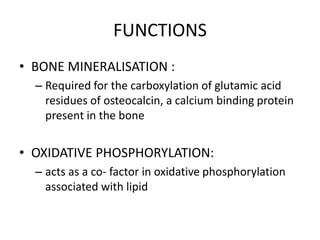
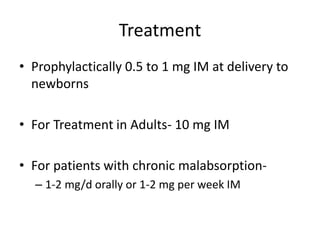
This document discusses vitamin E, including its structure, sources, absorption, functions, and deficiency. Some key points:
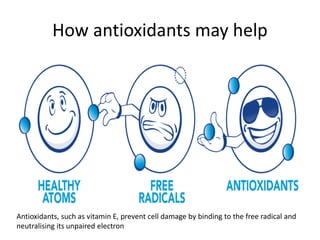
- Vitamin E refers to a family of antioxidants that protect cell membranes from free radical damage. Major food sources include plant oils, nuts, and green vegetables.
- It is absorbed along with fat in the small intestine and transported by lipoproteins in the bloodstream. Stores primarily in liver, adipose tissue, and muscle.
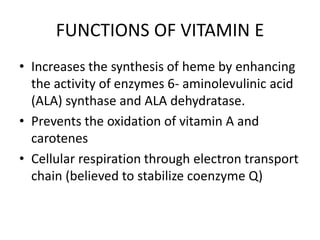
- Functions include protecting PUFAs from oxidation, maintaining cell membrane integrity, and supporting neurological and reproductive health.
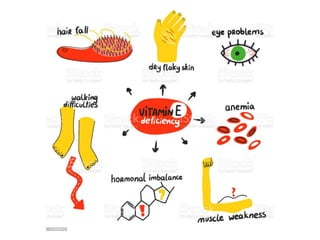
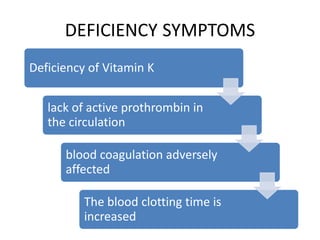
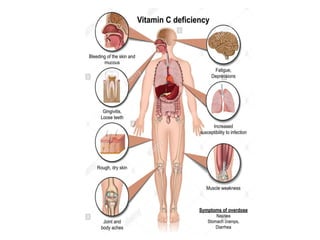
- Deficiency is rare in humans but may cause fragile red blood cells. Toxicity is also rare, with no adverse effects