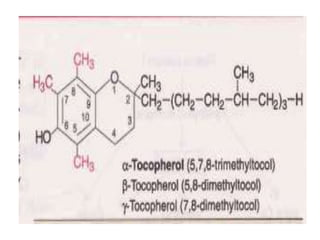
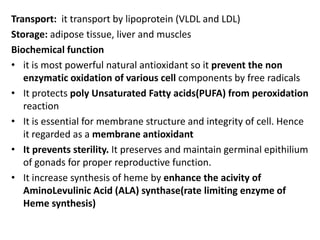
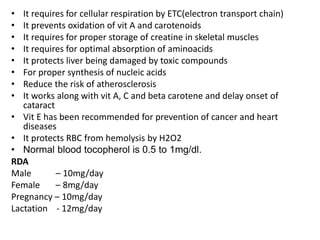
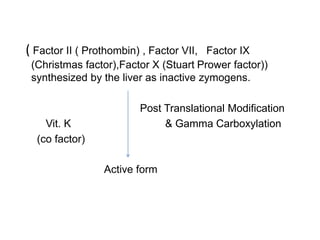
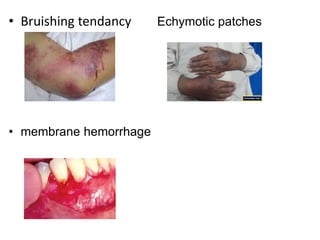
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for blood clotting. It acts as a cofactor for the post-translational modification of several blood clotting factors produced by the liver as inactive zymogens. This modification, called gamma-carboxylation, activates the clotting factors and allows them to bind calcium and participate in the coagulation cascade. A deficiency in vitamin K can result in bleeding disorders due to the production of inactive clotting factors.