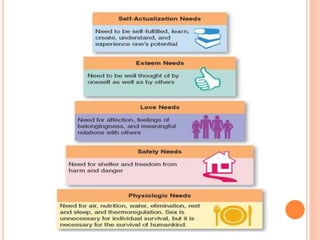
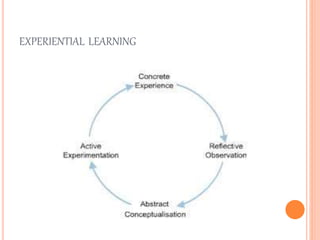
The document outlines key differences between adult and child learners in 3 areas:
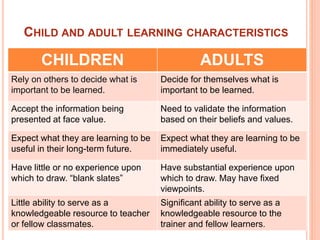
1. Child learners rely on others to decide what is important to learn, have little experience to draw from, and have limited ability to serve as a resource. Adult learners decide what's important for themselves, have substantial experience, and can significantly contribute as a resource.
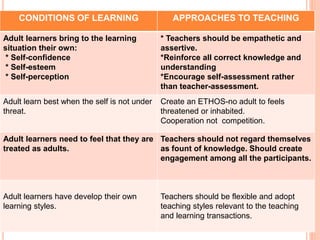
2. Conditions of learning differ - children are motivated by disharmony while adults want immediate usefulness. Approaches also differ with children needing structure and adults preferring participation.
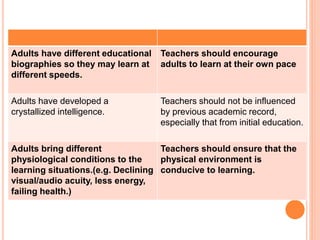
3. Adults bring their own experiences, needs, learning styles and educational backgrounds to learning. Teachers must be flexible and create a non-threatening environment for adult learners.