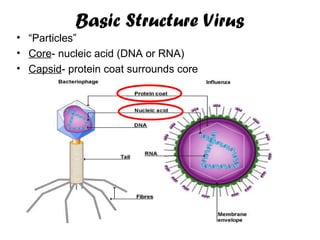
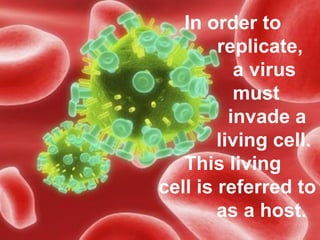
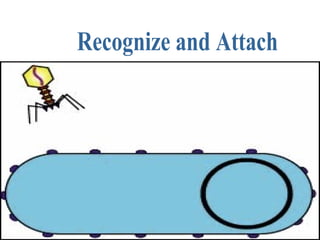
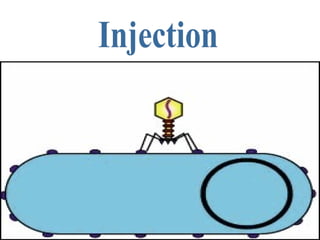
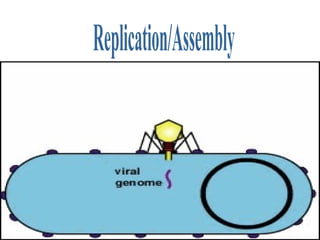
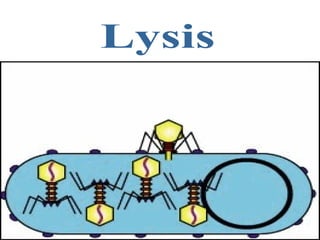
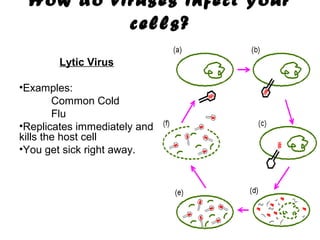
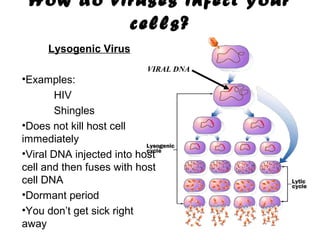
Viruses are microscopic particles that invade and replicate inside living host cells. They contain either DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. Viruses are not considered living because they cannot reproduce or metabolize outside of a host cell. In order to exist, a virus must infect a living host cell and use the cell's machinery to produce more viruses. There are two main types of viral infections - lytic infections immediately kill the host cell, while lysogenic infections integrate viral DNA into the host genome and lay dormant. Vaccines can provide protection against viruses that do not evolve rapidly.