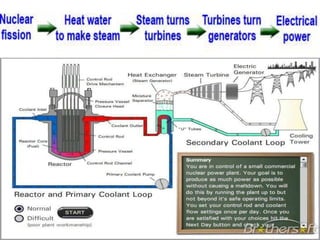
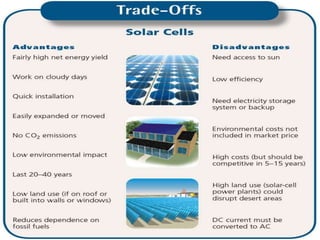
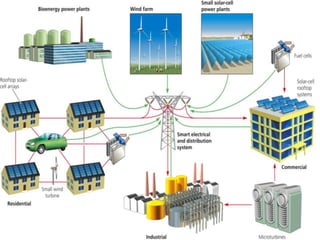
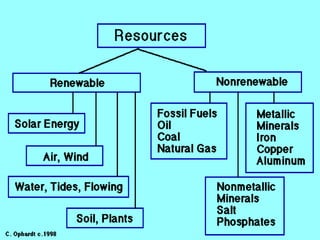
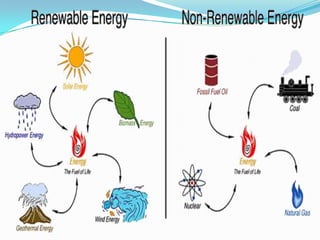
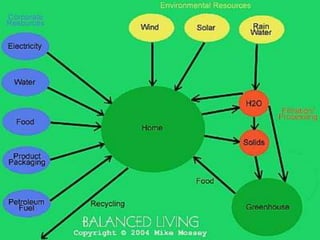
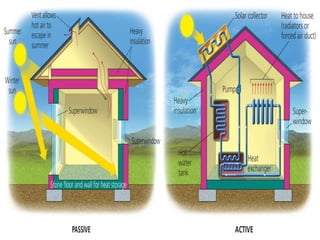
This document discusses various types of renewable energy sources including solar, wind, geothermal, hydro, and tidal energy. It provides details on solar energy and how photovoltaic panels work to convert sunlight directly into electricity via the photovoltaic effect. It also describes thin film solar cell technology and the process used to deposit materials to form solar panels. Additionally, it briefly touches on other renewable technologies like wind turbines, nuclear energy, and harvesting energy from natural resources and the environment. The document outlines some advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources.






![PHOTOVOLTAIC SOLAR PANALS
It convert sunlight directly into electricity.
It consists of several connected 0.6-V dc PV cells, which are made out of a
semiconducting material sandwiched between two metallic electrodes.
The photovoltaic effect refers to the separation of minority carriers [electrons and
holes] by a built-in electric field, such as a PN-junction or Schottky barrier.
Thin-film crystalline-silicon solar cells consist of layers about 10 µm thick compared
with 200- to 300-µm layers for crystalline-silicon cells.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/renewableenergyandresources-120728101205-phpapp01/85/Renewable-energy-and-resources-11-320.jpg)