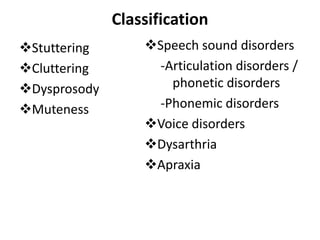
This document defines and classifies different types of speech disorders, including stuttering, cluttering, dysprosody, muteness, articulation disorders, phonemic disorders, voice disorders, dysarthria, and apraxia. It lists various causes of speech disorders such as hearing loss, neurological disorders, brain injury, and physical impairments. Speech therapy is identified as the primary treatment, with the speech language pathologist using language intervention activities, articulation exercises, and oral-motor exercises to help patients improve their speech.