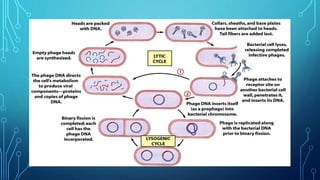
The lytic cycle involves a virus infecting a host cell, using its cellular machinery to replicate itself, and then causing the cell to burst and release new virus particles. It follows 5 steps - attachment, penetration, synthesis of viral components, assembly of new viruses, and release of viruses. The lysogenic cycle involves the viral DNA integrating into the host genome without killing the cell. The viral DNA is passed on to daughter cells until it is triggered to enter the lytic cycle.