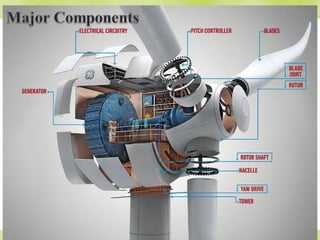
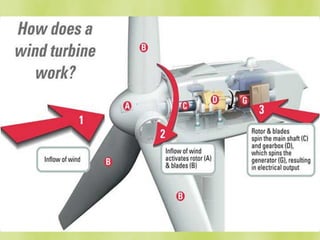
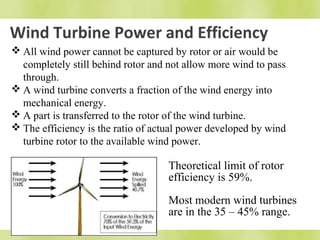
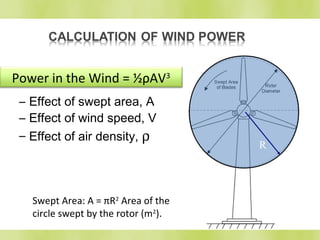
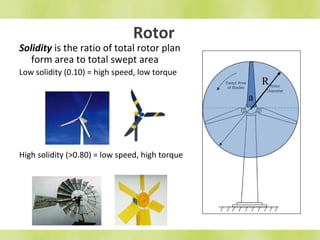
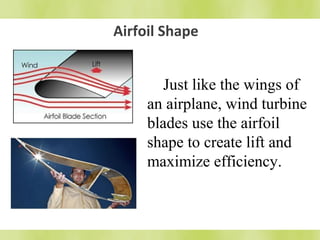
The document discusses wind turbines and wind energy. It covers the basic principles of how wind turbines work by converting kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical power. Specifically, it discusses how factors like swept area, wind speed, air density, rotor solidity, airfoil shape, number of blades, and blade composition and manufacturing can affect a wind turbine's efficiency and power output. The document also lists some advantages of wind energy like being renewable and producing no emissions, as well as disadvantages like intermittency of wind and potential noise issues.