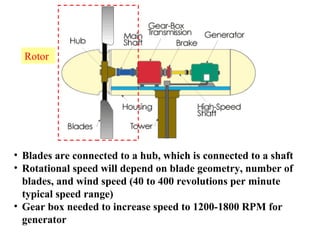
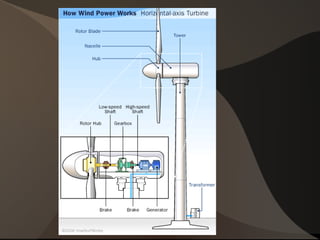
Wind energy is generated from the uneven heating of the atmosphere and is harnessed using wind turbines that convert kinetic energy into mechanical power or electricity. While wind power is renewable and has low operational costs, it faces challenges such as variability in wind strength, noise pollution, and potential threats to wildlife. Overall, wind turbines provide a sustainable energy source that can be utilized in various applications, particularly in remote areas.