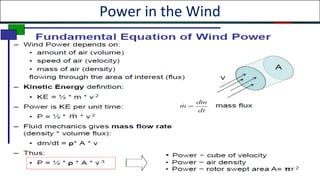
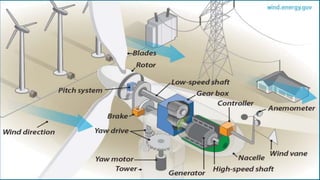
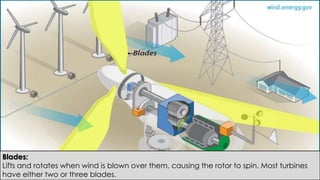
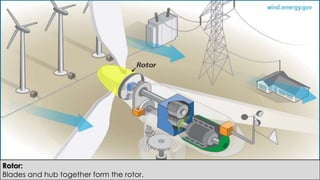
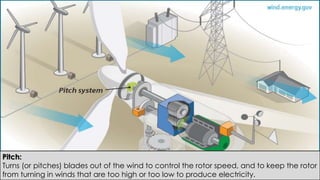
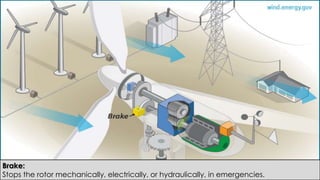
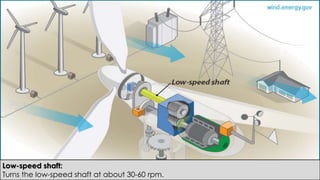
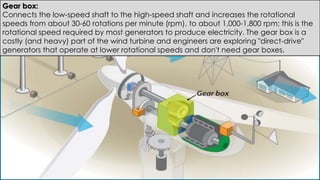
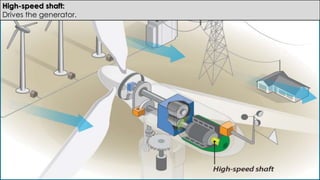
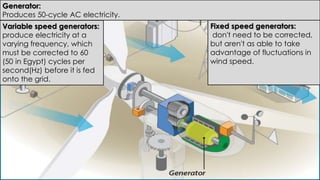
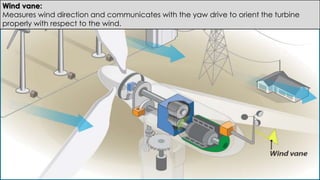
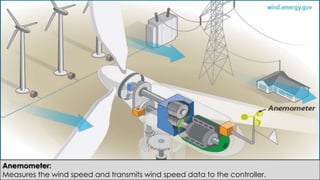
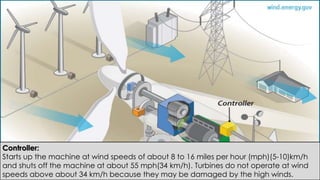
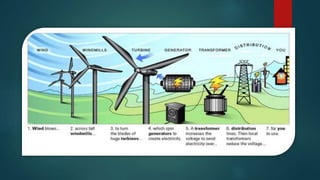
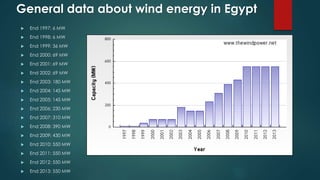
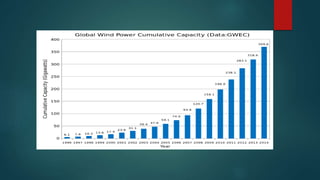
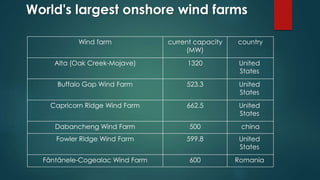
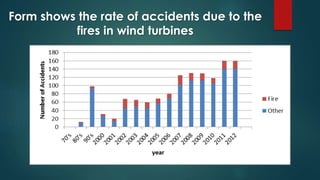
Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. They consist of blades, a rotor, a nacelle housing a generator and gearbox, and a tower. As wind passes the blades, they spin the rotor which turns the shaft and gearbox to increase rotational speed and power the generator to produce electricity. Egypt has over 500MW of installed wind power capacity concentrated in farms along the Red Sea coast. The advantages of wind power are that it is renewable and produces no emissions, while the disadvantages include intermittent availability and potential negative impacts on landscapes and communities. Problems faced by wind power include noise, transmission issues due to intermittent wind, social impacts, and fire risks from overheated or failed components inside nacelles.