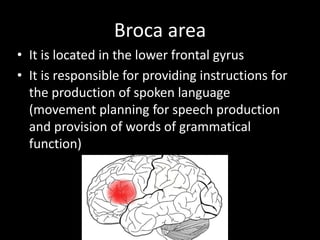
- Aphasia is the loss of ability to communicate through speech and understanding, usually caused by poor brain blood flow. It affects areas like Wernicke's area, involved in language understanding, and Broca's area, involved in speech production.
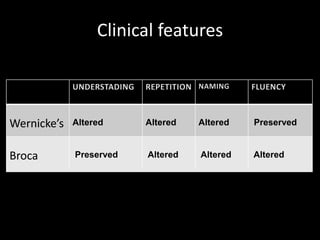
- Wernicke's aphasia results in fluent but meaningless speech, while Broca's aphasia causes non-fluent, labored speech.
- Aphasia is diagnosed through evaluations by professionals like speech therapists, neurologists, and psychologists. Treatment requires multidisciplinary rehabilitation to stimulate language and compensate lost functions.