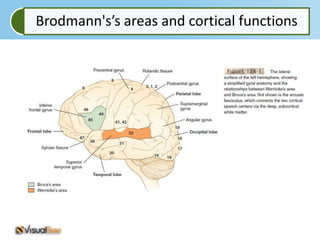
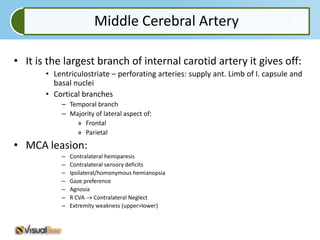
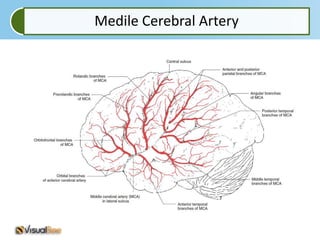
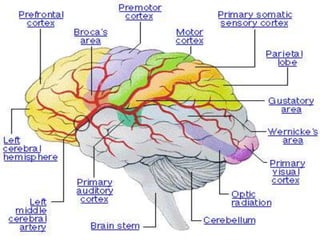
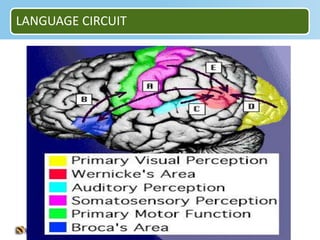
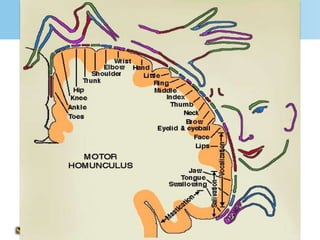
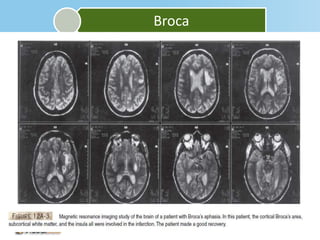
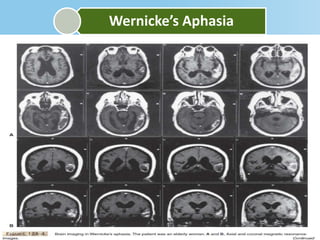
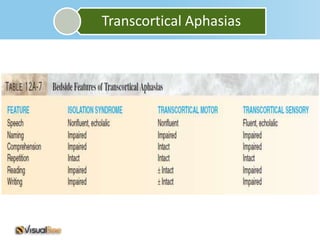
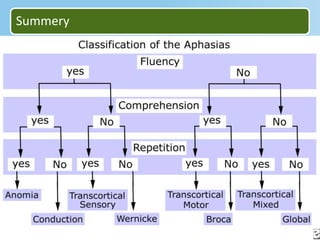
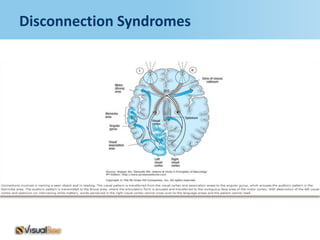
Aphasia is an acquired communication disorder that impairs a person's ability to process language. It can cause problems with speaking, listening, reading, and writing. The type and severity of aphasia depends on the location of brain damage, usually in the left hemisphere. Broca's aphasia involves non-fluent speech and impaired comprehension of syntax. Wernicke's aphasia features fluent but meaningless speech and impaired comprehension. Global aphasia combines deficits of both Broca's and Wernicke's aphasia.