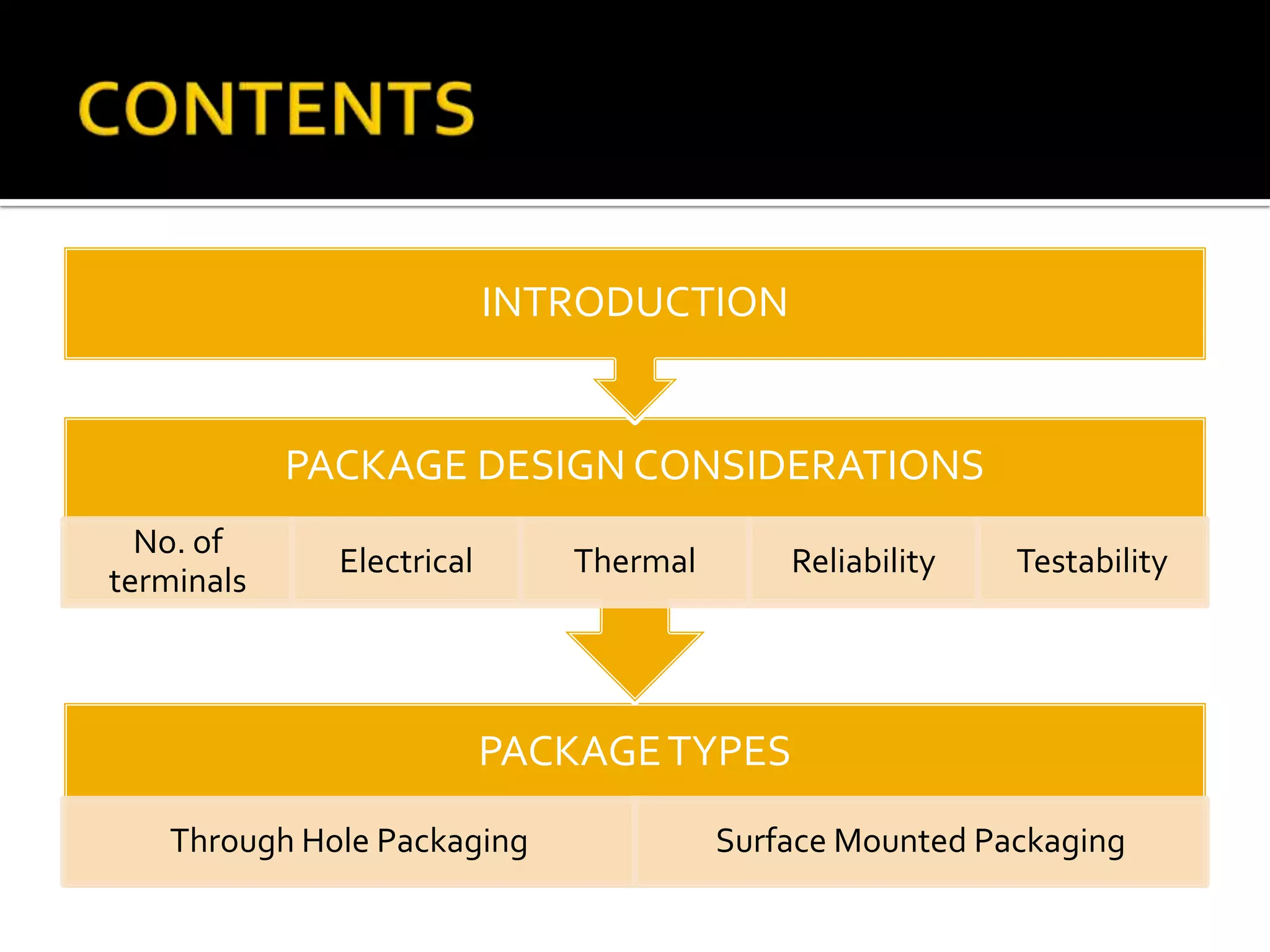
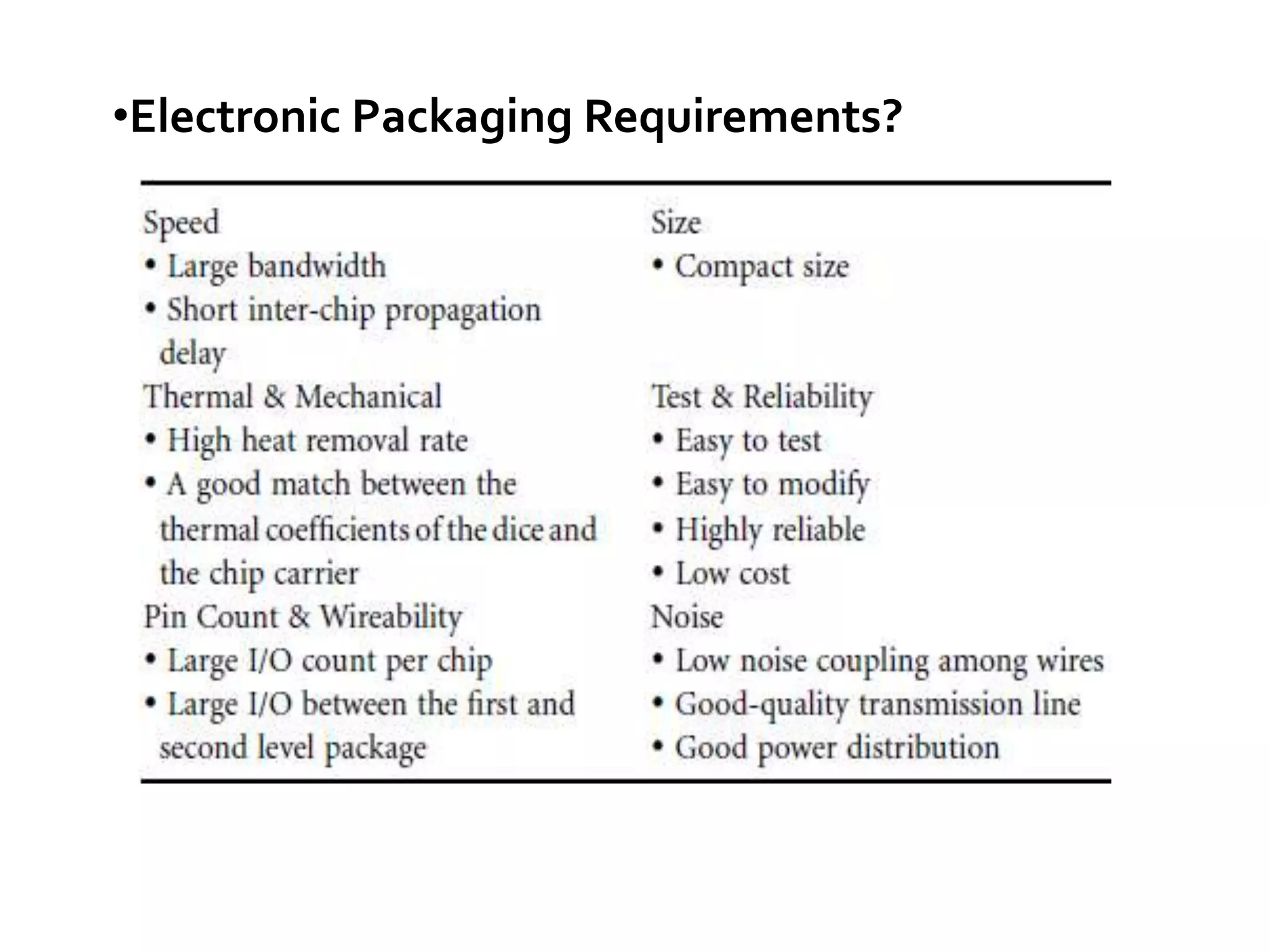
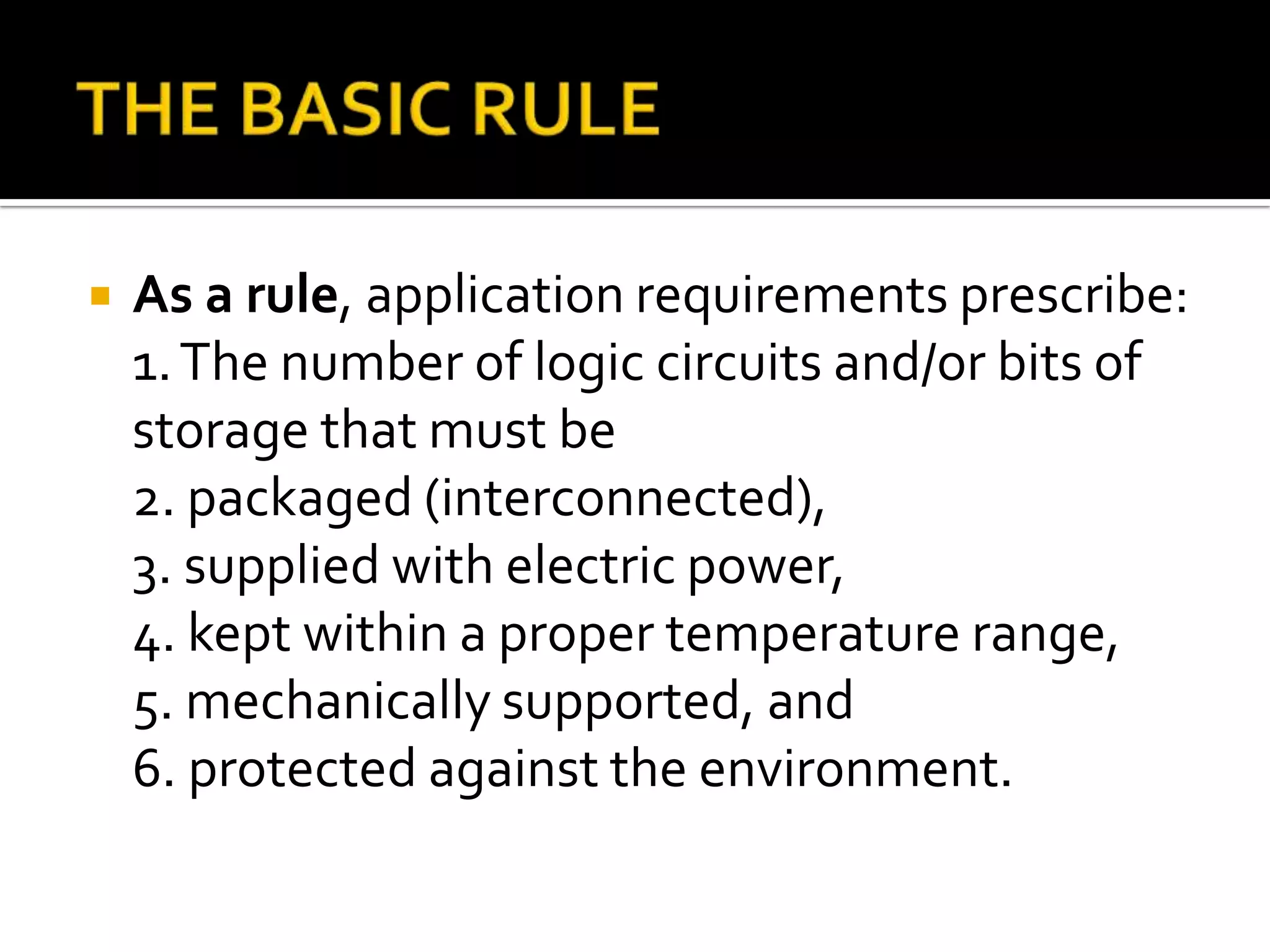
