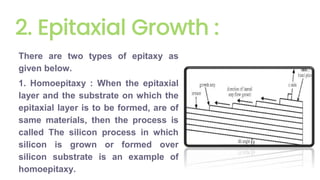
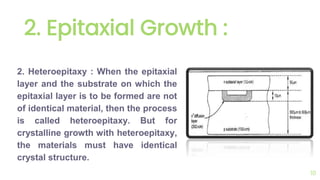
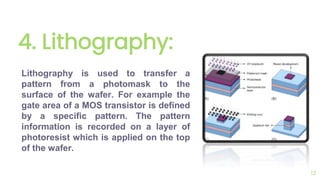
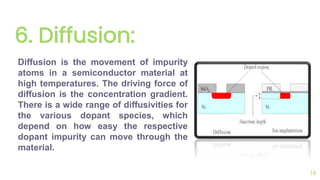
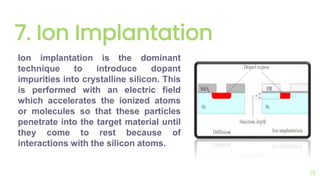
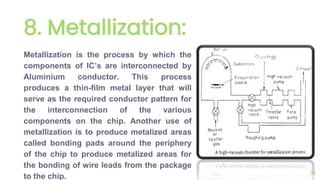
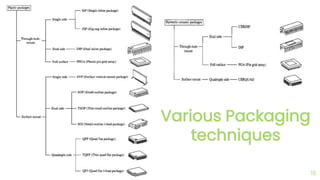
The document outlines the planar fabrication technology used in the semiconductor industry to manufacture components for transistors. It details the basic planar processes involved, including crystal growth, wafer preparation, epitaxial growth, oxidation, lithography, etching, diffusion, ion implantation, metallization, and packaging techniques. Each process is crucial for producing high-quality integrated circuits and involves various sub-processes and techniques.