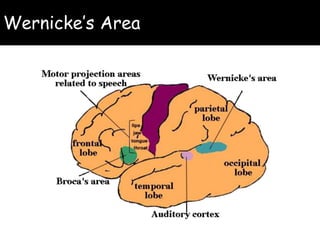
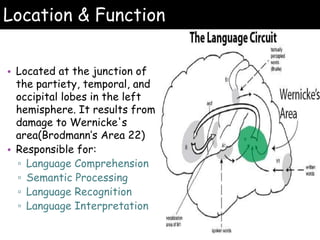
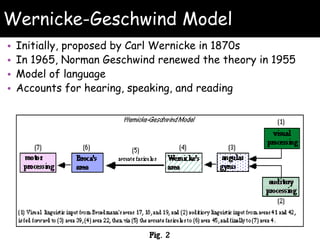
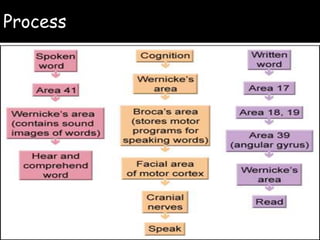
Wernicke's aphasia is a neurological disorder that affects a person's ability to understand language. It results from damage to Wernicke's area in the left temporal lobe of the brain. People with Wernicke's aphasia have fluent speech but cannot comprehend what they or others say. Treatment involves daily speech and language therapy exercises to improve auditory comprehension, word finding skills, and expressive language abilities through techniques like answering yes/no questions, naming categories and opposites, and describing pictures. With practice, significant improvements in communication can be achieved.