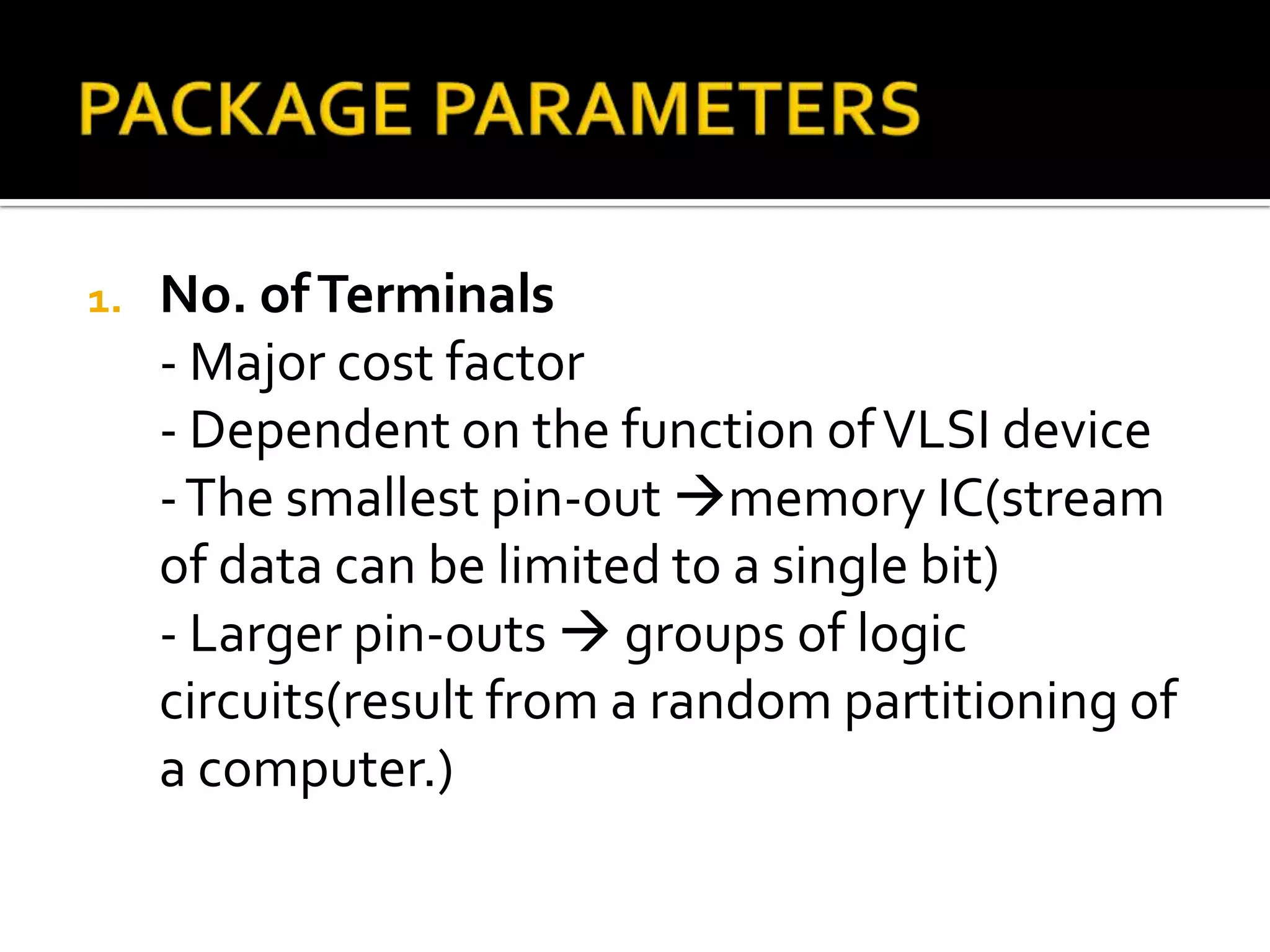
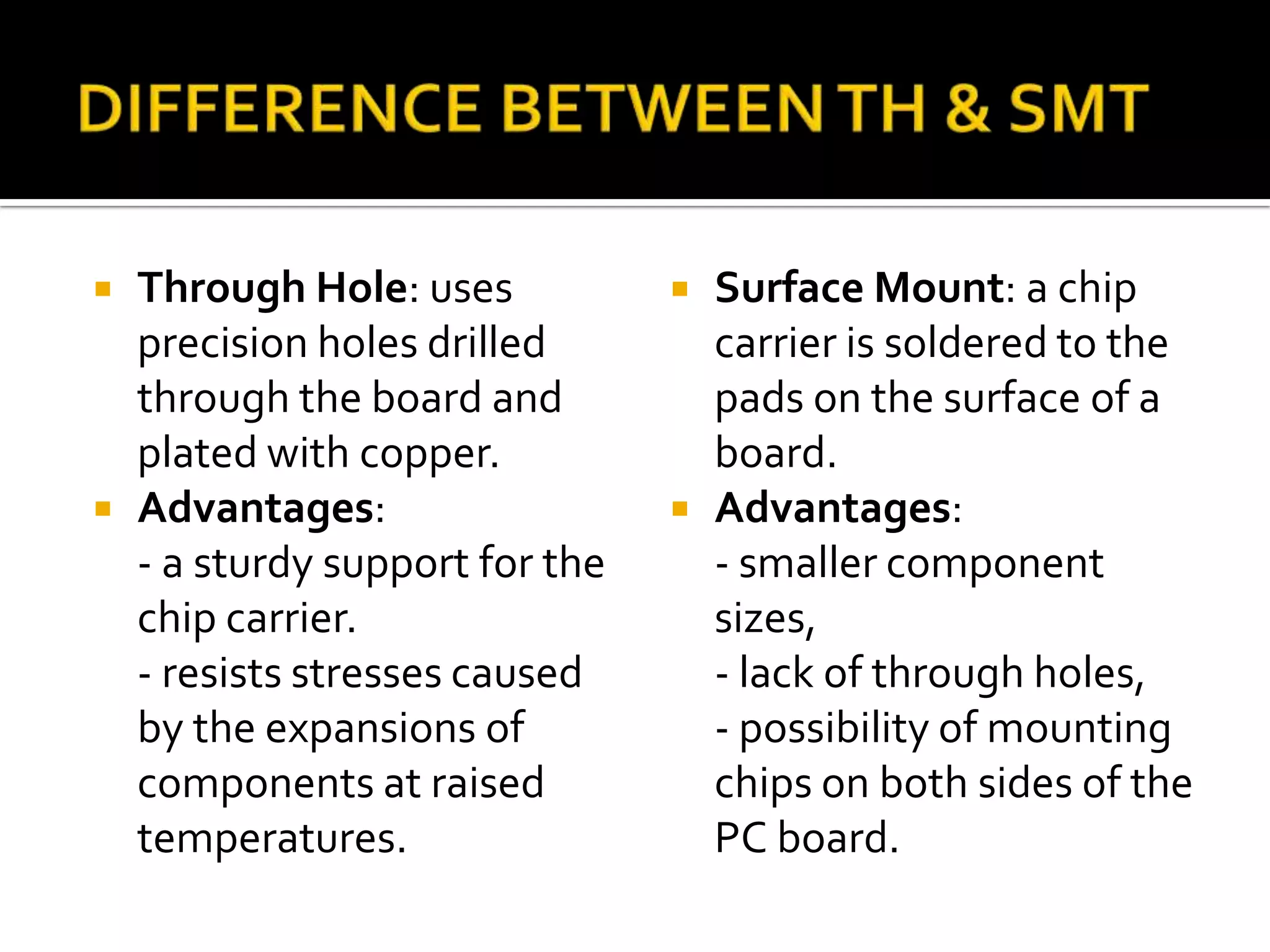
