The document discusses the key steps in wafer processing:
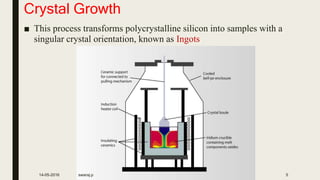
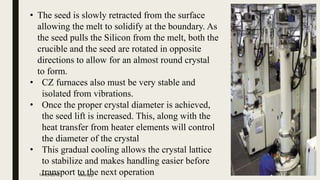
1) Crystal growth involves transforming polysilicon into silicon ingots with a singular crystal orientation using a Czochralski furnace, which slowly pulls a silicon seed crystal up from a silicon melt.
2) Wafer shaping turns the ingots into wafers using multi-wire sawing, which uses hundreds of parallel wire segments to slice through the ingot.
3) Wafer polishing removes saw marks and defects from the wafer surfaces using lapping and chemical etching to create flat and smooth wafers.