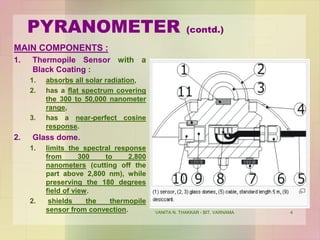
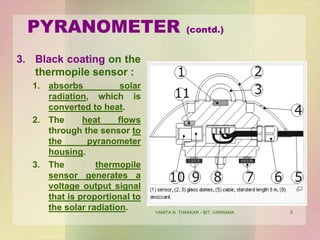
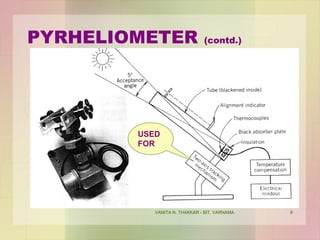
This document discusses different instruments used to measure solar radiation. It describes a pyranometer, which measures broadband solar irradiance on a planar surface using a thermopile sensor and glass dome. A pyrheliometer specifically measures direct solar irradiance and requires solar tracking to keep it aimed at the sun. Both instruments adhere to ISO and WMO standards and are used in meteorology, climatology and solar energy studies. A sunshine recorder measures the amount of sunshine at a location using either the sun or a clock as a timescale.