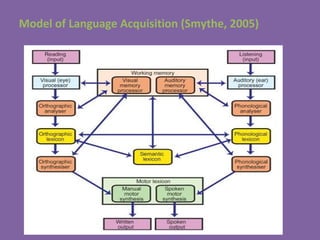
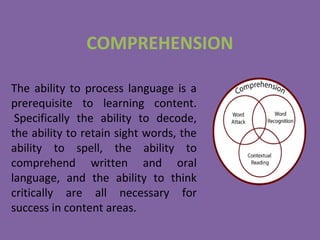
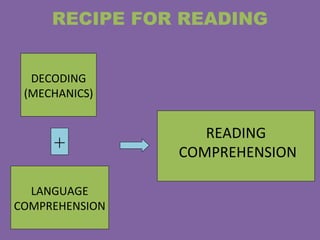
Dyslexia is a neurological condition that impairs a person's ability to read, write, and spell. It is caused by genetic anomalies in areas of the brain related to language processing. There are several proposed models to explain dyslexia, including a phonological model which argues dyslexics have an impaired ability to connect letters to sounds, preventing word identification and comprehension. Dyslexia is diagnosed through tests that evaluate a person's reading ability compared to their intelligence. Treatments focus on strengthening weaknesses, such as using multisensory techniques to help connect letters to sounds. There is no cure for dyslexia, but treatment plans involving specialized instruction can help dyslexic individuals learn compensatory strategies.



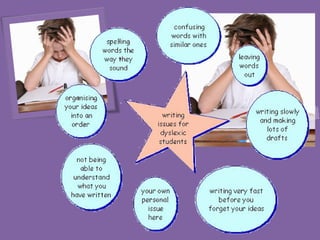
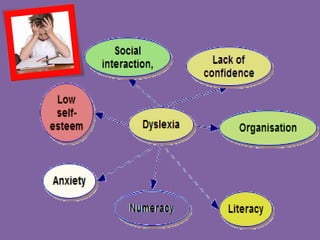




![SIGN AND CLUES OF DYSLEXIA…
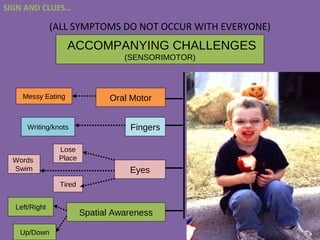
• Diagnosed for the first time in third grade. Since
dyslexic readers often do not use a decoding strategy to
identify a word and instead rely heavily on the
surrounding context to figure out.
• Depend on context for understanding rather than
written words de-coding.
• Poor spelling is often a sign of dyslexia.
• Handwriting [can] be an important clue to dyslexia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dyslexiafinal-150509094821-lva1-app6892/85/Dyslexia-10-320.jpg)




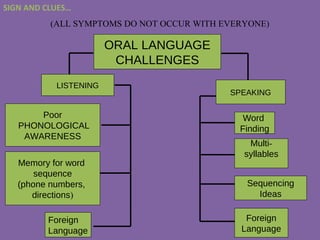
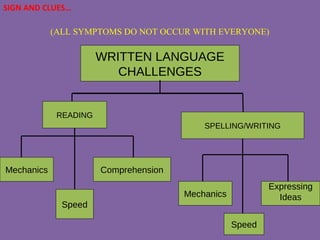
























![Dyslexia writting
[1]http://www.brainhe.com/students/types/dyslexia.html
[2]http://www.cheapwebhostingservices.org/go/dyslexia-in-adults-test.html
1) Dyslexia, by Sally E. Shaywitz , on the Scientific American web site
2) What is Dyslexia, by Roger P. Harrie and Carol Weller SITE, on the Kid Source web
site
3) Advances in dyslexia research , on the Geocities web site
4)10 Years of Brain Imaging Research Shows The Brain Reads Sound by Sound , on the
Healthy Place web site
5) Dyslexia and Brain Activity , on the Harvard web site
6) Dyslexia: Cultural Diversity and Biological Unity by Paulesu et al. , on the Science
Magazine Online web site
7) Dyslexia: Same Brains, Different Languages by Laura Helmuth , on the Science
Magazine Online web site
8) Fact Sheet: Dyslexia , on the Learning Disabilities Association web site
9) Beginning Reading And Phonological Awareness For Students With Learning
Disabilities by Michael M. Behrmann , on the Kid Source web site
10) Brief Introduction to FMRI , on the FMRIB web site
11) I world multimedia Education, www.iwmme.com working for delayed learners.
http://www.dyslexia-parent.com/mag30.html
References:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dyslexiafinal-150509094821-lva1-app6892/85/Dyslexia-46-320.jpg)



