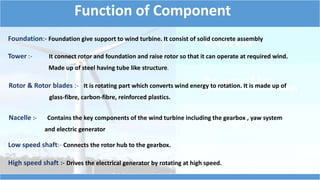
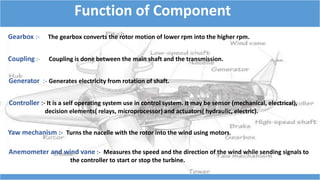
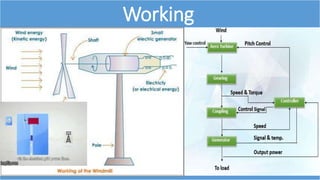
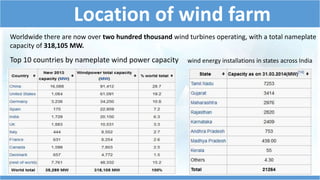
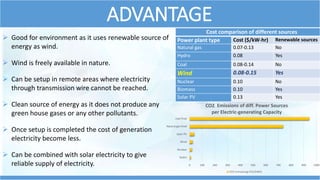
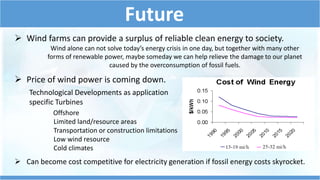
This document summarizes information about wind turbines, including their components, types, sizes, and how they work. It discusses how wind turbines convert kinetic wind energy into electrical power. It describes the key components of wind turbines like the foundation, tower, rotor blades, nacelle, gearbox, generator, and controller. It also summarizes the different types of wind turbines, including horizontal axis and vertical axis turbines. Finally, it covers wind farms, site selection factors, safety systems, advantages, and disadvantages of wind turbines.