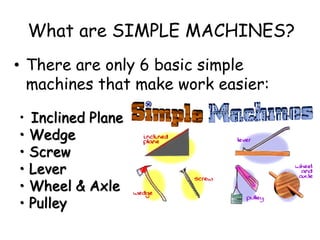
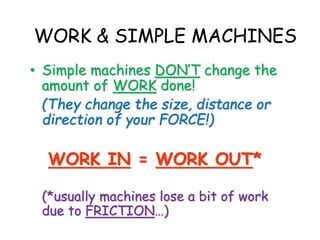
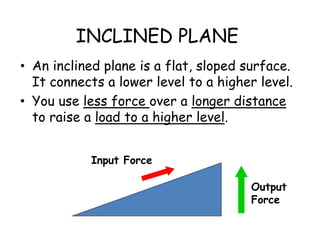
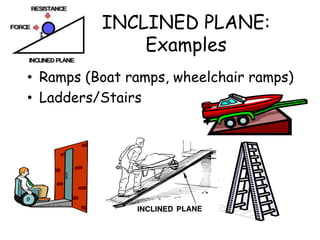
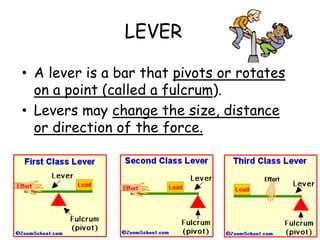
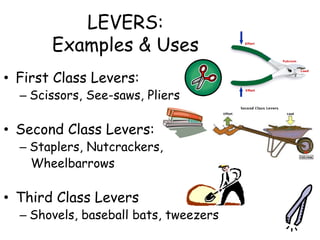
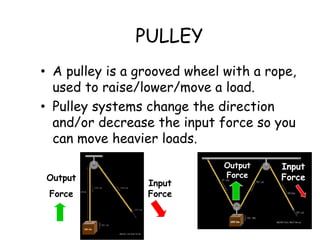
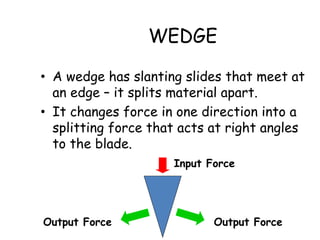
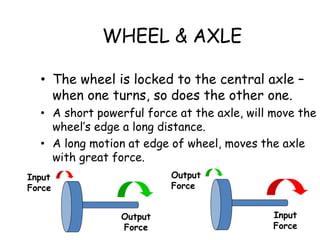
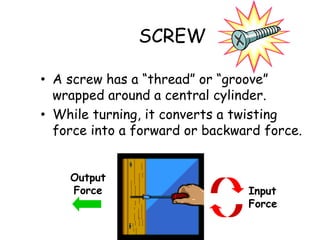
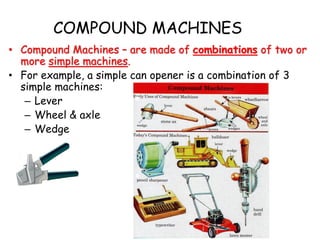
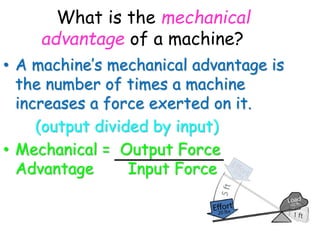
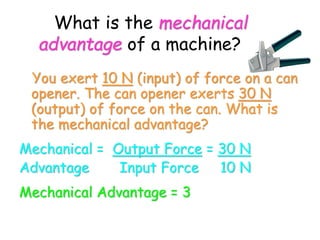
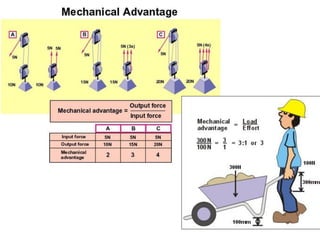
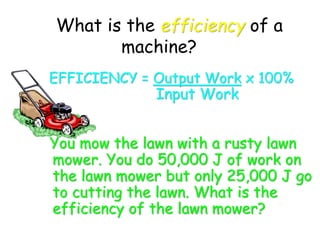
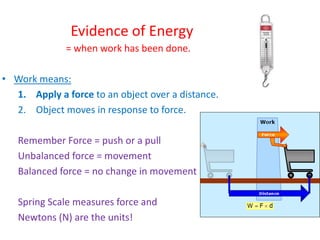
This document provides information about simple machines. It describes the six basic simple machines: inclined plane, lever, pulley, wedge, wheel and axle, and screw. It explains that simple machines make work easier by changing the amount of force needed, the distance over which force is applied, or the direction of the applied force. The document gives examples of each type of simple machine and discusses how compound machines are combinations of two or more simple machines. It also defines mechanical advantage as the ratio of output force to input force and efficiency as the ratio of output work to input work.