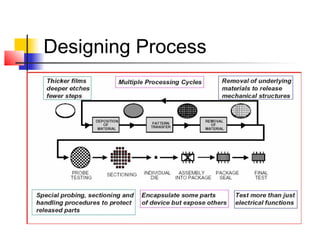
Micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) combine electrical and mechanical components on a small scale, ranging from sub-micrometers to millimeters. MEMS are fabricated using integrated circuit processes like deposition, lithography, and etching to create structures out of silicon, polymers, and metals. They have a variety of applications as sensors, including in pressure sensors, accelerometers, and tire pressure monitors. MEMS provide advantages like low cost and improved performance compared to macro-scale components.