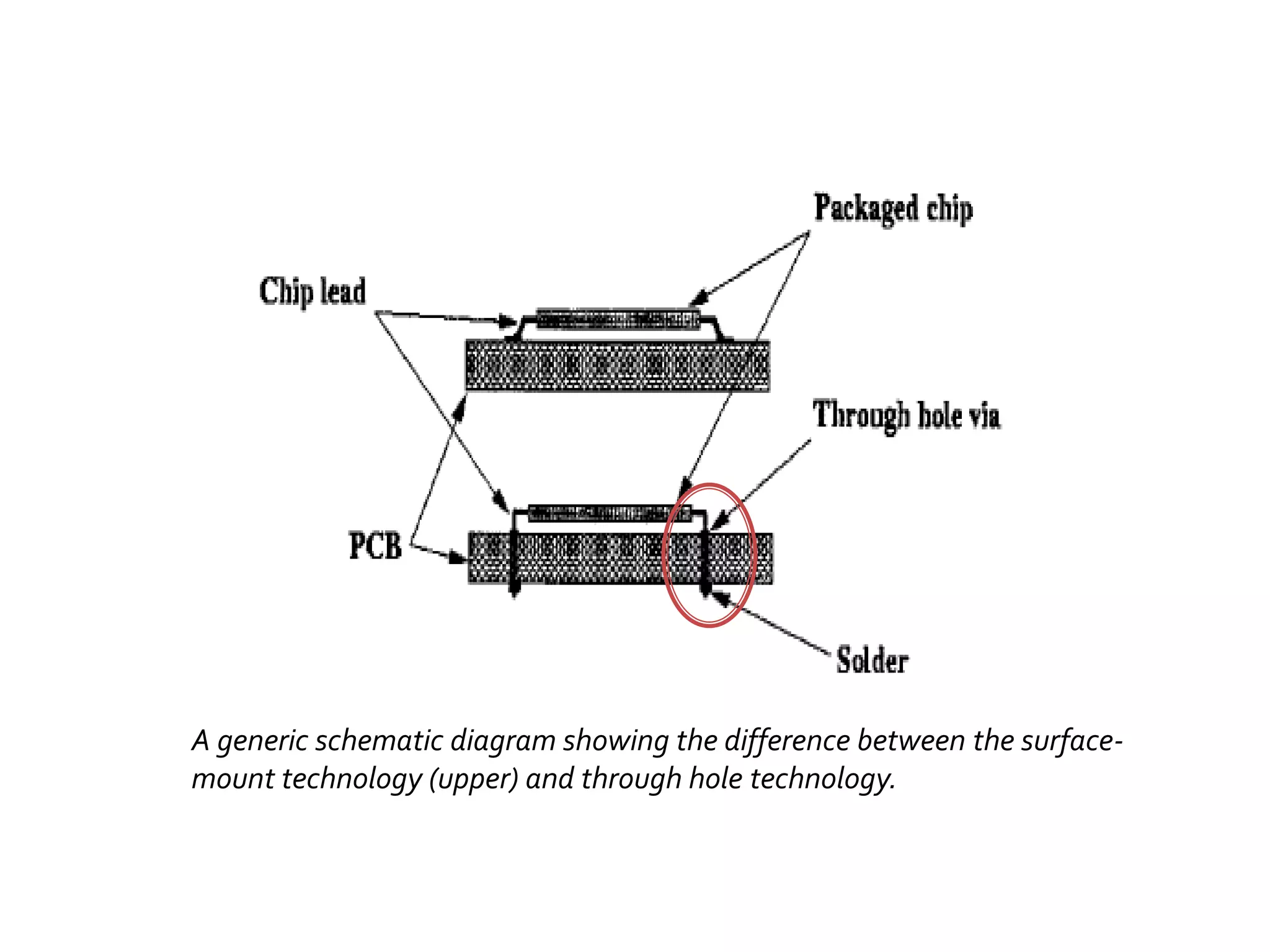
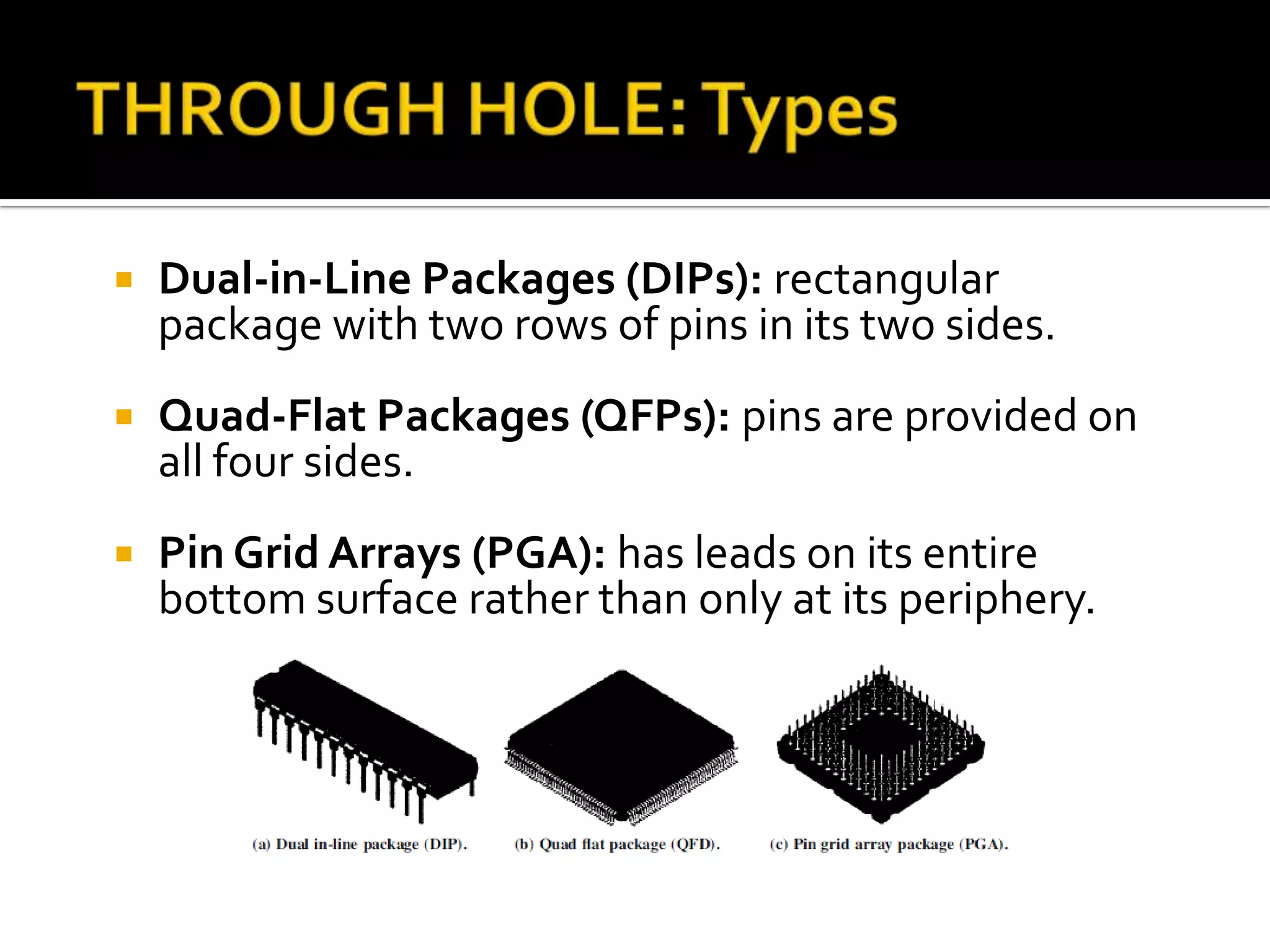
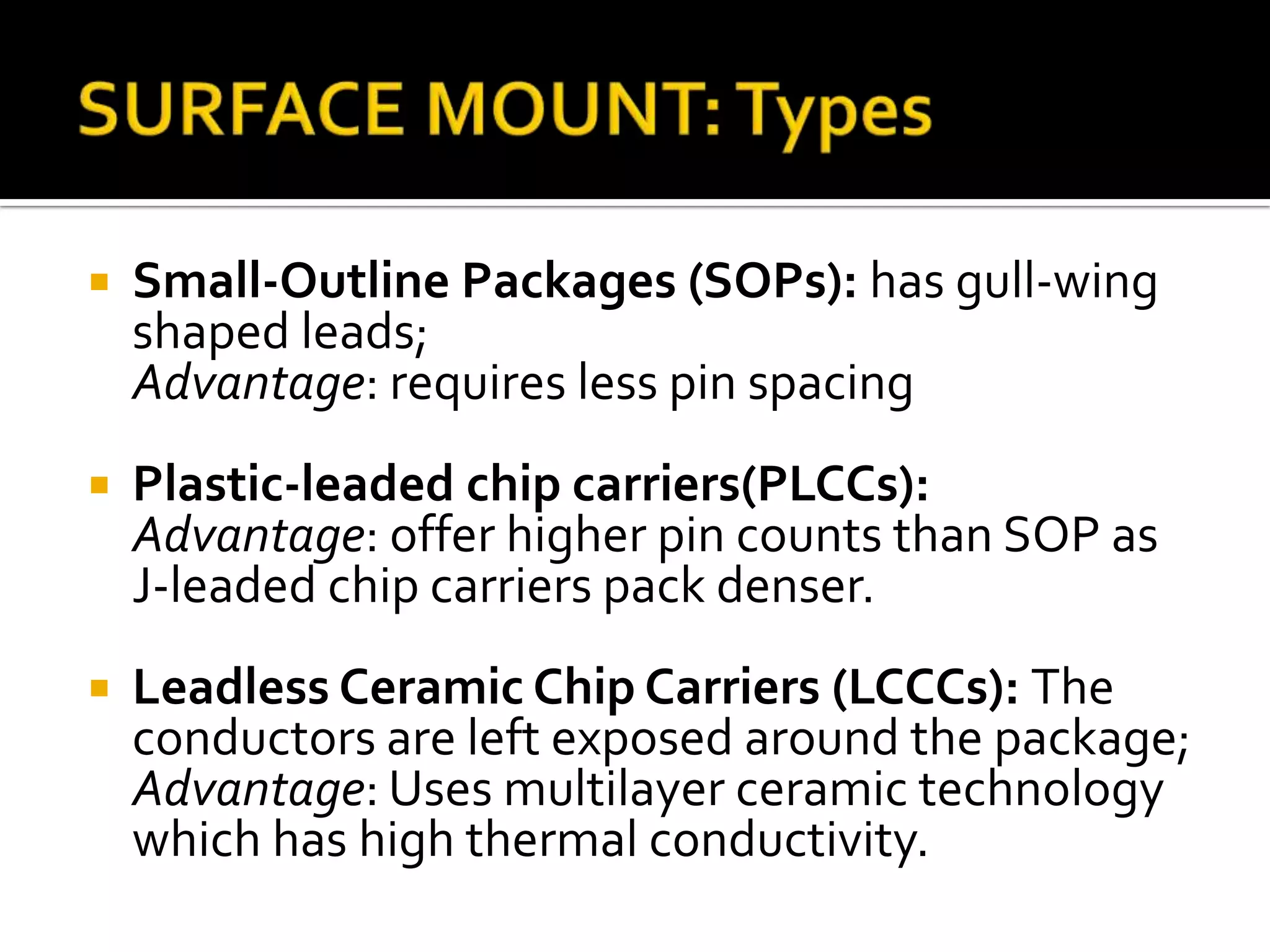
