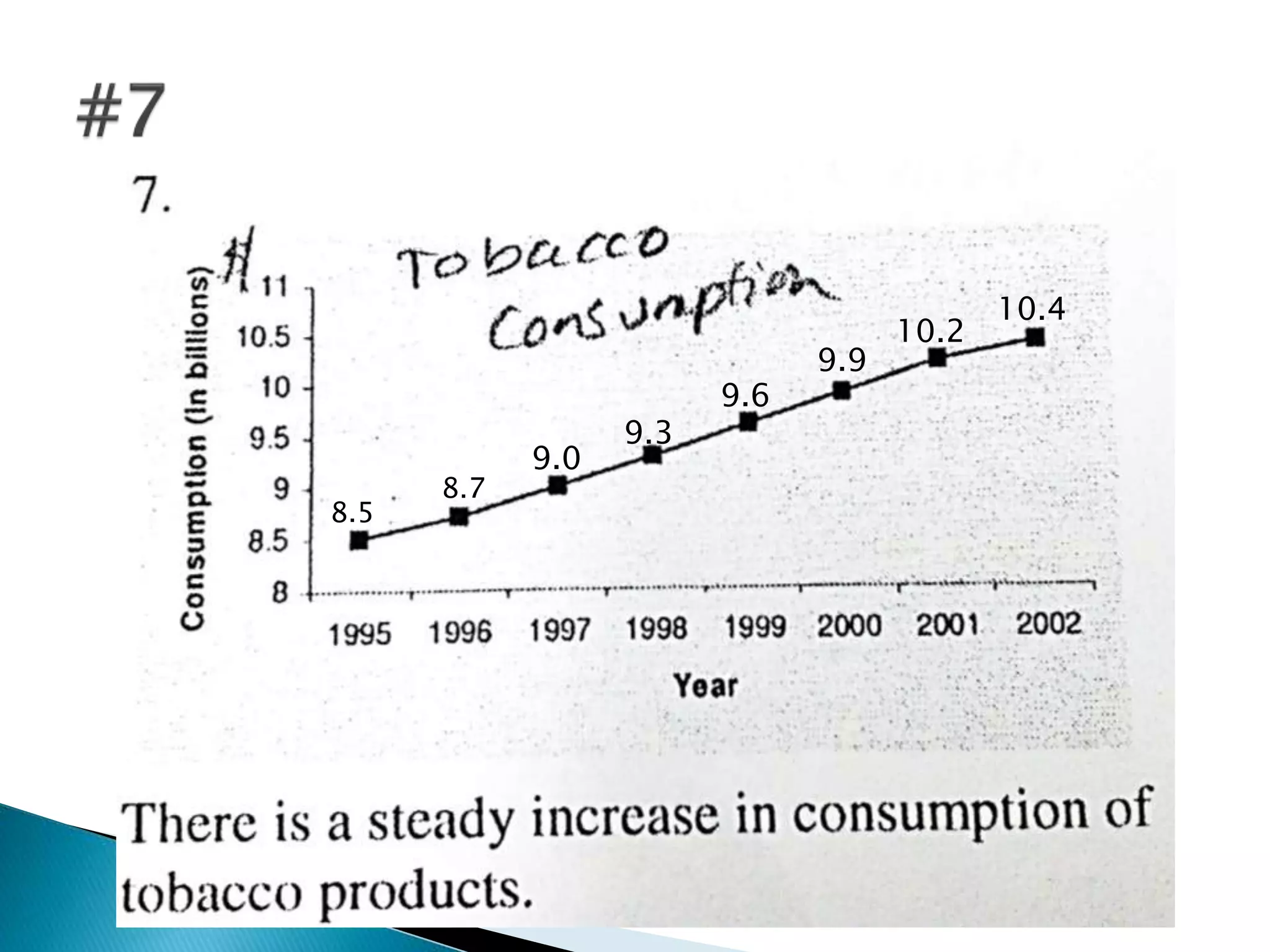
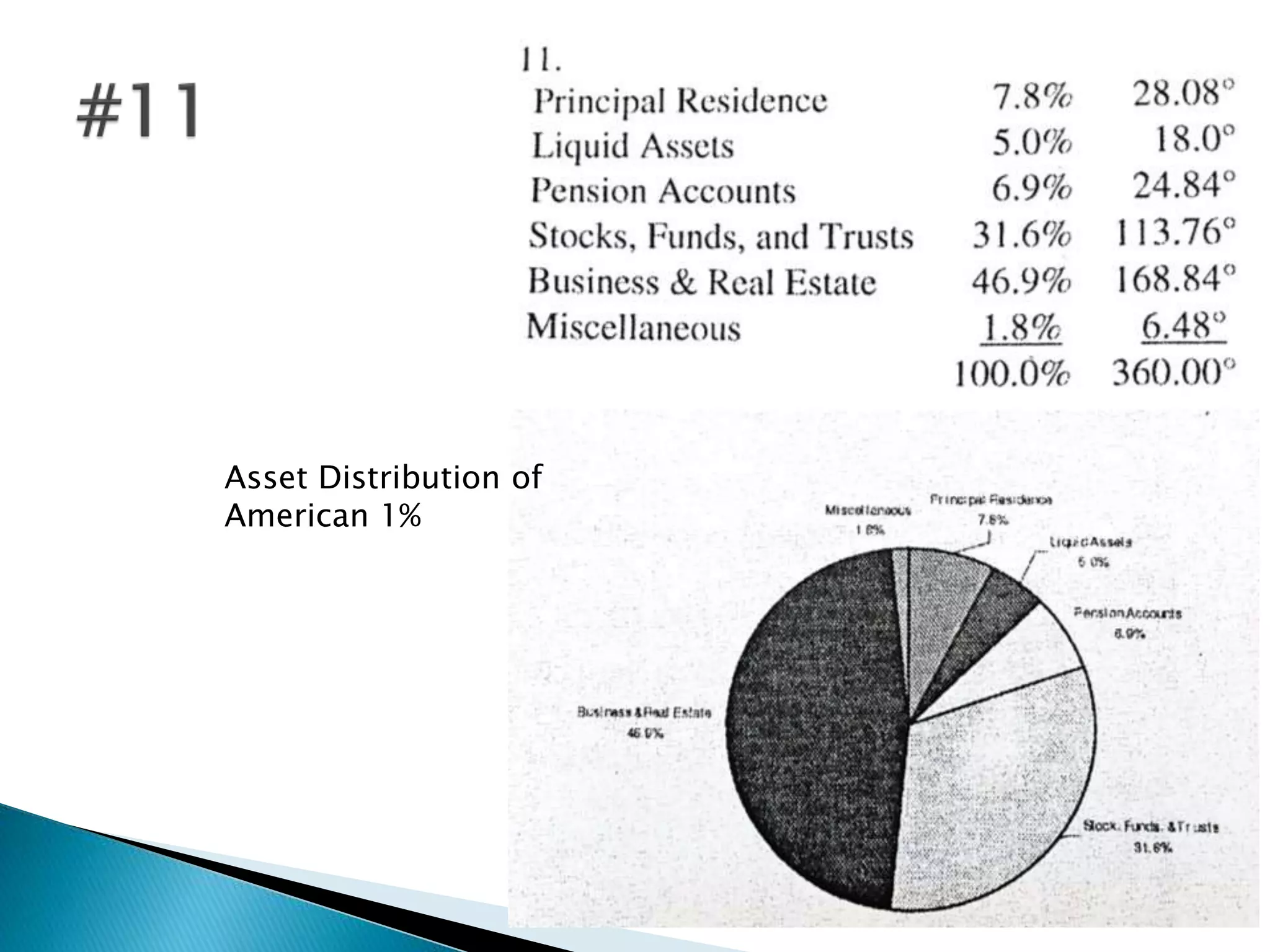
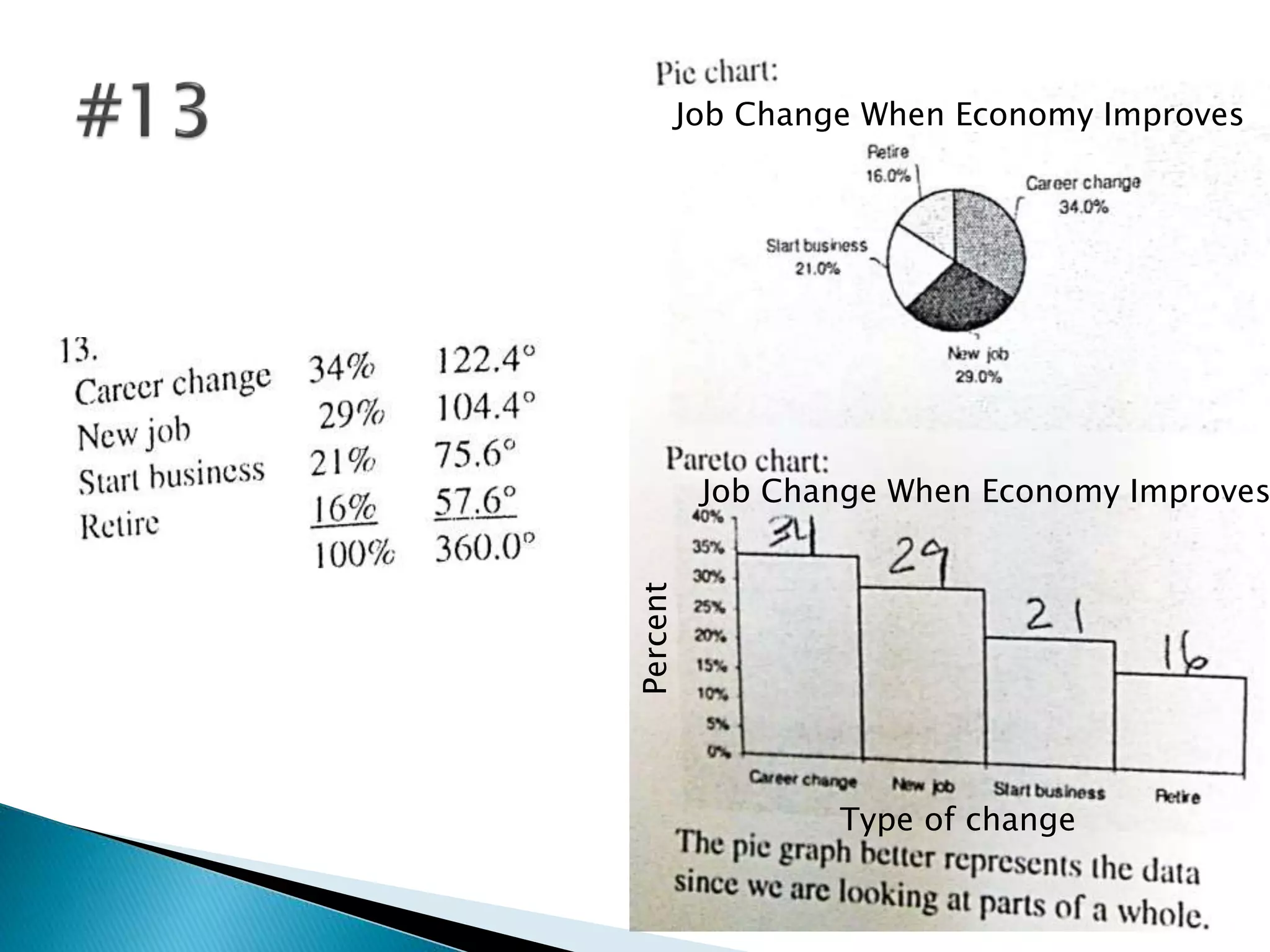
This document discusses different types of graphs used to represent data including Pareto charts, time series graphs, and pie charts. It provides details on how to construct each graph type, including arranging bars from largest to smallest frequency for a Pareto chart and dividing a circle into wedges according to category percentages for a pie chart. Examples and steps are given for drawing each graph. Additional topics covered include stem and leaf plots and comparing data sets using different graph types.