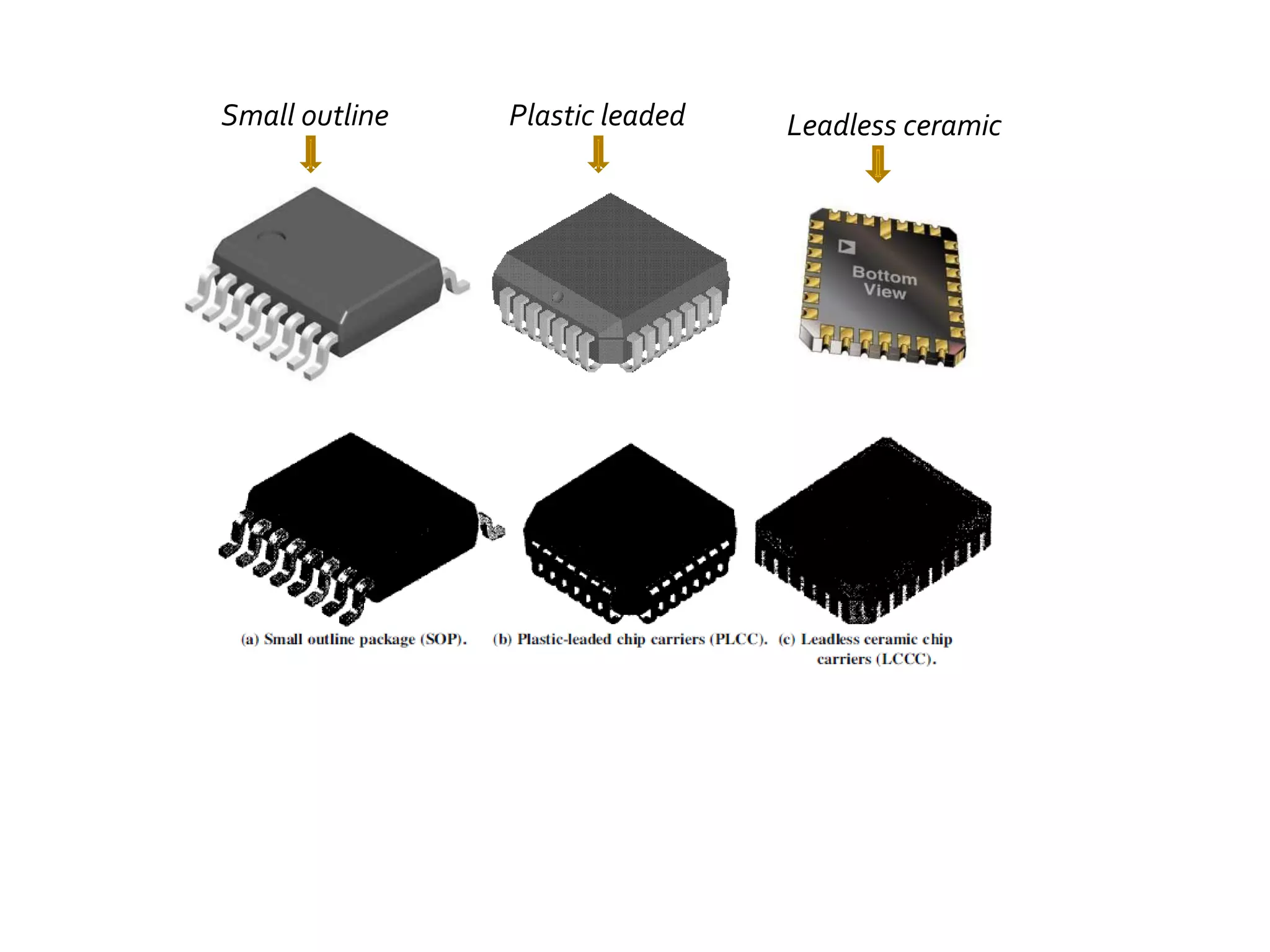
This document discusses package design considerations and types of semiconductor packages. It covers key factors in package design like the number of terminals, electrical, thermal, and reliability requirements. The main package types discussed are through-hole packages like DIP and QFP, and surface mount packages like SOP, PLCC, and LCCC. Through-hole packages use precision holes drilled through the board while surface mount packages solder directly to the board surface.